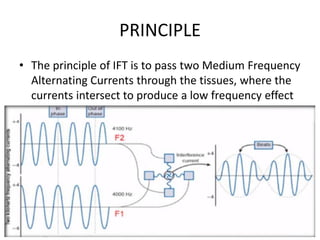
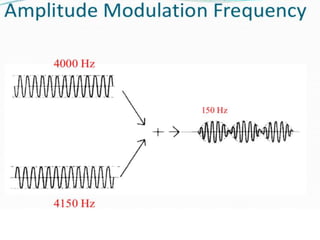
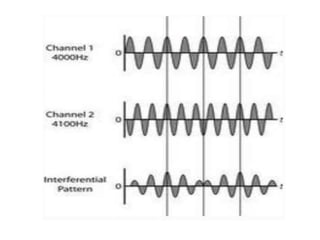
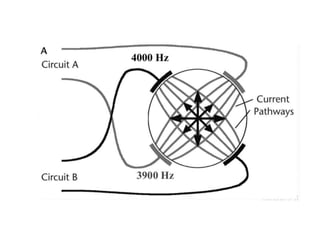
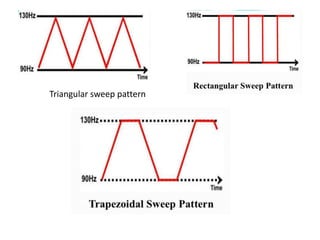
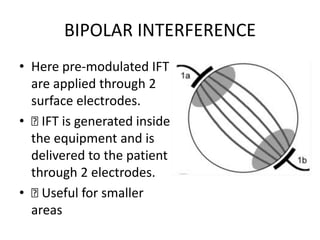
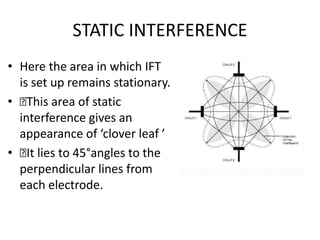
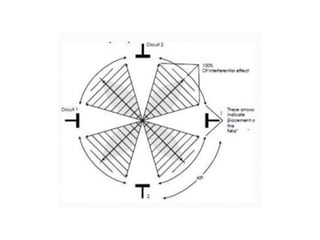
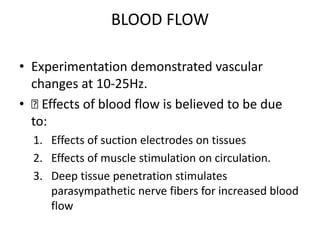
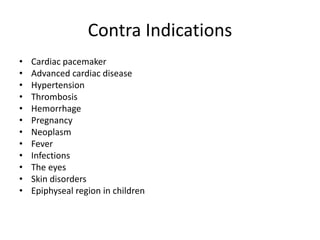
Interferential therapy involves applying two medium frequency alternating currents intersecting in the body to produce a low frequency interference current. This current is able to penetrate deeper into tissues than direct current, allowing for pain relief and muscle stimulation. The interference current is modulated to create a beat frequency effect. Different electrode types and application methods exist to target specific areas. Physiological effects include reducing pain, increasing blood flow and muscle stimulation. Treatment parameters like frequency, duration and method of application are chosen based on the condition and treatment goals.