The document provides an overview of hydroponics, including:
- Hydroponics is a technique for growing plants without soil by having roots absorb nutrients dissolved in water.
- It was popularized in the 1920s and was used by the US Army during WWII to grow fresh food for troops.
- There are several types of hydroponic systems that circulate nutrient solutions to plant roots, including wick, water culture, nutrient film technique, ebb and flow, and drip systems.
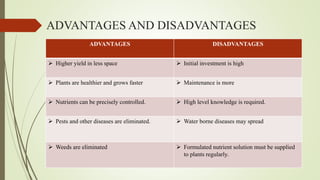
- Hydroponics has advantages like higher yields, healthier plants, and less water use than traditional agriculture but requires more initial investment and maintenance than soil-based gardening.