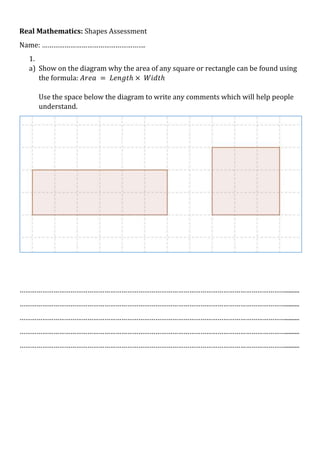
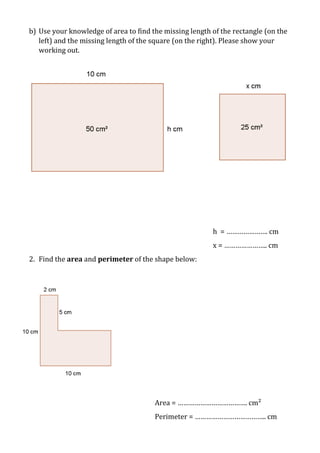
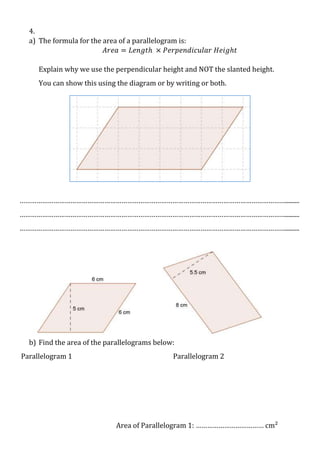
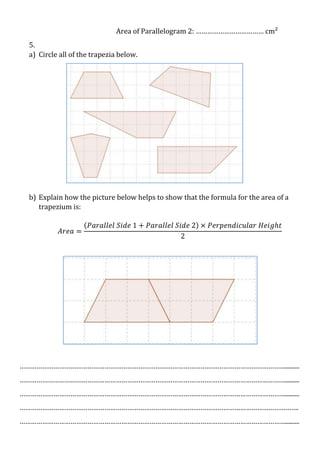
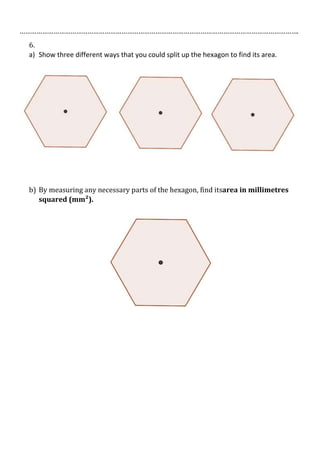
This document is a mathematics assessment on shapes that tests a student's knowledge of area formulas for squares, rectangles, triangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and hexagons. It contains questions that require the student to find missing lengths, calculate areas and perimeters, explain area formulas visually or in writing, and apply the formulas to find the areas of various shapes. The assessment provides space for work and explanations to demonstrate understanding of geometric concepts and area calculations.