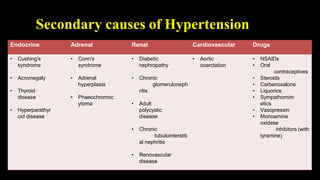
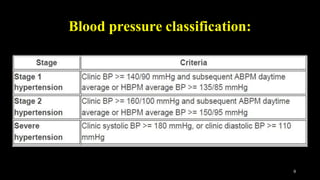
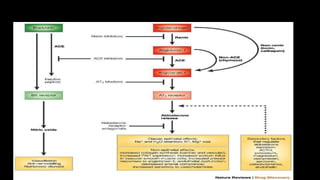
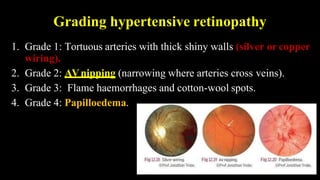
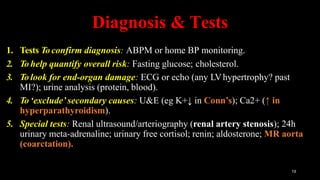
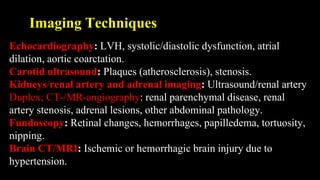
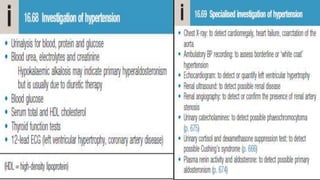
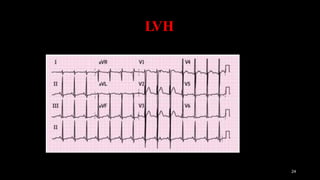
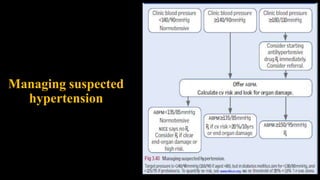
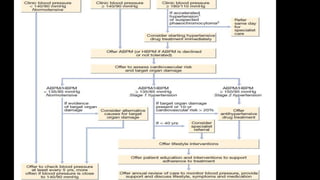
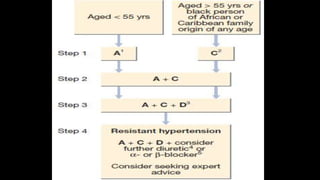
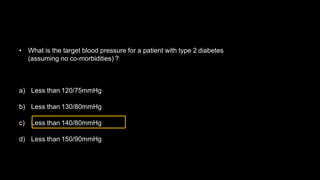
Hypertension is defined as persistent blood pressure readings of 140/90 mmHg or higher. It is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease and premature death. While usually asymptomatic, regular screening is important for detection. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications and medication to lower blood pressure to under 140/90 mmHg to reduce health risks. Malignant hypertension is a medical emergency characterized by severely high blood pressure that requires urgent treatment and hospitalization.