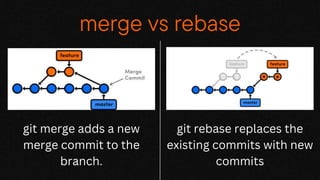
This document provides an overview of version control and the Git version control system. It explains that Git can help collaborators work in parallel and merge changes automatically. It also describes how to install Git and some common Git commands like git init, git add, git commit, git push, git remote, git log, git stash, and git merge. It discusses features of Git like repositories, branches, commits, and resolving merge conflicts. It encourages exploring GitHub as a platform for code collaboration using Git for version control.