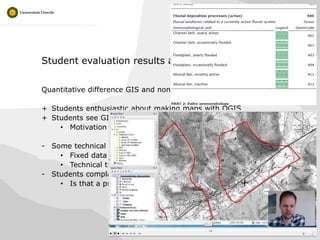
The document discusses the integration of GIS technologies into fieldwork for geosciences to enhance spatial analysis and mapping for students without prior GIS experience. A pilot study conducted in the French Alps showed that a hybrid approach combining traditional fieldwork and GIS was successful, although it required technical instructions for effective usage. Evaluations indicated student enthusiasm for GIS and its relevance as a skill, despite some technical challenges faced by both students and staff.