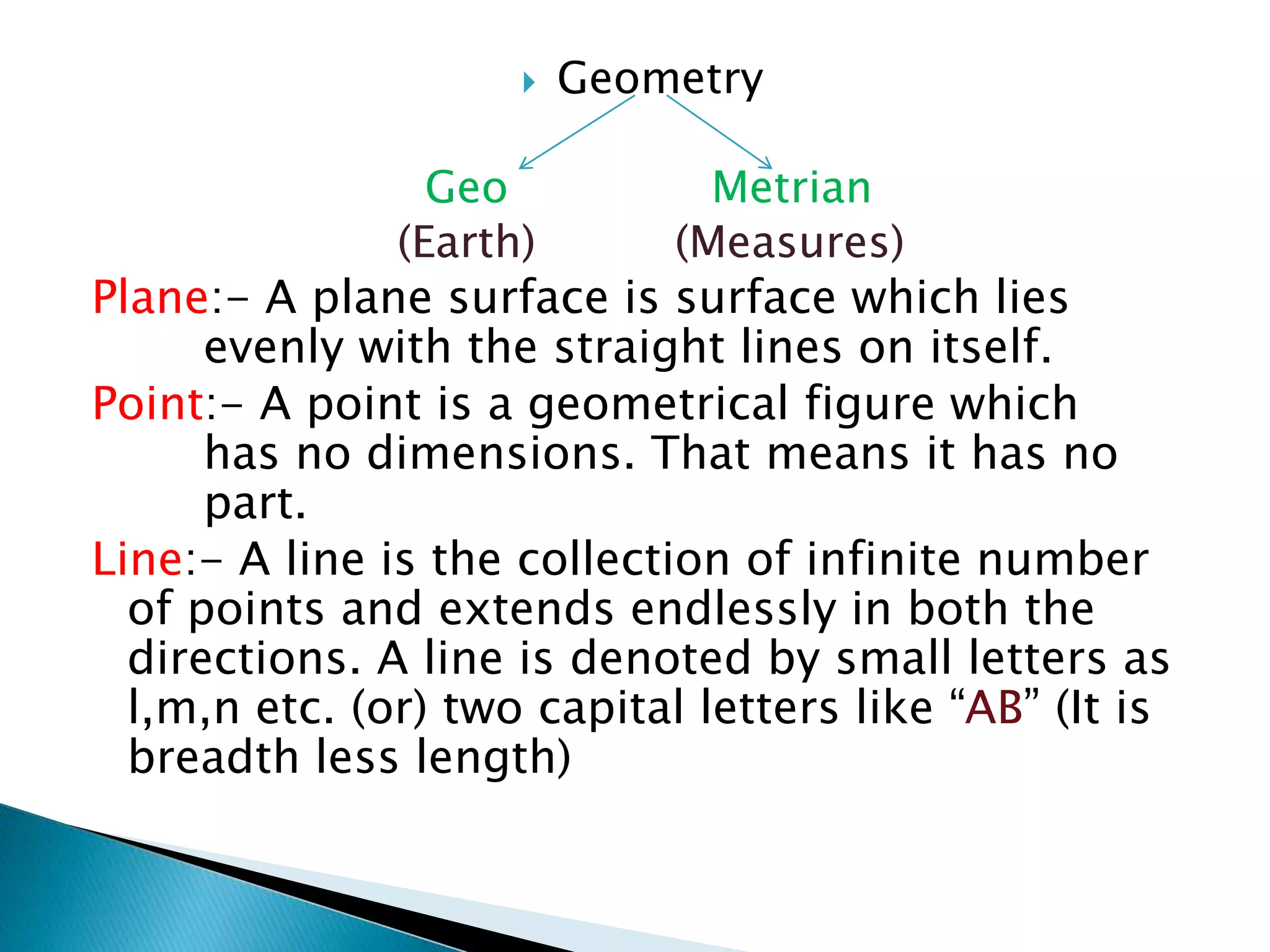
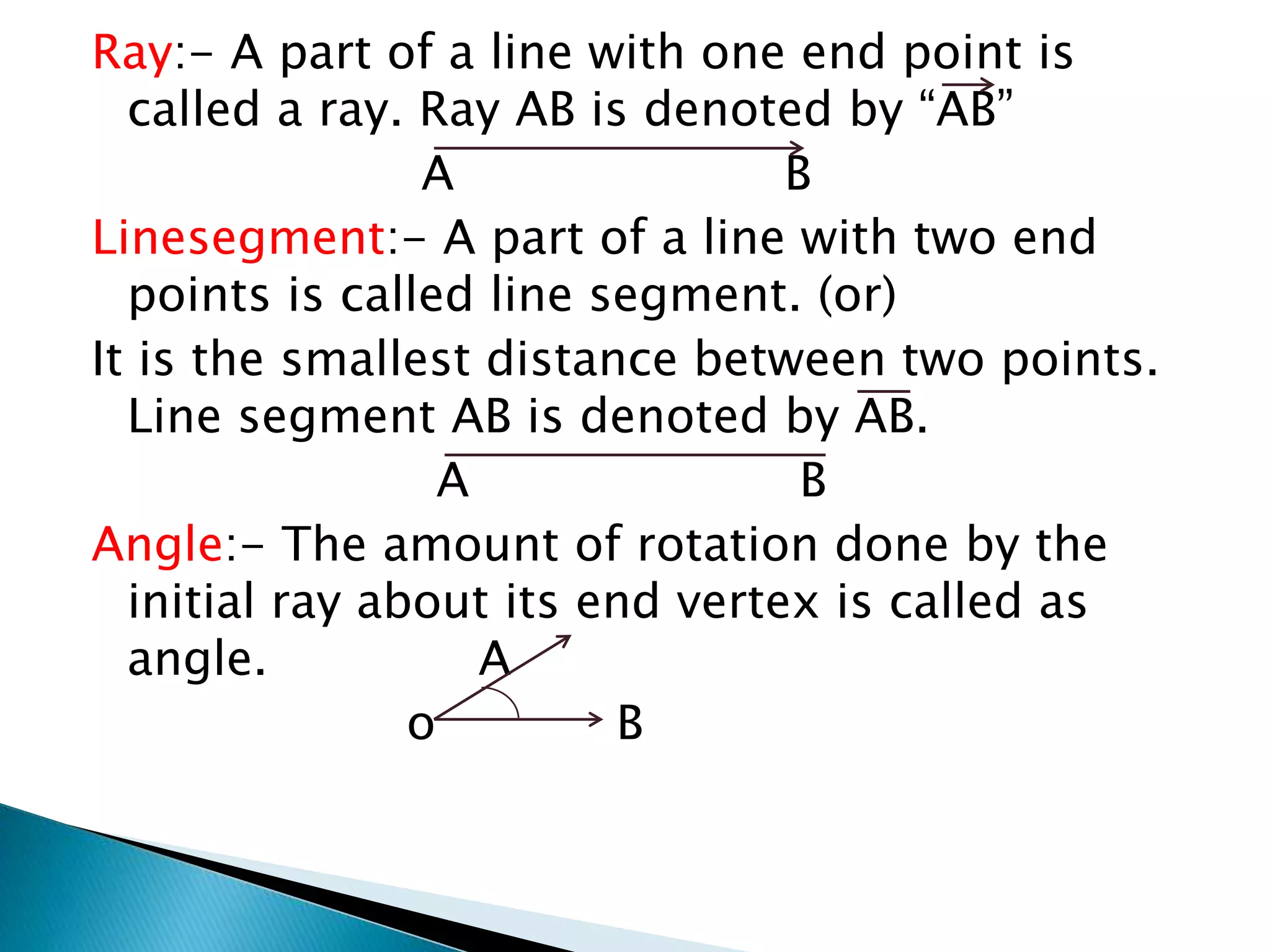
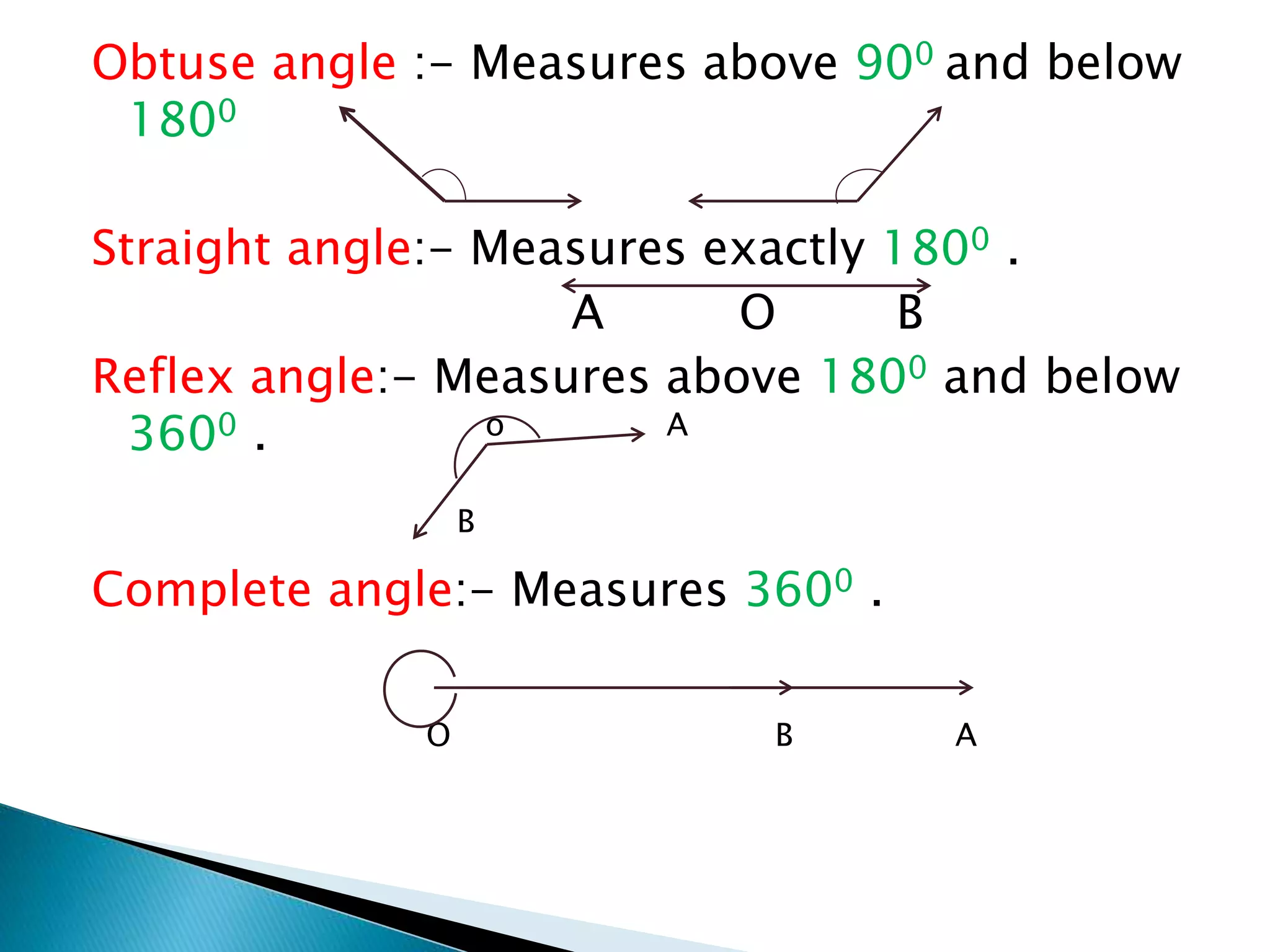
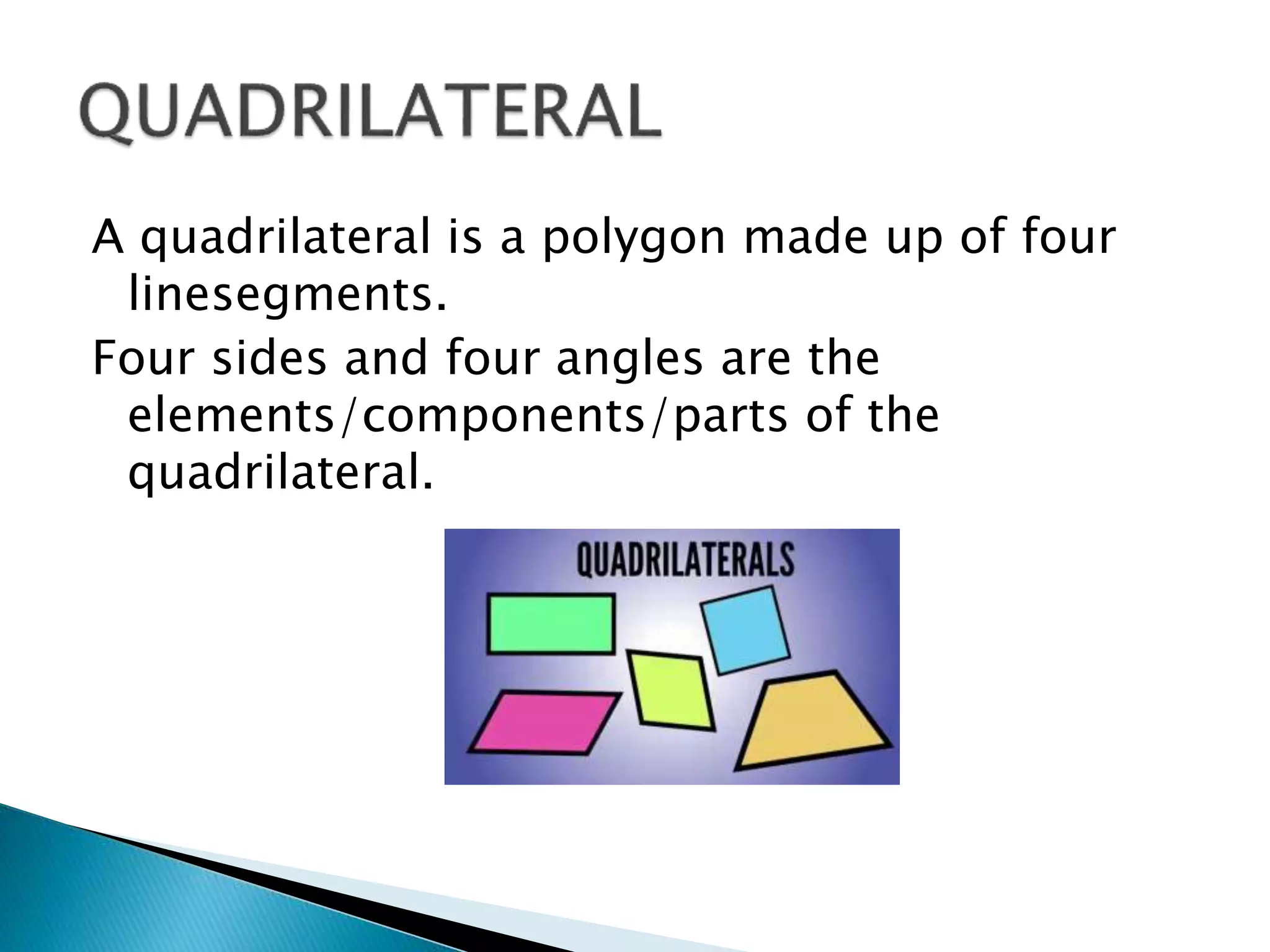
This document defines and describes basic geometric shapes and terms. It defines points, lines, rays, line segments, angles, polygons, quadrilaterals and various types of each. Points have no dimensions, lines are made up of infinite points, rays have one endpoint, line segments have two endpoints, angles are measures of rotation. Polygons are closed figures made of line segments and can be regular, convex or concave. Quadrilaterals specifically have four sides and four angles.