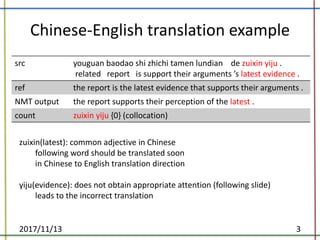
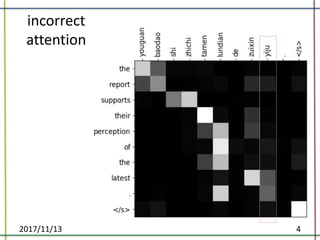
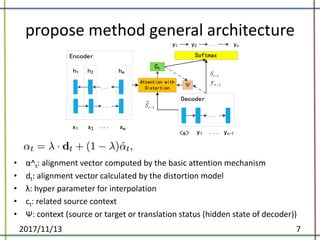
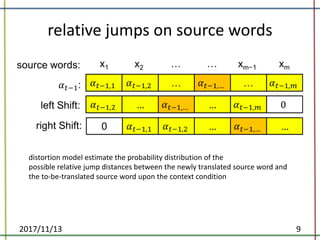
The document proposes a method to incorporate word reordering knowledge into attention-based neural machine translation using a distortion model. The method extends the attention mechanism to consider both the semantic requirements and a word reordering penalty. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on translation quality and improves word alignment quality compared to baseline neural machine translation and prior work.