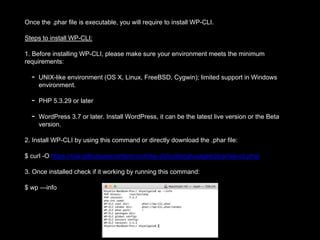
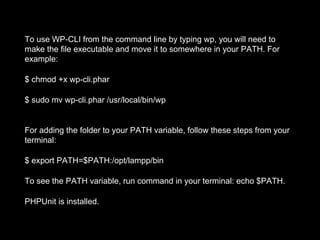
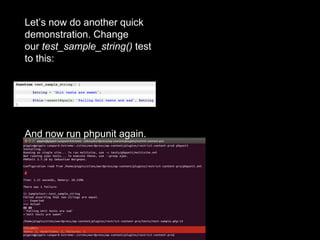
The document discusses the importance of early testing in software development, emphasizing its role in preventing bugs and ensuring product features function correctly. It provides an overview of PHPUnit, a PHP testing framework, detailing installation prerequisites, installation methods, and steps to set up and run unit tests within a WordPress environment. It also includes guidance on generating test environments, creating unit tests, running them, and setting up automated testing with Travis CI.