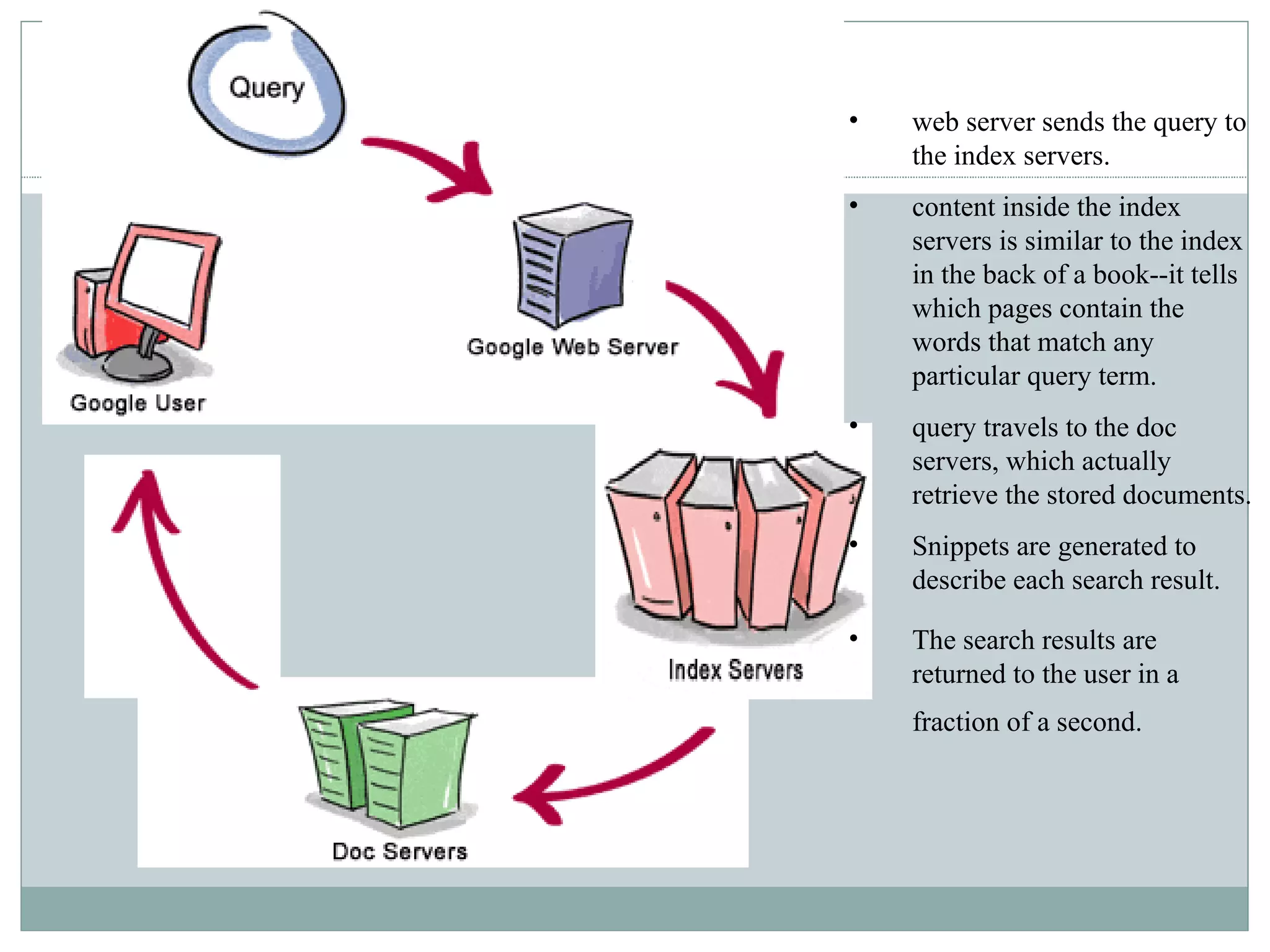
Google works by using thousands of computers that crawl the web, index pages, and process search queries in parallel. Googlebot, Google's web crawler, fetches web pages from across the internet and hands them off to Google's indexer. The indexer then creates an alphabetical index of terms found on each page along with their locations. When a user searches, Google's query processor matches the terms to results from the indexer and returns relevant pages within seconds.