Embed presentation
Download to read offline


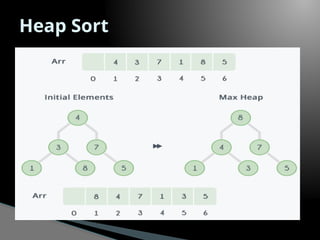


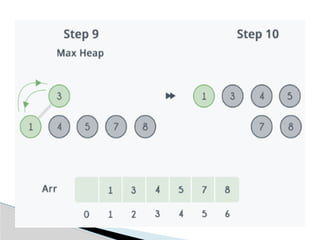
Heap Sort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm that uses a binary heap data structure to organize and manipulate data. It operates in two main phases: first, the array is transformed into a max-heap (or min-heap, depending on the sorting order), where the largest (or smallest) element is always at the root. Then, the heap property is repeatedly used to extract the root element and place it in its correct sorted position by swapping it with the last element in the heap and reducing the heap size. The process of maintaining the heap property, called "heapification," ensures that the remaining elements still satisfy the heap structure after each extraction. Heap sort has a time complexity of � ( � log � ) O(nlogn) for all cases—best, average, and worst—making it efficient and reliable. It is an in-place sorting algorithm, as it requires no extra space beyond the input array, but it is not stable, meaning the relative order of equal elements may not be preserved.





