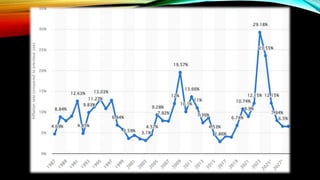
This document discusses inflation including its definition, causes, effects, types, and methods for controlling it. Inflation is defined as a rise in the general level of prices for goods and services over time which reduces purchasing power. The main causes are demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and built-in inflation. Effects include changes to interest rates, exchange rates, unemployment, and purchasing power. Types include open vs suppressed inflation and sectoral vs comprehensive inflation. Methods for controlling inflation involve monetary policy measures like interest rates and fiscal policy measures like taxation.