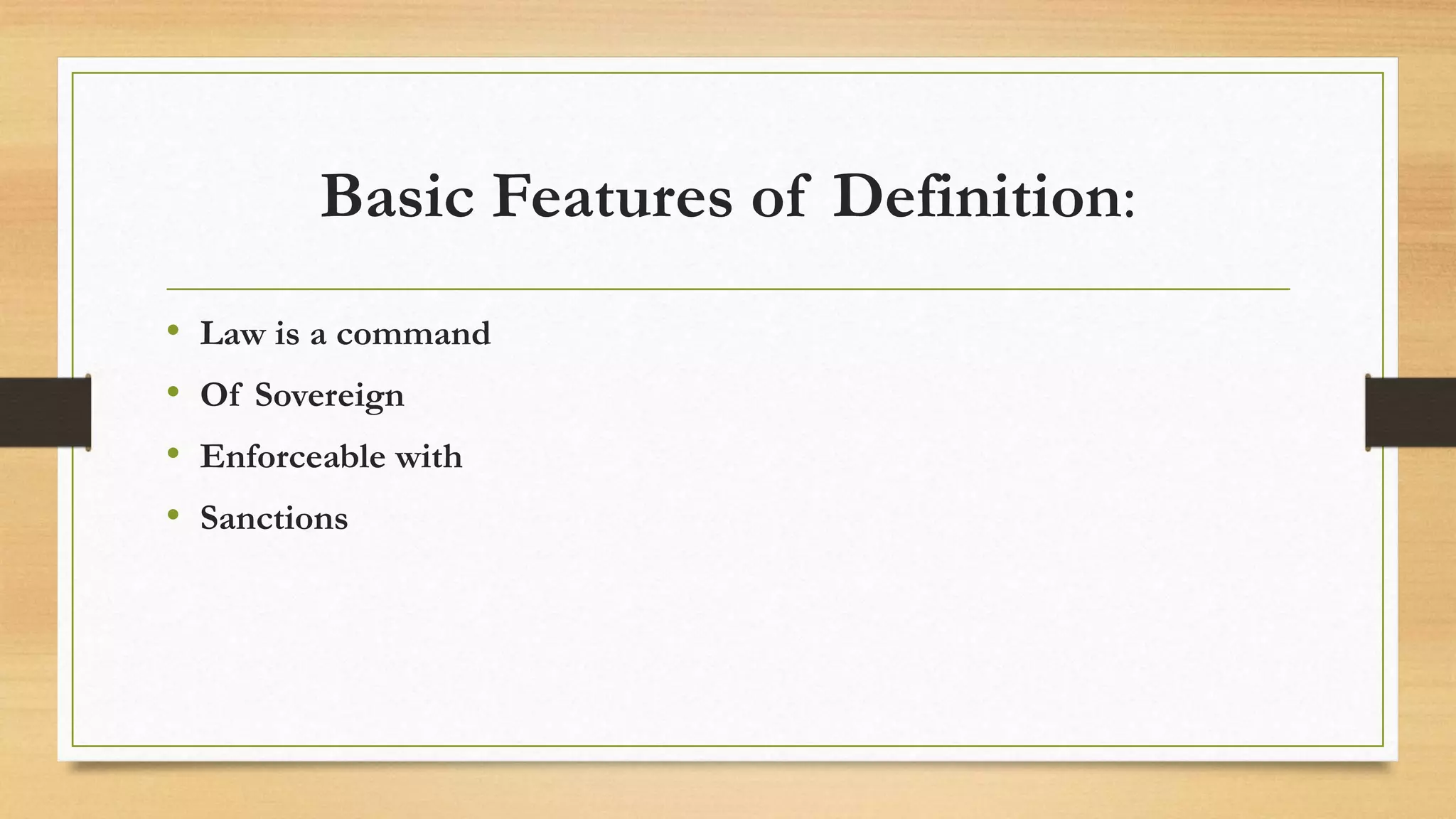
The Imperative Theory of Law was proposed by John Austin, who defined law as "the command of a sovereign, backed by sanctions." According to Austin, law derives from human lawmakers rather than divine authority. Austin's theory viewed the sovereign as the clear source of authority whose commands constituted law. However, the theory has also been criticized for ignoring customary law, morality, precedents, and its incompatibility with constitutional democracies. While criticized, the Imperative Theory provides a useful interpretation of law as positive and objective rules created by humans.