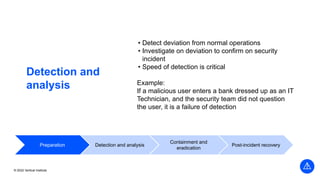
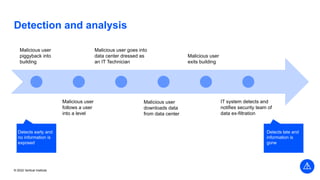
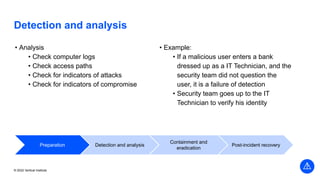
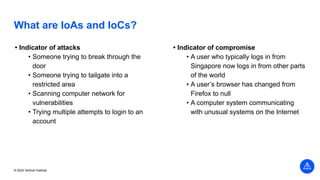
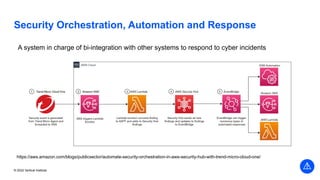
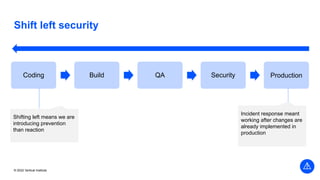
The document outlines the agenda and key components of a cybersecurity bootcamp focused on incident preparedness and response, including preparation, detection, analysis, containment, eradication, and post-incident recovery. It emphasizes the importance of a proactive incident response plan, collaboration among various stakeholders, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Additionally, the bootcamp features hands-on activities and discussions to develop practical skills in addressing cyber incidents, particularly for small and medium enterprises.