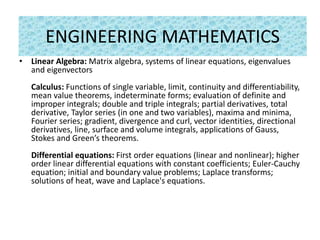
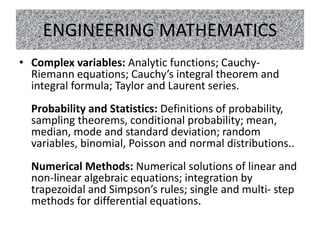
The document outlines the syllabus for the GATE-2017 Mechanical Engineering exam, covering topics in engineering mathematics, mechanics, materials, thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, heat transfer, machine design, manufacturing, and production management. Key areas include linear algebra, calculus, differential equations, mechanics, strength of materials, theory of machines, vibrations, dynamics, thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, heat transfer, manufacturing processes, metrology, computer integrated manufacturing, and operations research.