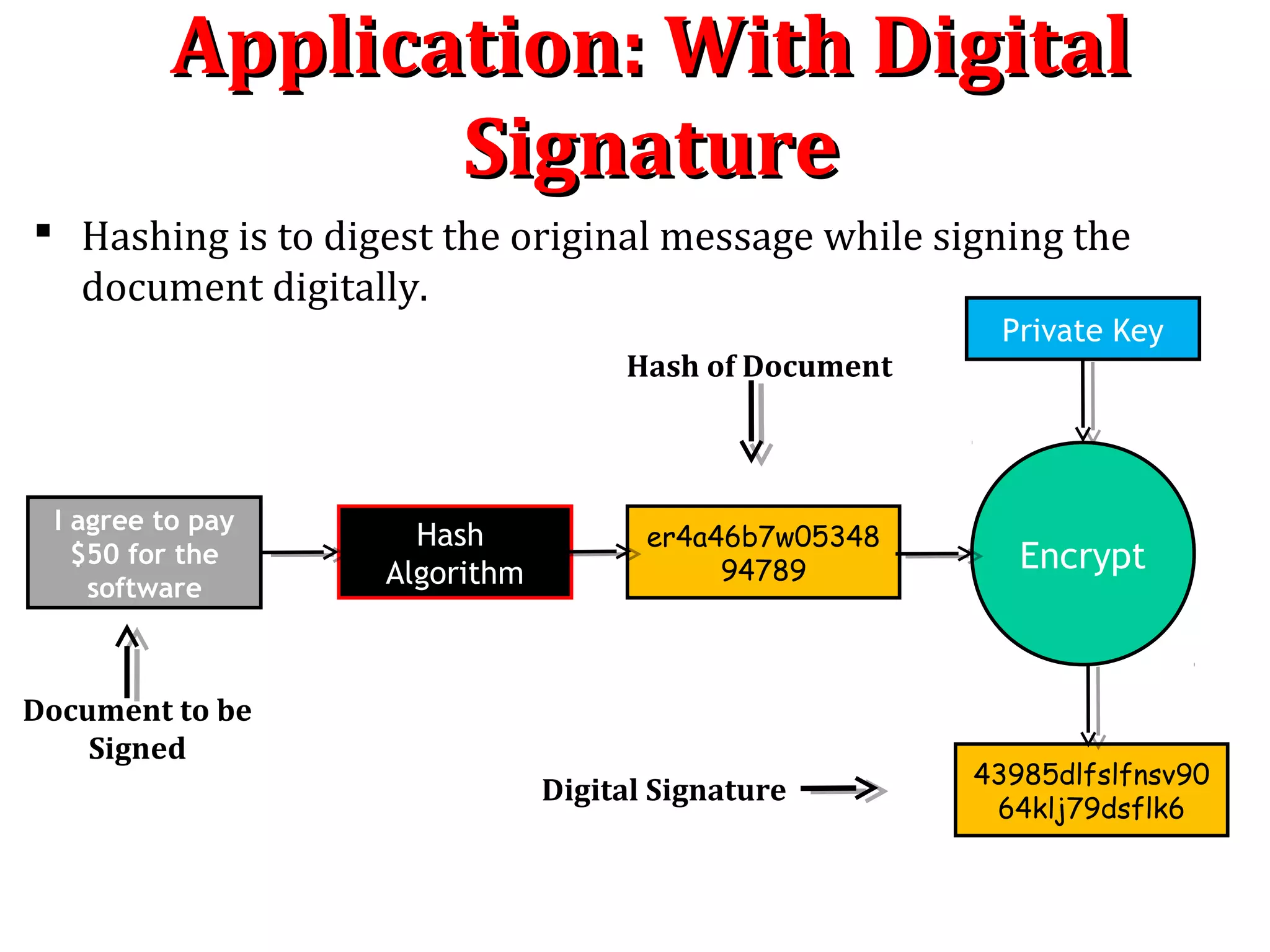
A hash algorithm is a one-way function that converts a data string into a numeric string output of fixed length. It is collision resistant, meaning it is very unlikely for different data to produce the same hash value. Common hash algorithms include MD5 and SHA-1. A one-way hash function takes a variable-length input and produces a fixed-length output. It is easy to compute the hash but very difficult to reverse it or find collisions. Hash functions are used for password verification, digital signatures, and ensuring data integrity.









![Applications of HashApplications of Hash
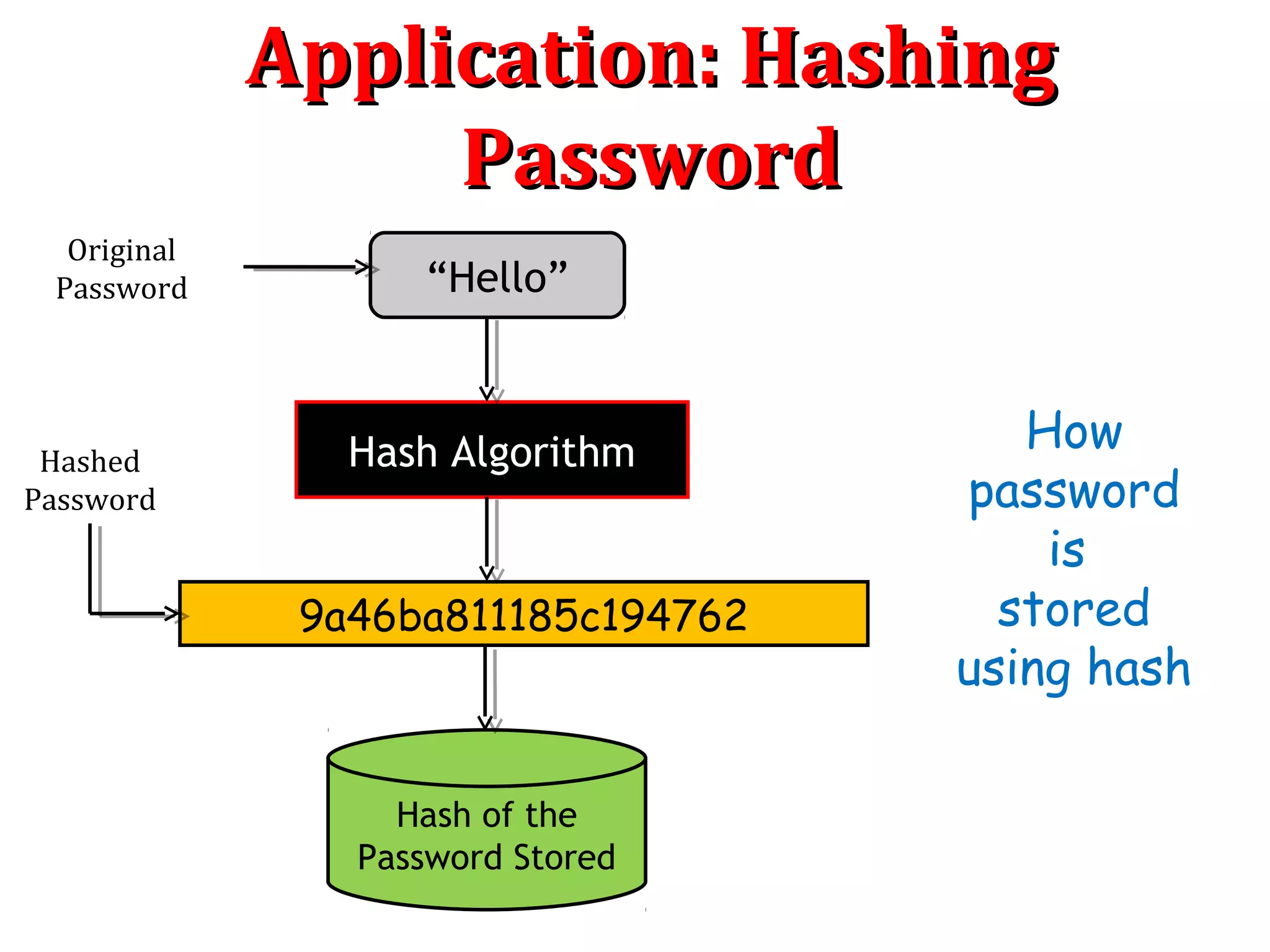
“World”
Hash Algorithm
Hash of the
Password Stored
Wrong
Password
9a46ba811185c194762er4a46b7w0534894789
Do Hashes
Matched?
Access GrantedAccess Denied
Hash Value
Mismatched
[Yes][No]
How
password
is
verified
using hash](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hashing-150802170222-lva1-app6891/75/Hashing-12-2048.jpg)












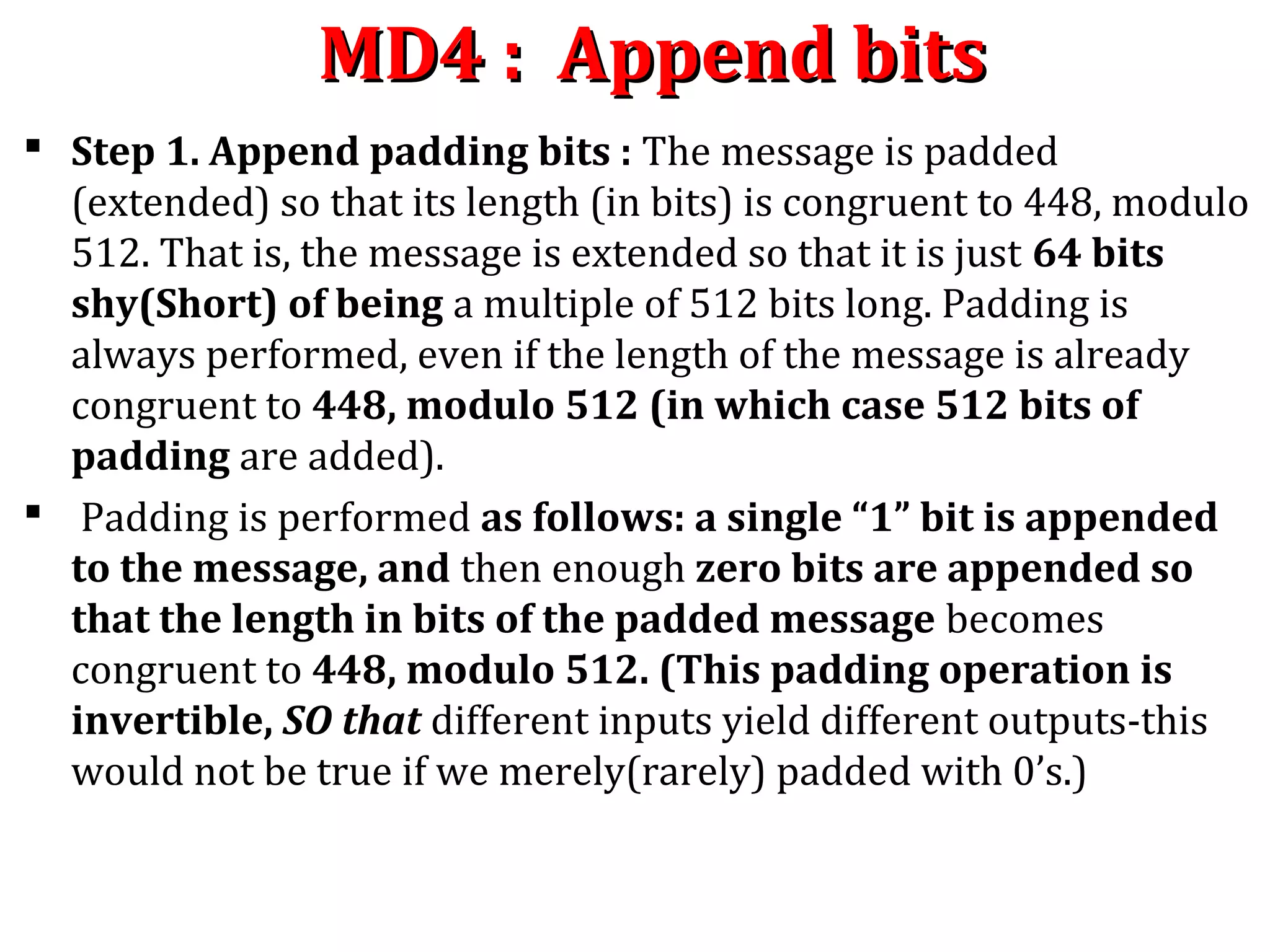
![MD4 : Append LengthMD4 : Append Length
Step 2. Append length: A 64-bit representation of b (the
length of the message before the padding bits were added) is
appended to the result of the previous step. These bits are
appended as two 32-bit words and appended low-order word
first in accordance with the previous conventions. In the unlikely
event that b is greater than 264
, then only the low-order 64 bits of b
are used.
At this point the resulting message (after padding with bits and
with b) has a length that is an exact multiple of 512 bits.
Equivalently, this message has a length that is an exact multiple
of 16 (32-bit) words. Let M[O.. . N – 1] denote the words of the
resulting message, where N is a multiple of 16.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hashing-150802170222-lva1-app6891/75/Hashing-29-2048.jpg)
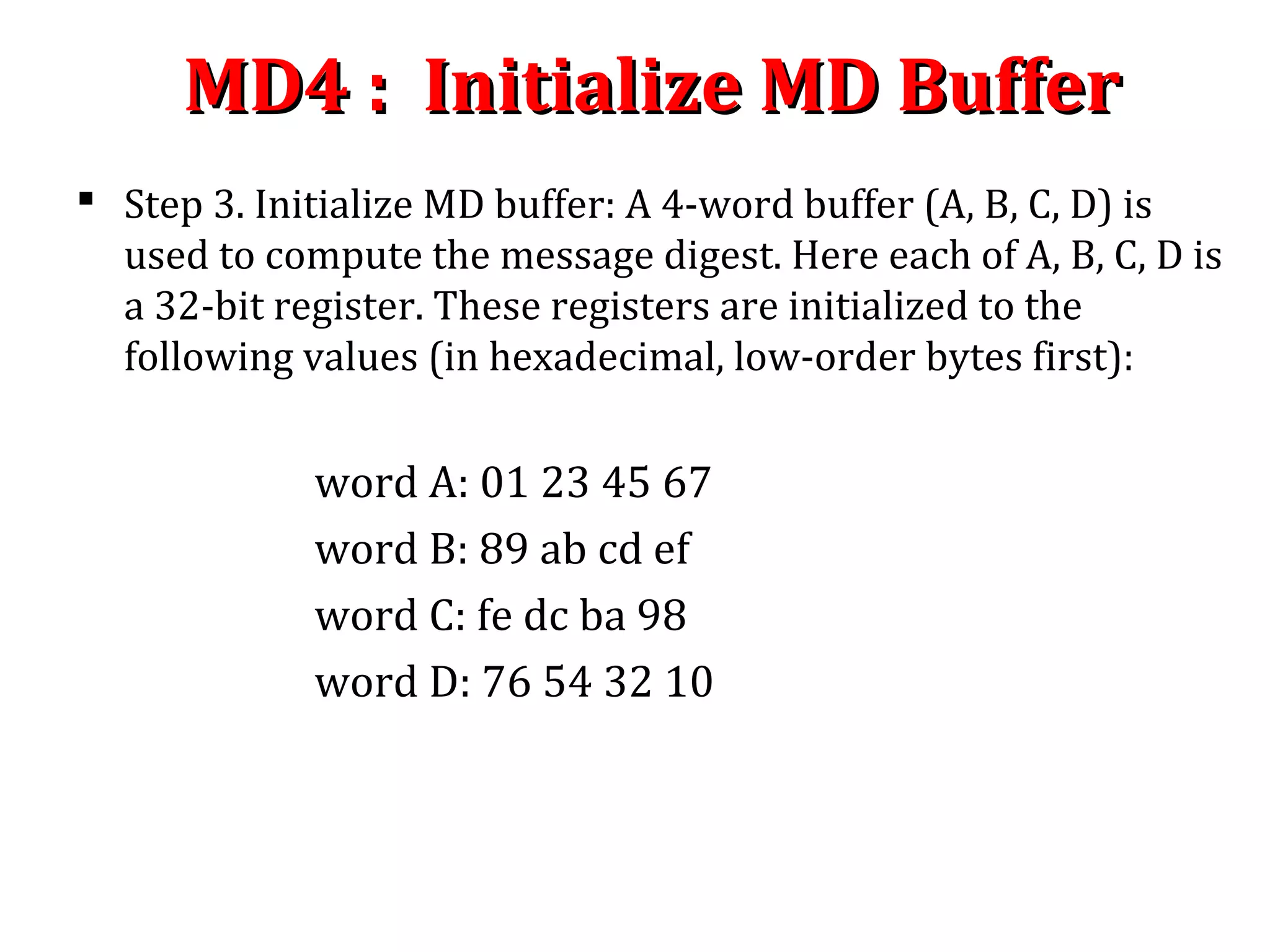
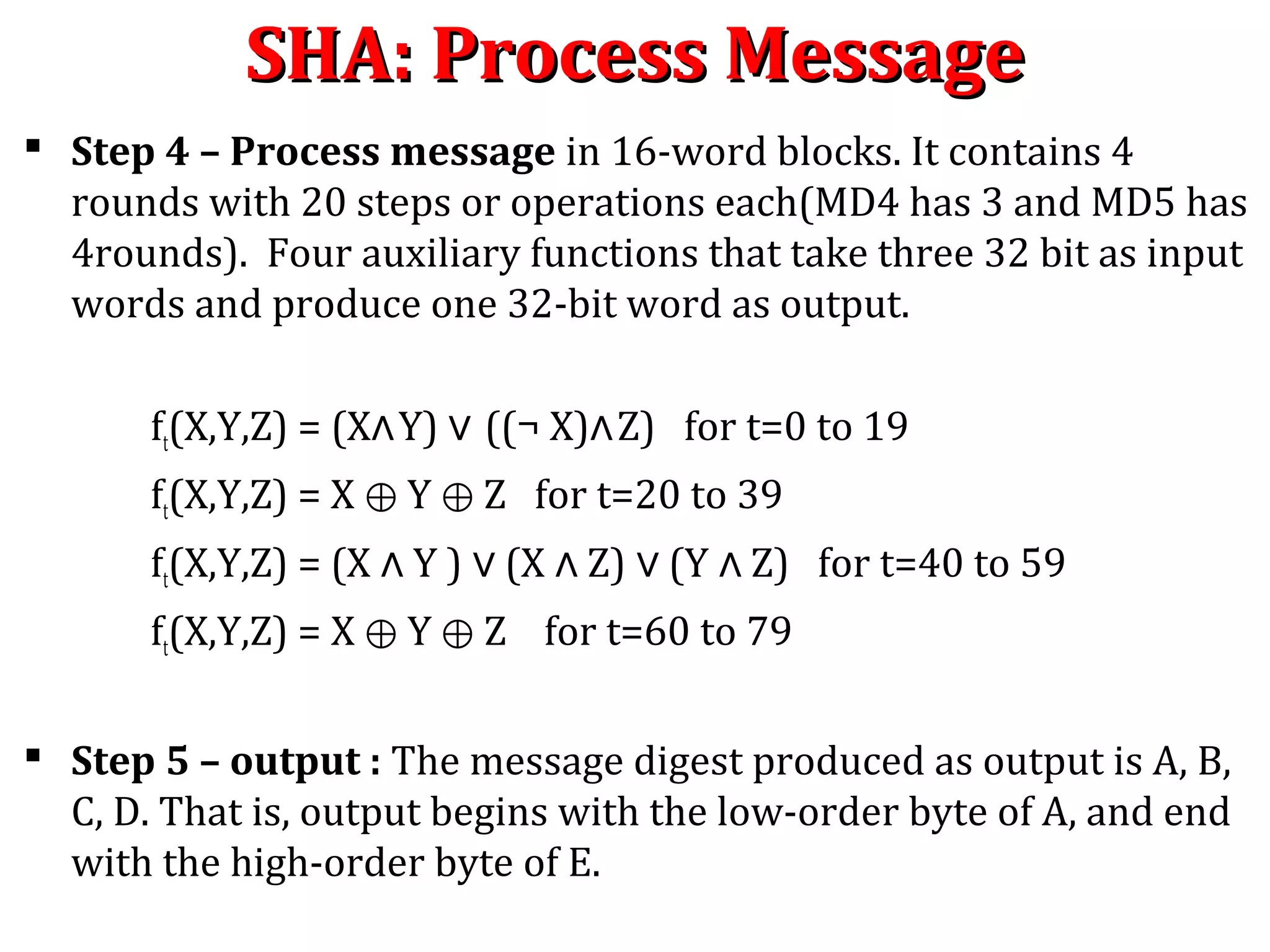
![MD4 : Process MessageMD4 : Process Message
Step 4. Process message in 16-word blocks : Process message in 16-
word blocks. It contain 3 round with 16 steps or operation each(MD5
has 4 rounds). It take three 32 bit words as input and produce one 32
bit word as output.
We first define three auxiliary functions that each take as input three
32-bit words and produce as output one 32-bit word.
F(X, Y, Z)=(X Y ) (¬X Z) [Step 0 to 15]∧ ∨ ∧
G(X, Y, Z)=(X Y ) (X Z) (Y Z) [Step 16 to 31]∧ ∨ ∧ ∨ ∧
H(X, Y, Z)=X Y Z [Step 32 to 47]⊕ ⊕
Where is XOR,⊕ is AND, is OR and∧ ∨ ¬ is NOT
In each bit position F facts as a conditional: if x then y else z. In each bit
position G acts as a majority function: if at least two of x,y, z are one,
then G has a one in that position. The function H is the bit-wise xor or
parity function.
MD4 utilizes two “magic constants” in rounds two and three.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hashing-150802170222-lva1-app6891/75/Hashing-31-2048.jpg)




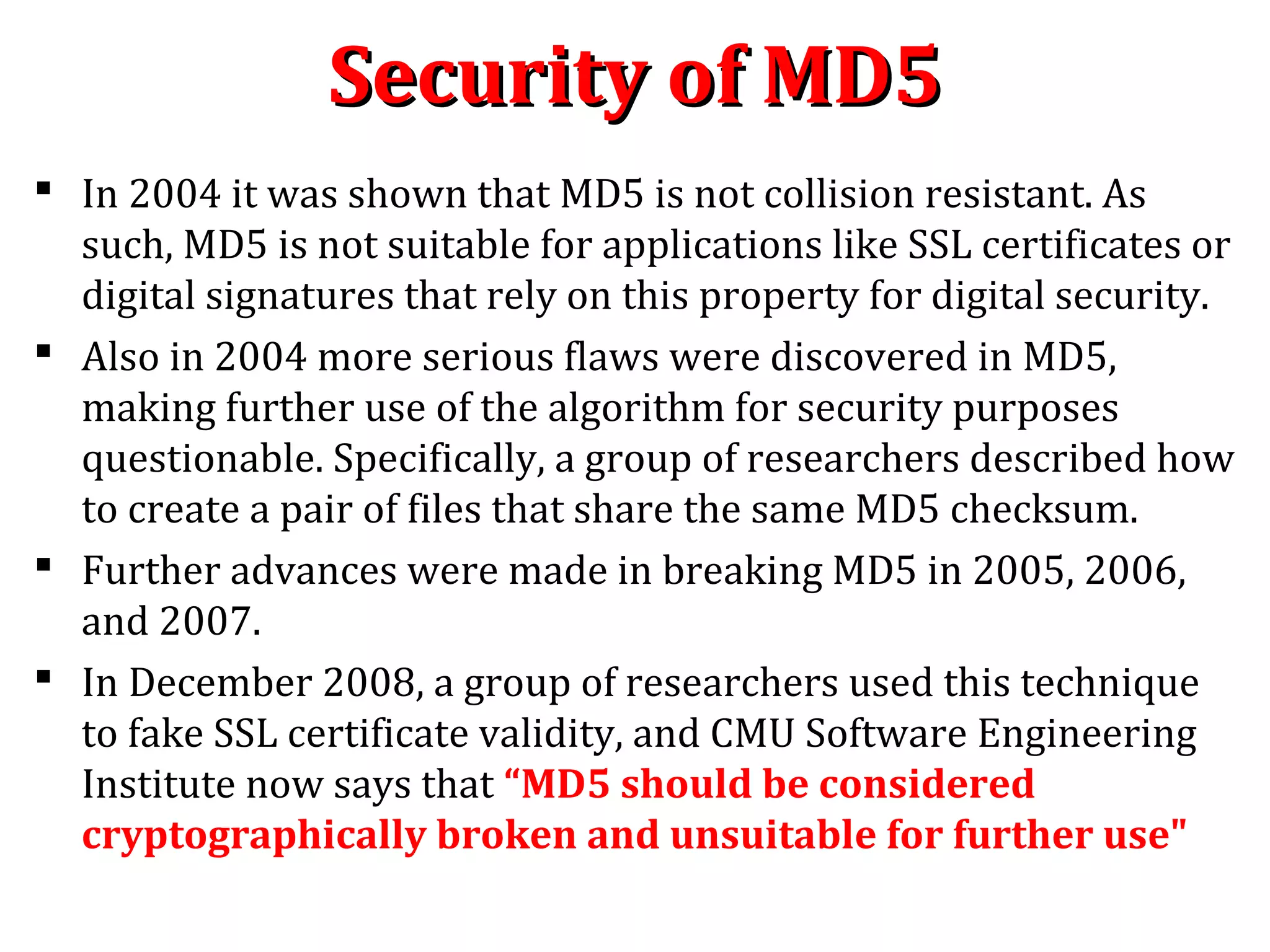
![MD5 : Append LengthMD5 : Append Length
Step 2. Append length: A 64-bit representation of b (the
length of the message before the padding bits were added) is
appended to the result of the previous step. These bits are
appended as two 32-bit words and appended low-order word
first in accordance with the previous conventions. In the unlikely
event that b is greater than 264
, then only the low-order 64 bits of b
are used.
At this point the resulting message (after padding with bits and
with b) has a length that is an exact multiple of 512 bits.
Equivalently, this message has a length that is an exact multiple
of 16 (32-bit) words. Let M[O.. . N – 1] denote the words of the
resulting message, where N is a multiple of 16.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hashing-150802170222-lva1-app6891/75/Hashing-39-2048.jpg)
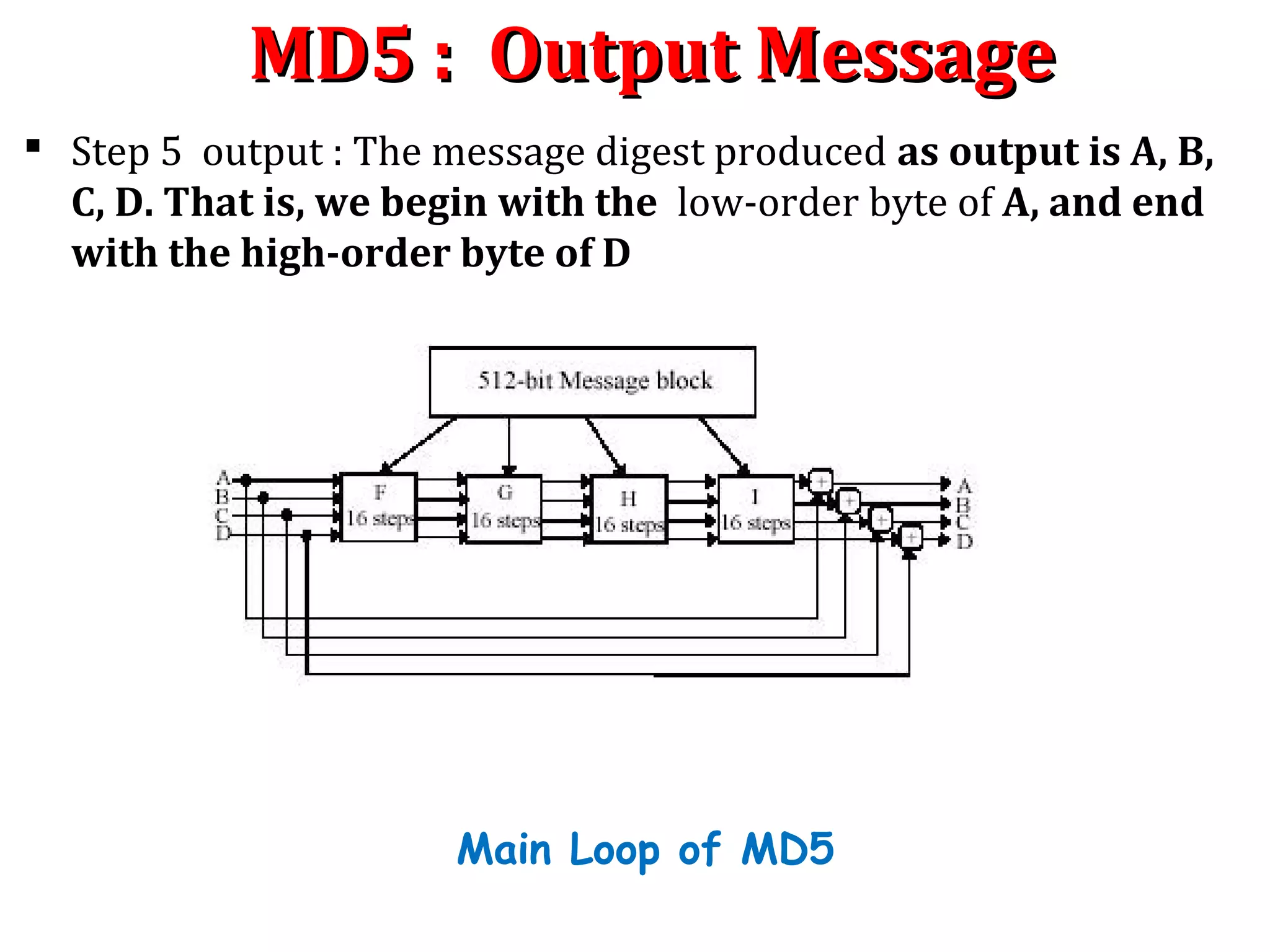
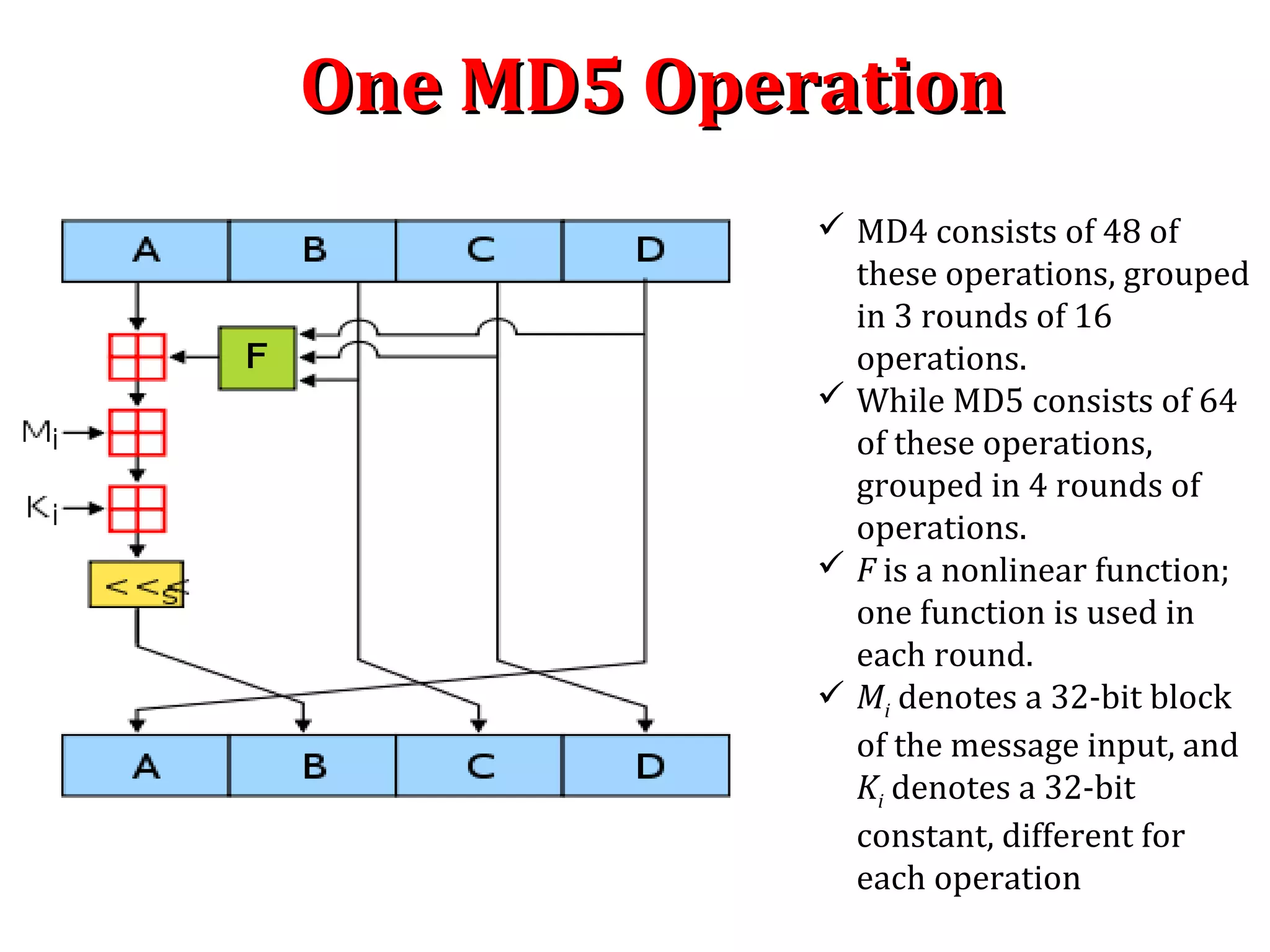
![MD5 : Process MessageMD5 : Process Message
Step 4. Process message in 16-word blocks : Process message in 16-
word blocks. It contain 4 round with 16 steps or operation each(MD4
has 3 rounds). It take three 32 bit words as input and produce one 32
bit word as output.
We first define three auxiliary functions that each take as input three
32-bit words and produce as output one 32-bit word.
F(X,Y,Z) = (X∧Y) ∨ ((¬ X)∧Z) [Step 0 to 15]
G(X,Y,Z) = (X∧Z) ∨ (Y∧(¬ Z)) [Step 16 to 31]
H(X,Y,Z) = X Y Z⊕ ⊕ [Step 32 to 47]
I(X,Y,Z) = Y ⊕ (X∨(¬ Z)) [Step 48 to 64]
In each bit position f acts as a conditional: if x then y else z. In each bit
position g acts as a majority function: if at least two of x,y, z are one,
then g has a one in that position. The function h is the bit-wise xor or
parity function.
MD4 utilizes two “magic constants” in rounds two and three. The round
two constant is fi and the round 3 constant is a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hashing-150802170222-lva1-app6891/75/Hashing-41-2048.jpg)