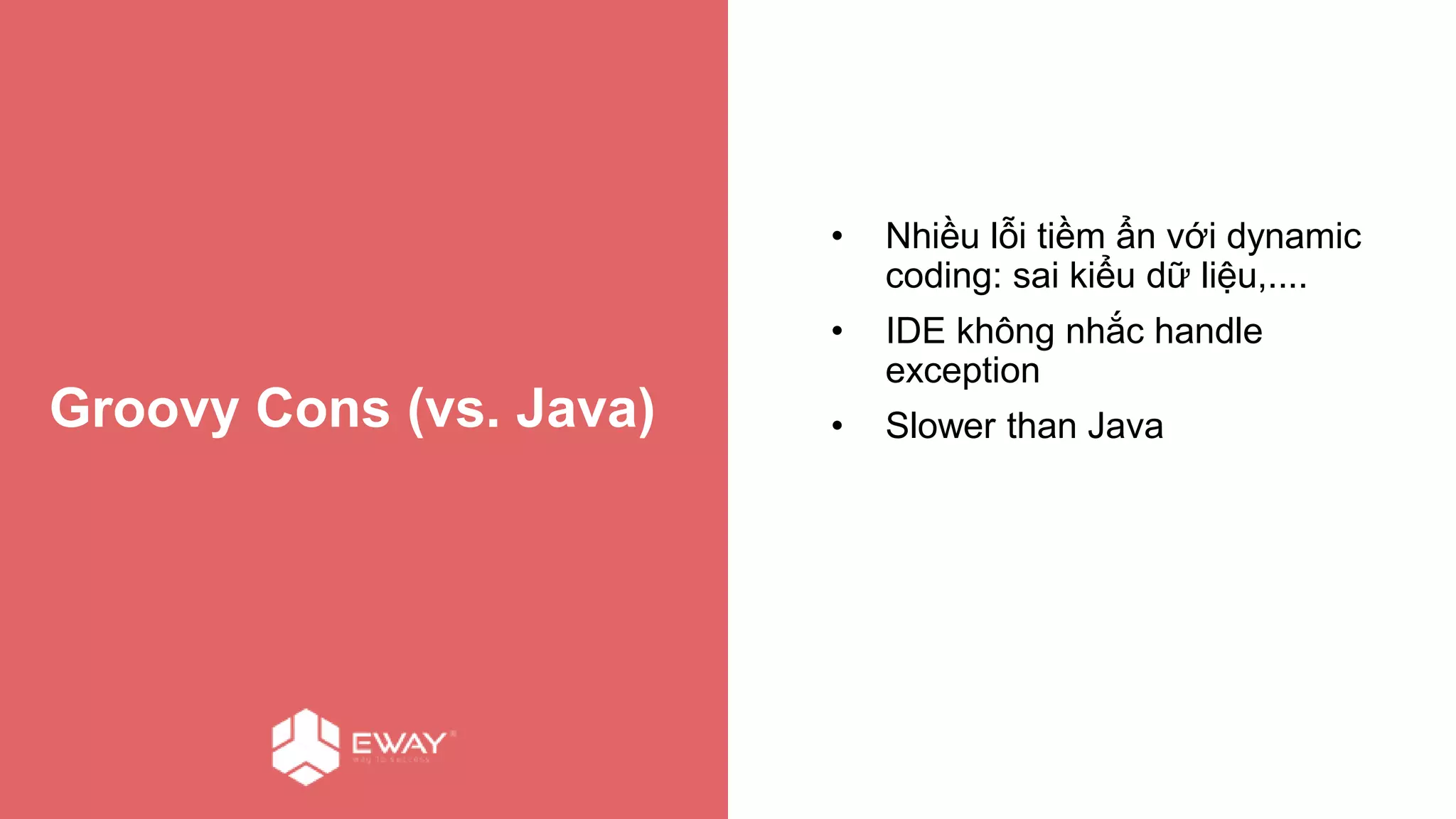
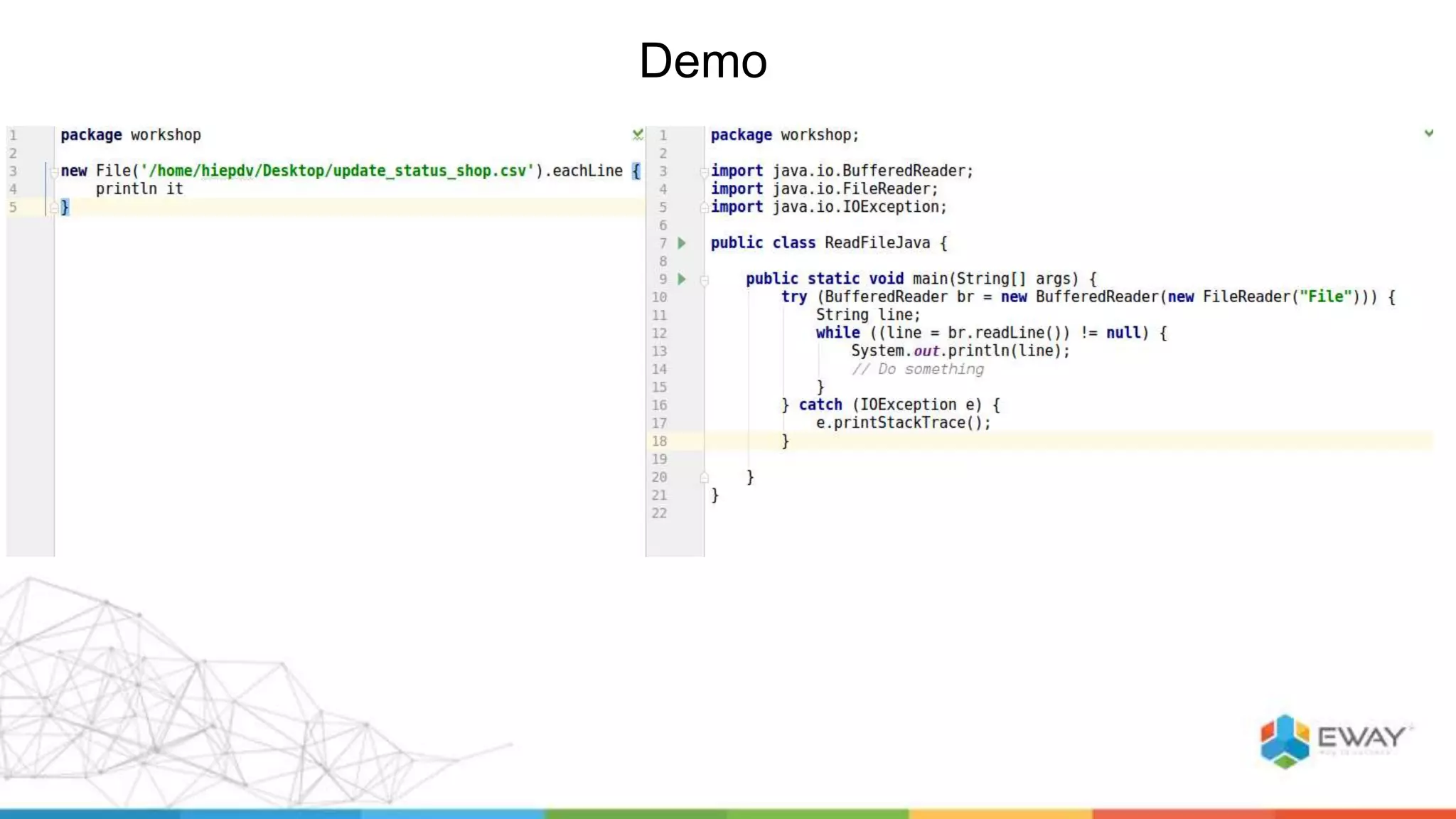
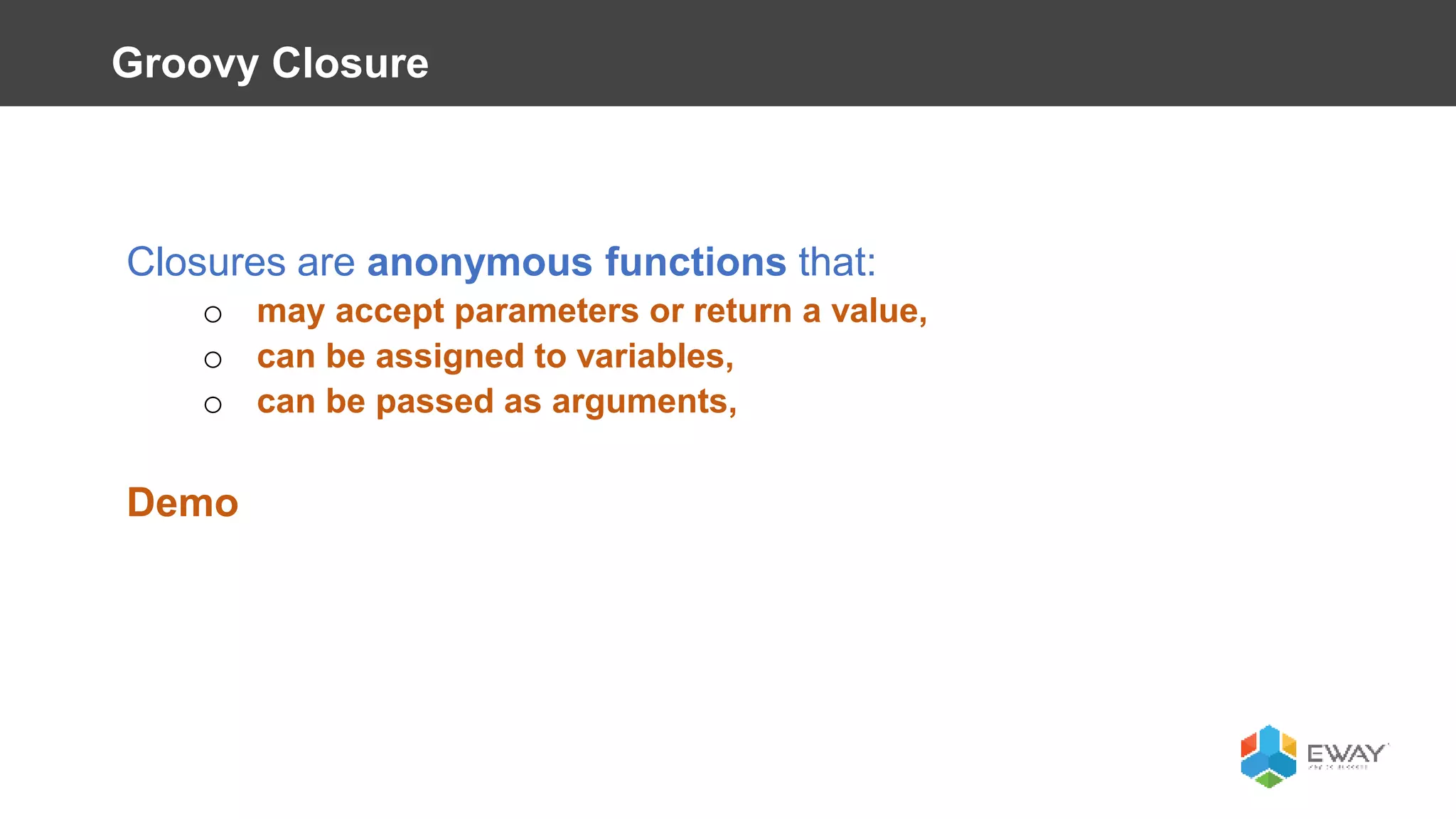
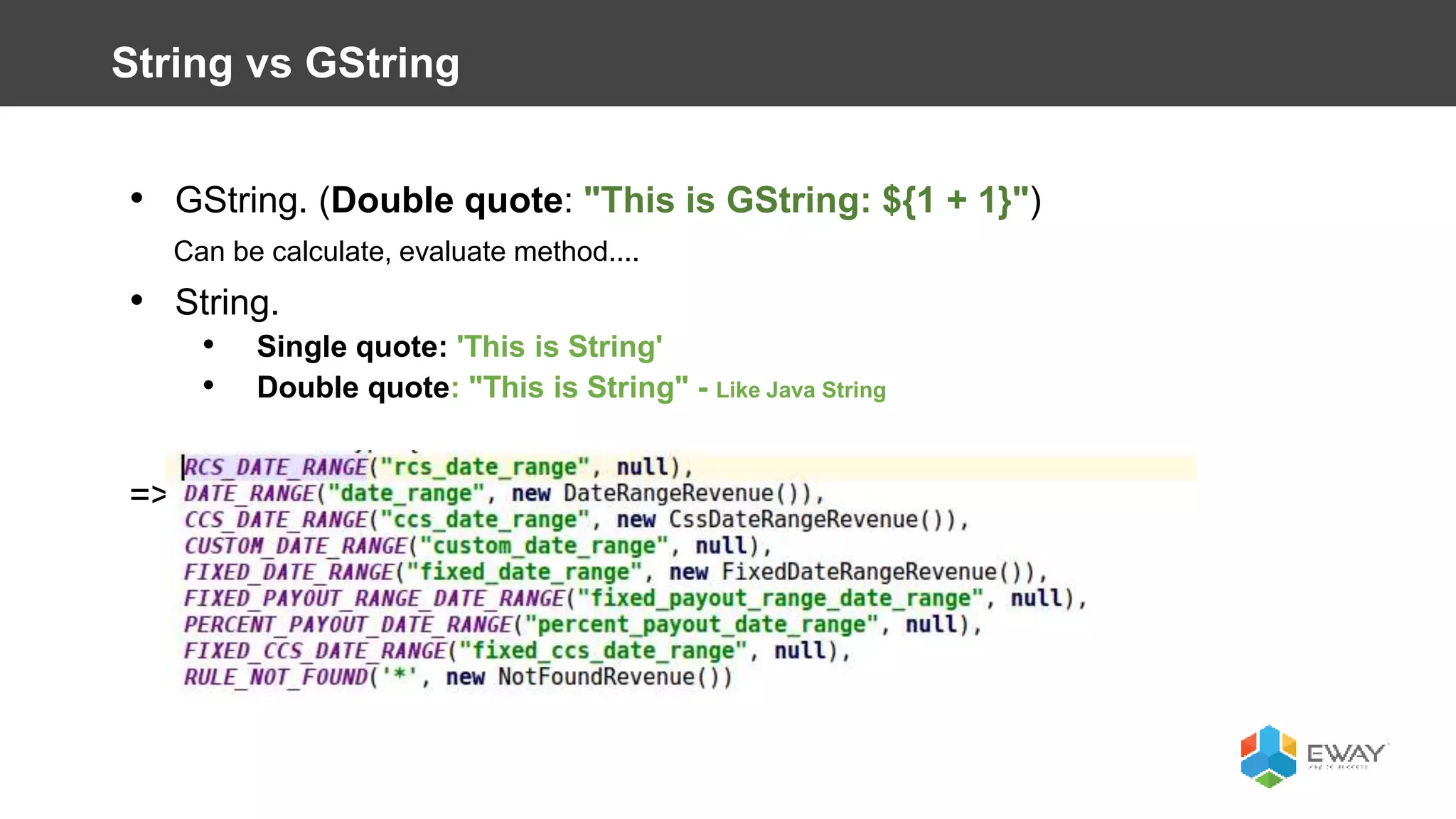
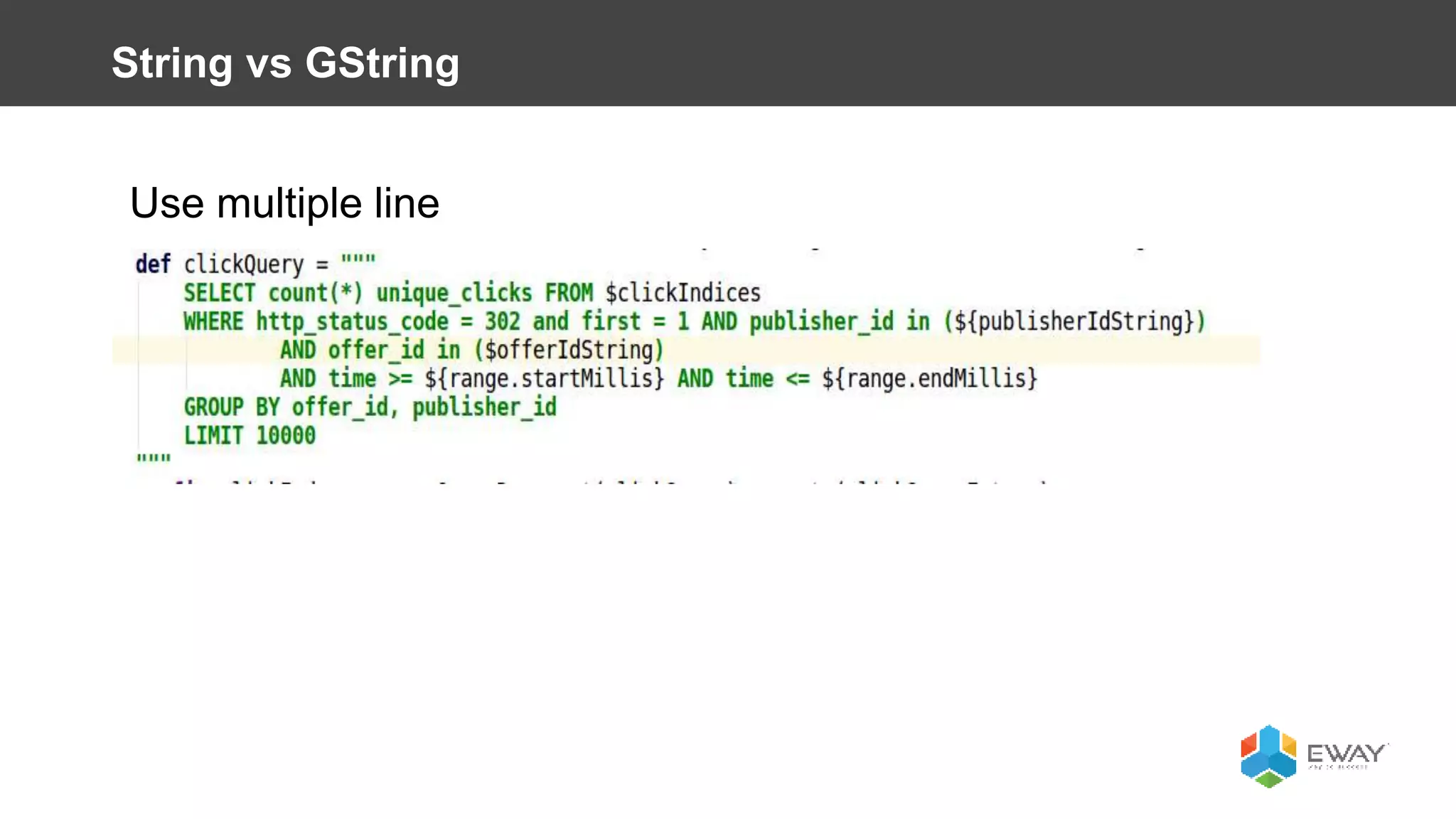
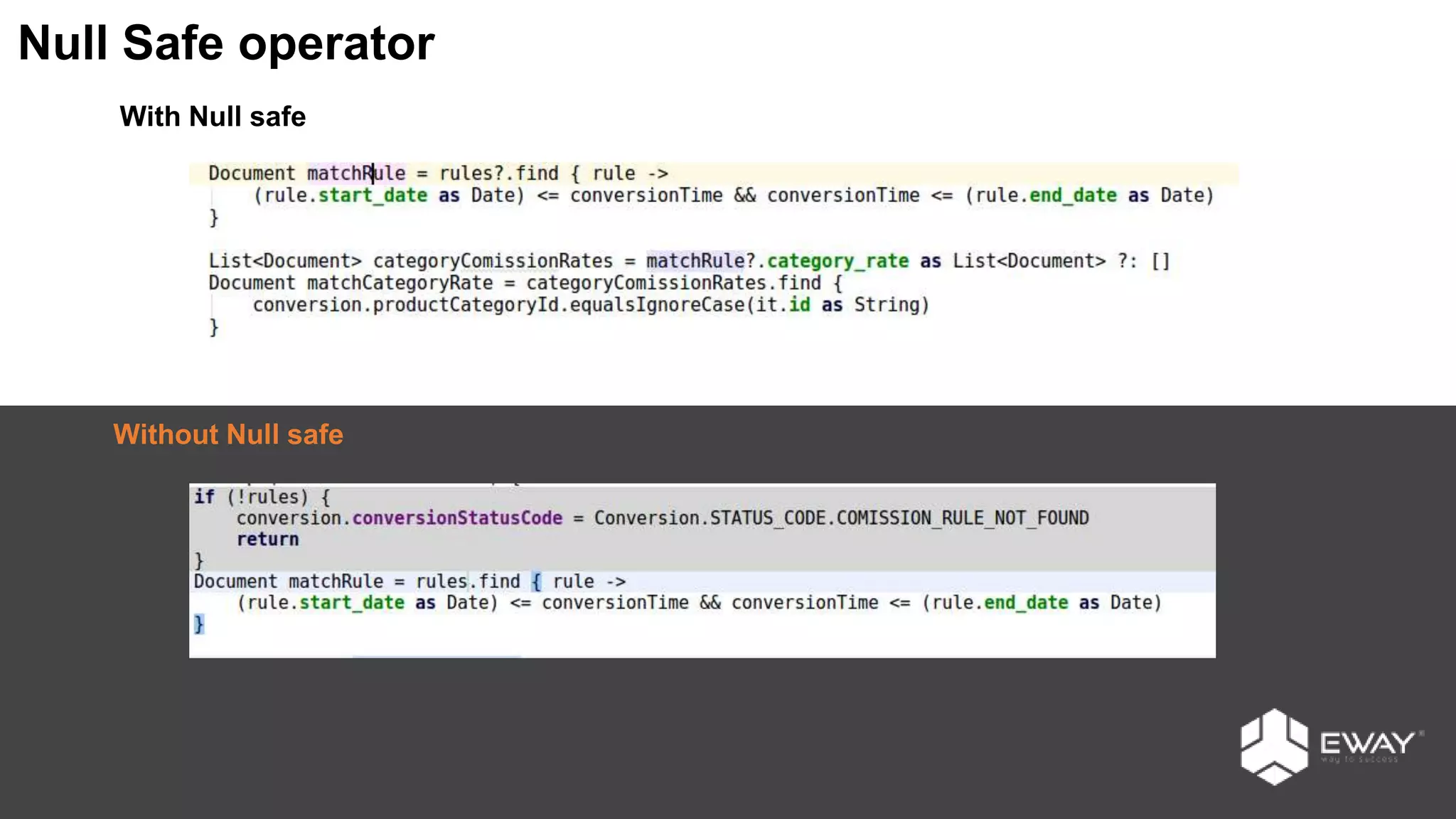
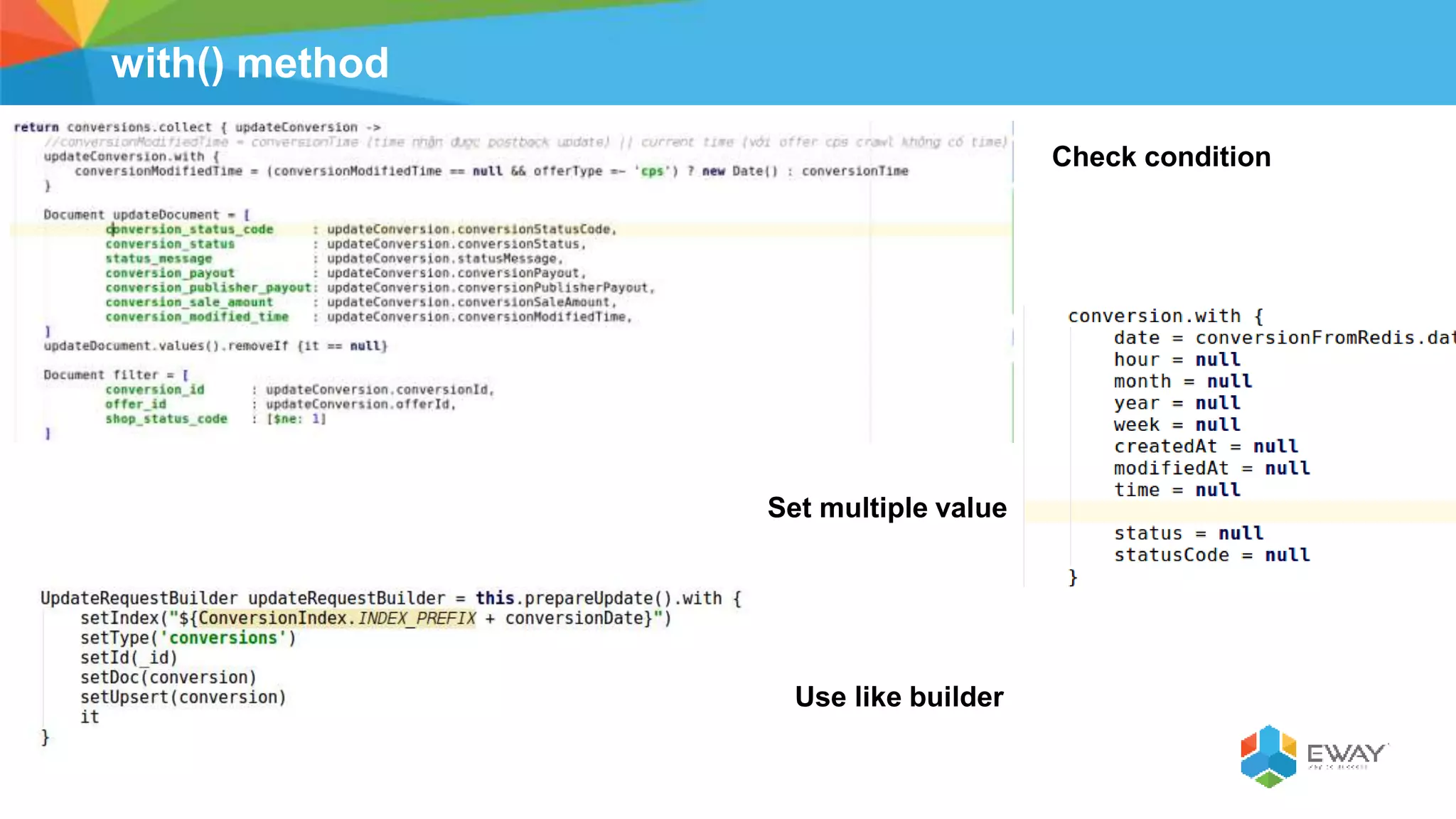
Groovy is a dynamic language for the Java Virtual Machine that aims to provide features similar to languages like Python, Ruby, and Smalltalk. It is syntactically similar to Java but with additional features like closures, builders, and categories. Some benefits of using Groovy over Java include increased productivity through more concise syntax, the ability to mix functional and object-oriented programming, and better support for testing. Best practices for Groovy include using the 'def' keyword instead of explicit types, avoiding 'if' statements with non-boolean objects, properly handling null values, and leveraging features like closures, operators, and collection handling.