Embed presentation
Download to read offline
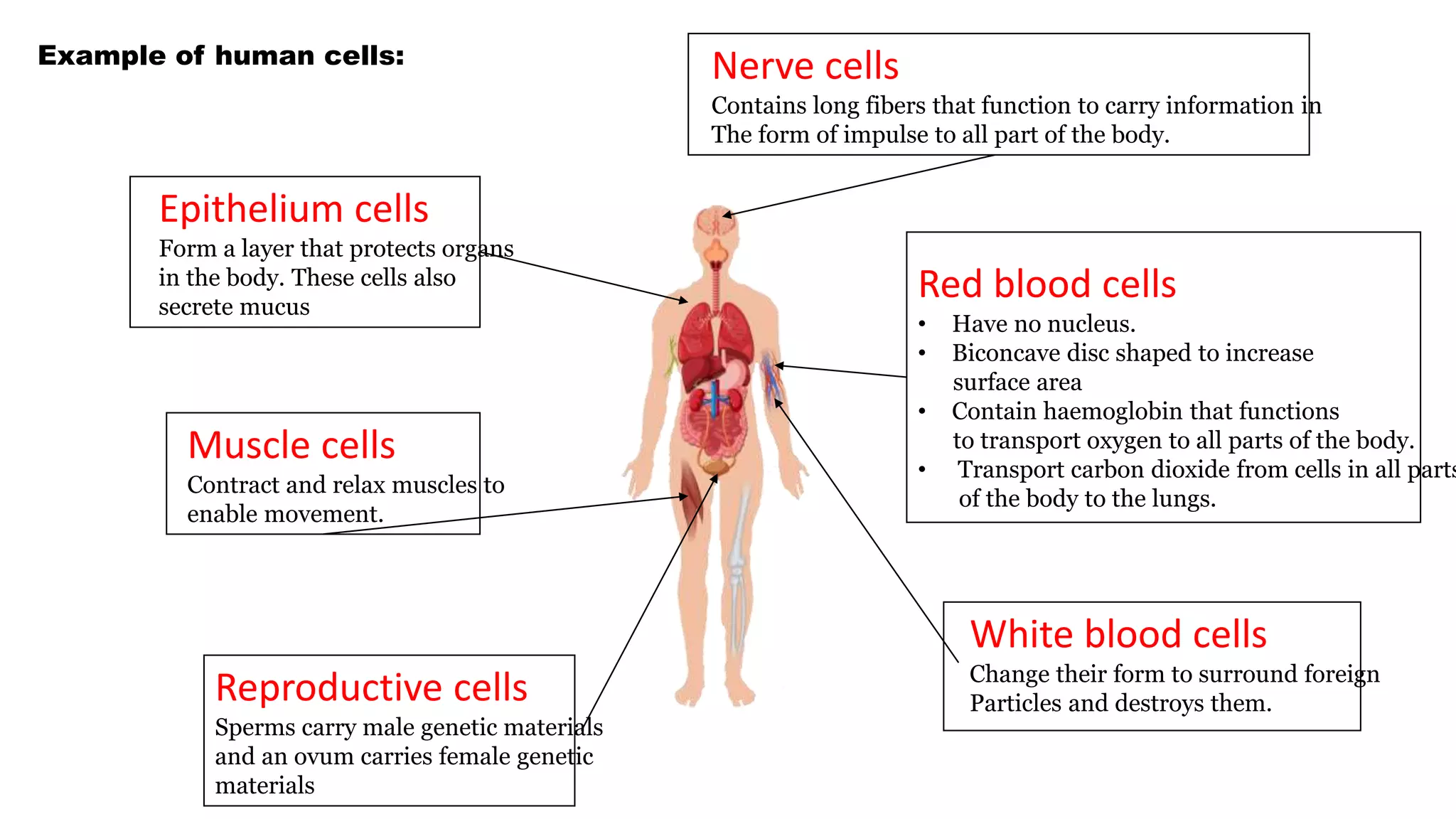

Red blood cells are biconcave discs without a nucleus that contain hemoglobin to transport oxygen from the lungs to cells and carbon dioxide from cells back to the lungs. White blood cells change shape to surround and destroy foreign particles. Epithelium cells form protective layers that secrete mucus while muscle cells contract and relax to enable movement. Reproductive cells are sperm and ova that carry genetic material and nerve cells have long fibers that transmit impulses around the body.



