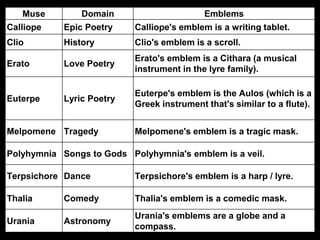
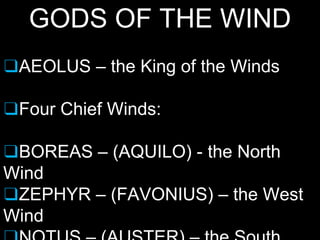
This document provides information on many important Greek gods and goddesses. It describes their roles and relationships. The supreme god Zeus ruled over the other Olympian gods who lived on Mount Olympus, such as his brothers Poseidon and Hades. Other major deities discussed include Apollo, Ares, Aphrodite, Athena, Artemis, Demeter, Dionysus, Hera, Hephaestus, and Hermes. The document also covers the Muses and Graces who inspired arts and cultivated beauty.