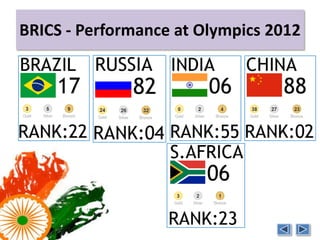
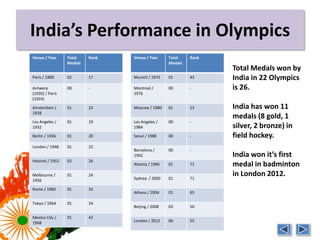
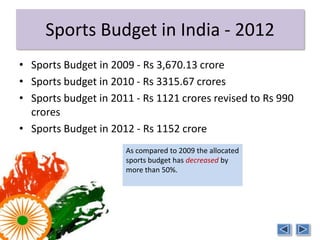
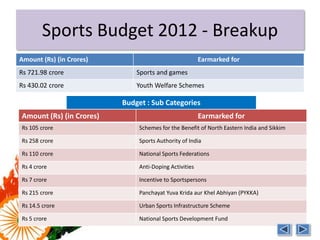
India is one of the emerging BRICS economies along with Brazil, Russia, China, and South Africa. Together the BRICS countries represent over 3 billion people and $4 trillion in foreign reserves. However, India's sports budget has decreased over 50% from 2009 levels, currently allocating only $1.15 billion in 2012. There is a lack of training facilities and infrastructure in India to develop athletes despite the large sports budget. Private organizations have had to fund many of India's Olympic medalists due to the lack of support from the government. Improving funding, facilities, and incentives is needed to enhance India's athletic performance going forward.