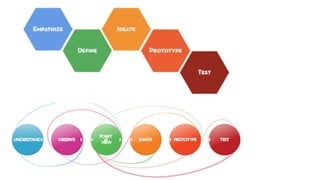
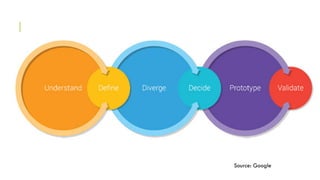
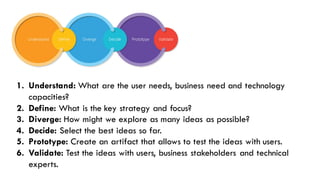
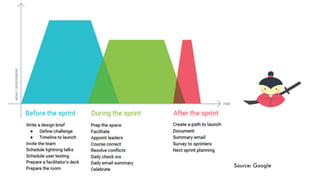
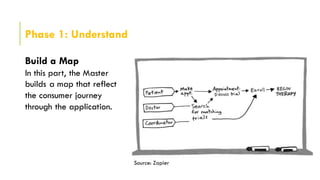
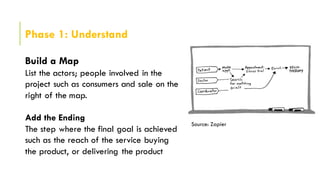
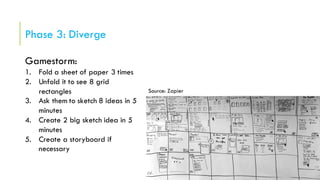
The document outlines the design sprinting framework, combining design thinking and agile methodologies to rapidly address design problems within 2-5 days. It consists of six phases: understand, define, diverge, decide, prototype, and validate, facilitated by a sprint master who organizes the team and manages the flow of the sessions. Key components include stakeholder involvement, brainstorming techniques, and user testing to create effective prototypes and solutions.