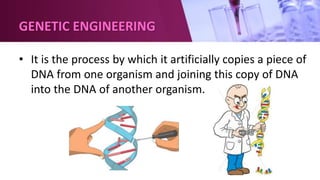
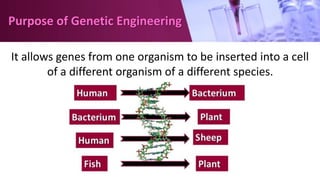
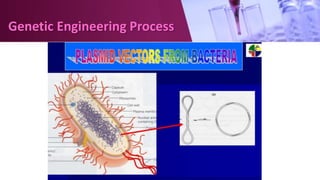
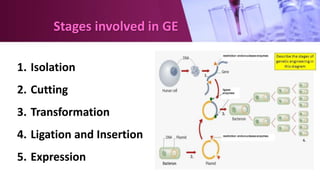
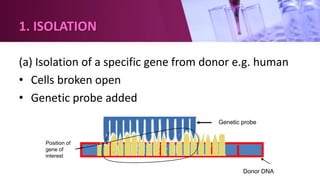
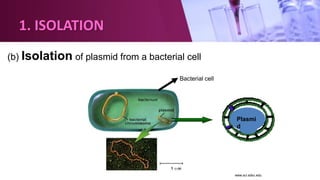
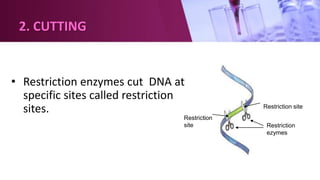
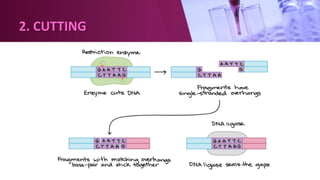
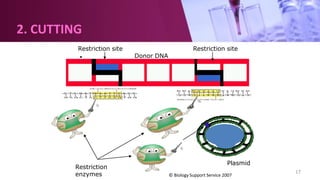
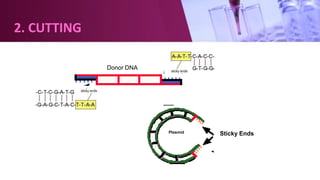
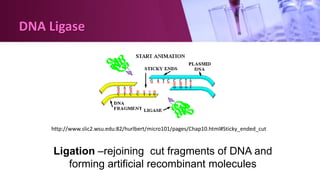
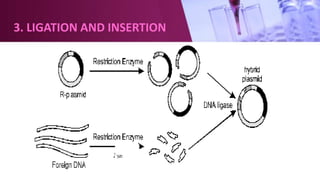
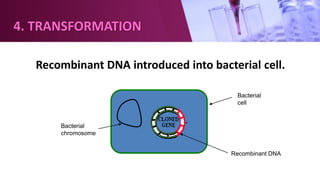
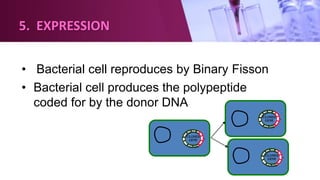
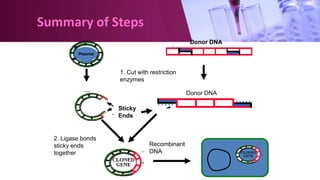
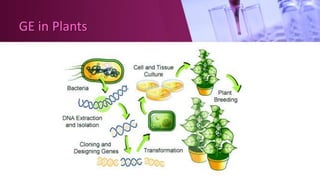
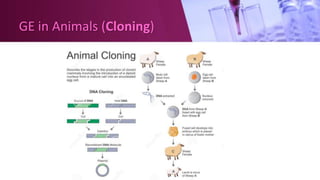
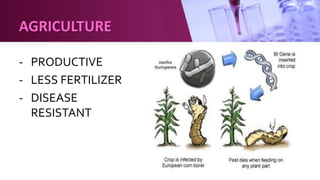
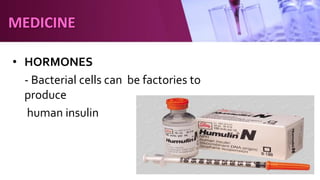
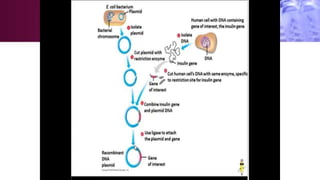
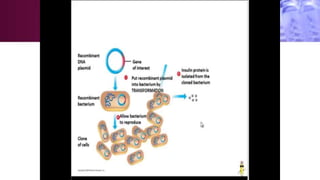
Genetic engineering involves directly manipulating an organism's genome using biotechnology. The process involves isolating a gene, cutting it using restriction enzymes, inserting it into a plasmid or other vector, and introducing this recombinant DNA into a host organism where it is expressed. Key applications of genetic engineering include agriculture, where genes are inserted into crops to make them pest-resistant or improve yields, and medicine, where genes or cells are modified to produce vaccines, hormones, or treat genetic diseases through gene therapy or gene pharming.