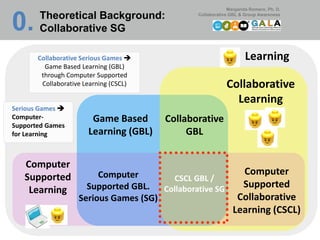
The document discusses the role of collaborative serious games (c-sg) in enhancing learning through computer-supported collaborative learning (CSCL) and explores different theoretical approaches to collaborative learning, including transmissive, conductivism, and constructivism. It reviews the dynamics of collaborative game environments and emphasizes the importance of group awareness, knowledge symmetry, and interdependence in learning outcomes. The efinance game design is presented as a practical application, highlighting research objectives related to knowledge elicitation and peer assessment in collaborative settings.