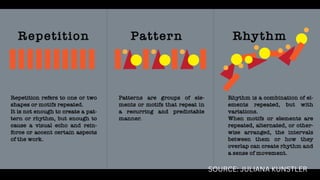
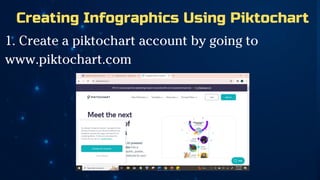
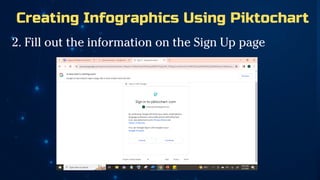
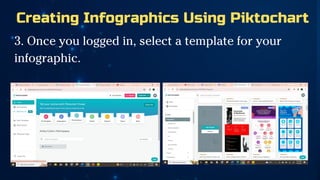
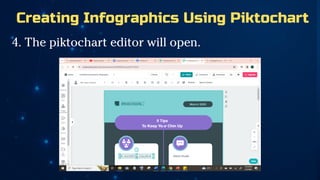
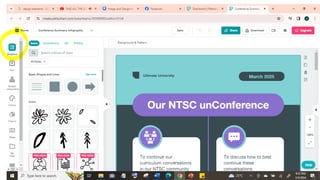
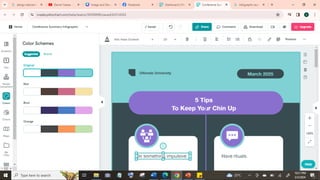
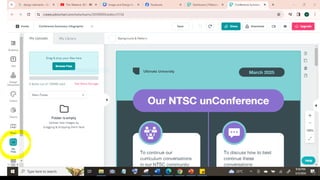
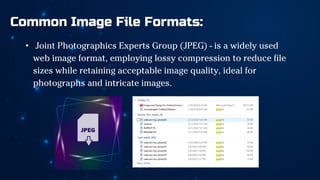
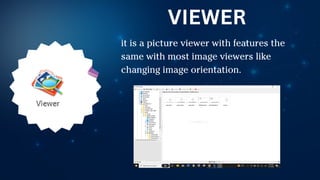
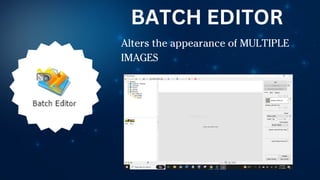
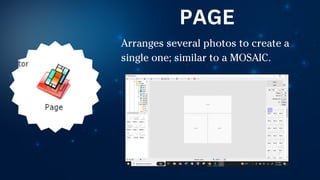
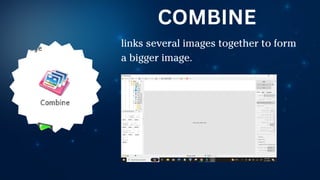
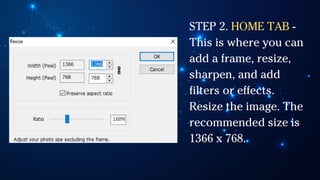
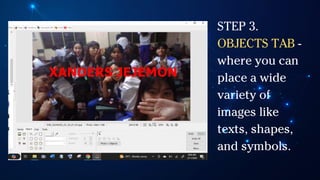
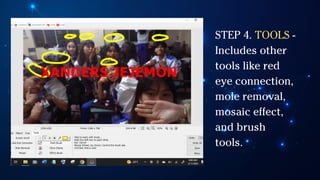
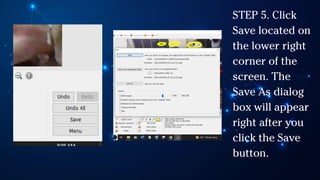
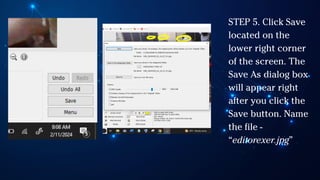
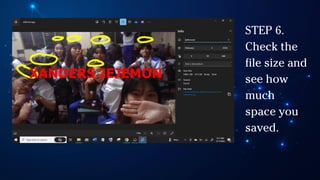
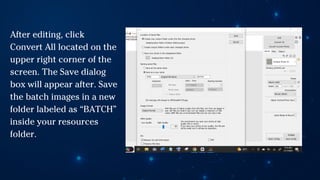
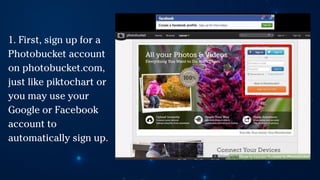
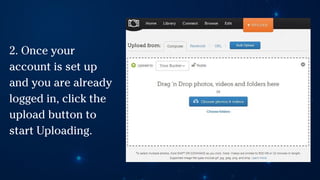
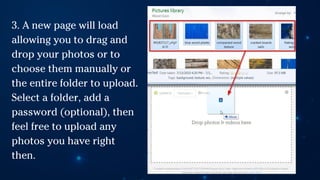
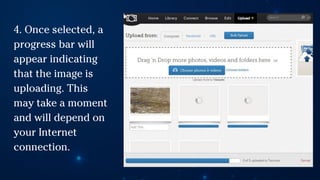
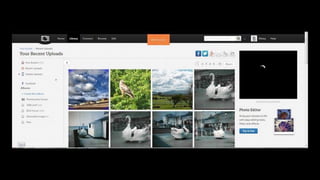
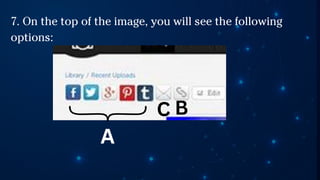
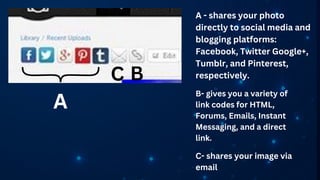
The document outlines essential principles of graphic design and image manipulation for an online environment, including creating infographics and effective image file formats. It covers tools like Piktochart for designing infographics and Photoscape for image editing, as well as tips for managing image quality for web use. Additionally, it provides guidance on using image hosts like Photobucket for uploading and sharing photos online.