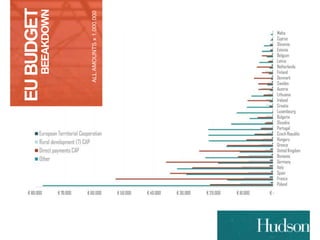
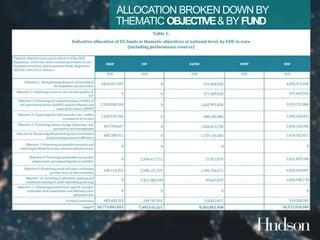
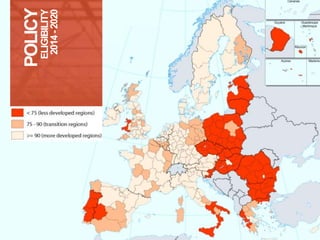
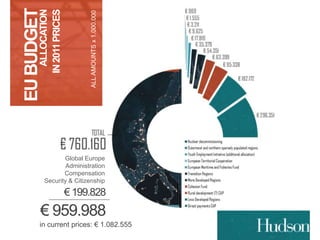
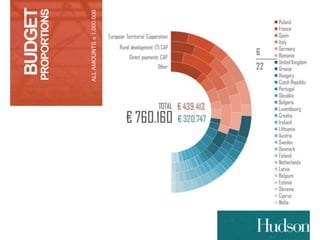
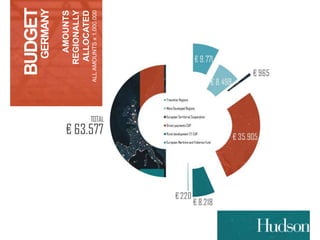
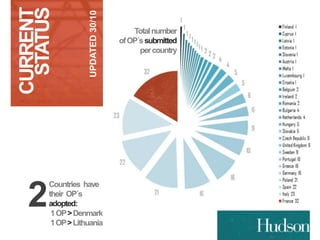
This document provides information on EU budgets and funding for Germany for 2014-2020. It discusses the five European Structural and Investment Funds and how Partnership Agreements are used to implement strategic plans for these funds. It also outlines the maximum aid percentages for regional investment, thematic objectives for the European Regional Development Fund and European Social Fund, and financial allocations for Germany under these funds as well as the European Agricultural Fund for Rural Development.











![FUNDING
PRIORITIES
For Germany as a whole, the ESF-supported Investitionen in die Köpfe
[Investment in minds] will make visible contributions to smart, sustainable
and inclusive growth and to adaptation to demographic change.
In particular, results are to be expected from the mobilization of additional
economic potential, with a key role to be played by hitherto unutilized
economic potential among women.
The development of human resources is supported on the supply side and
the demand side in order to help secure the skills base and improve the
situation of the disadvantaged.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/germanyv5-141117155219-conversion-gate02/85/EU-Budget-Germany-2014-2020-update-November-2014-19-320.jpg)