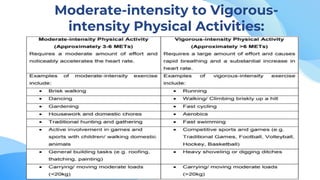
This document discusses principles of physical fitness and activity. It outlines the learning outcomes of identifying principles of activity, appreciating the importance of FITT (Frequency, Intensity, Time, Type) for physical activities, and performing moderate to vigorous activities according to a fitness plan. It then explains the principles of overload, progression, specificity, and reversibility as they relate to physical training. It defines the components of FITT - frequency as number of weekly sessions, intensity as effort level, type as chosen activity, and time as duration. Cardiovascular, flexibility, and strength exercises are listed as examples for developing different fitness domains.