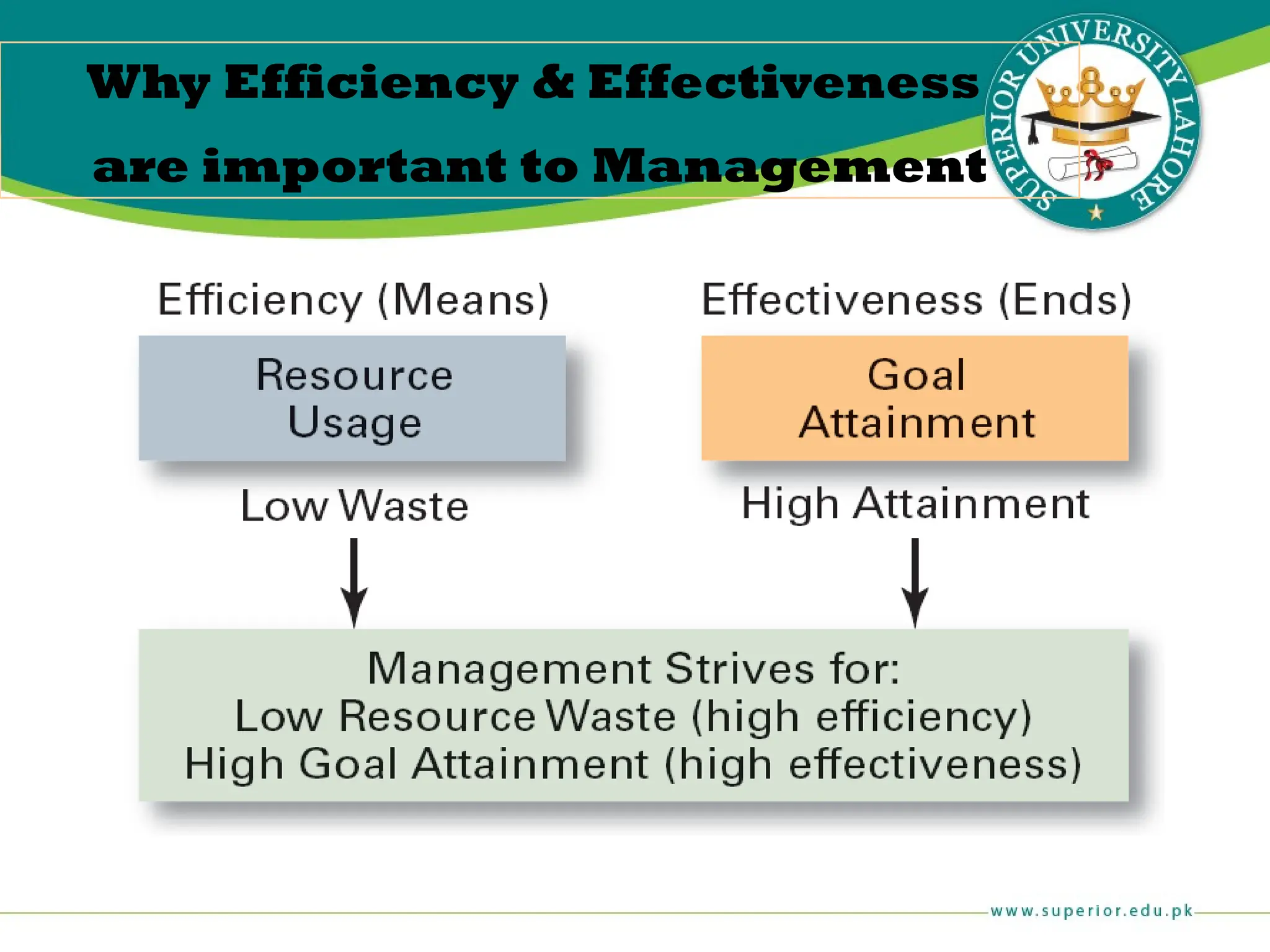
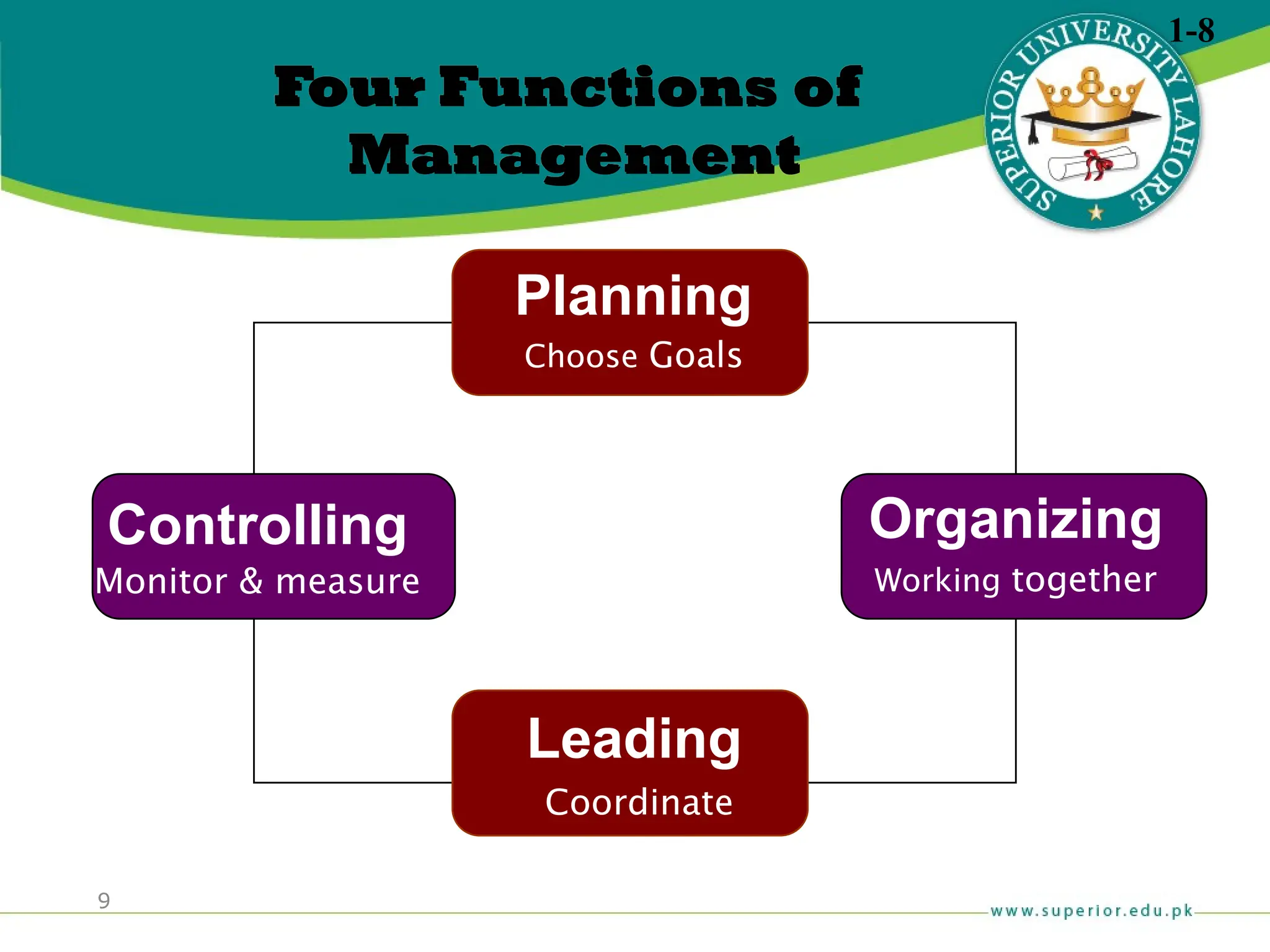
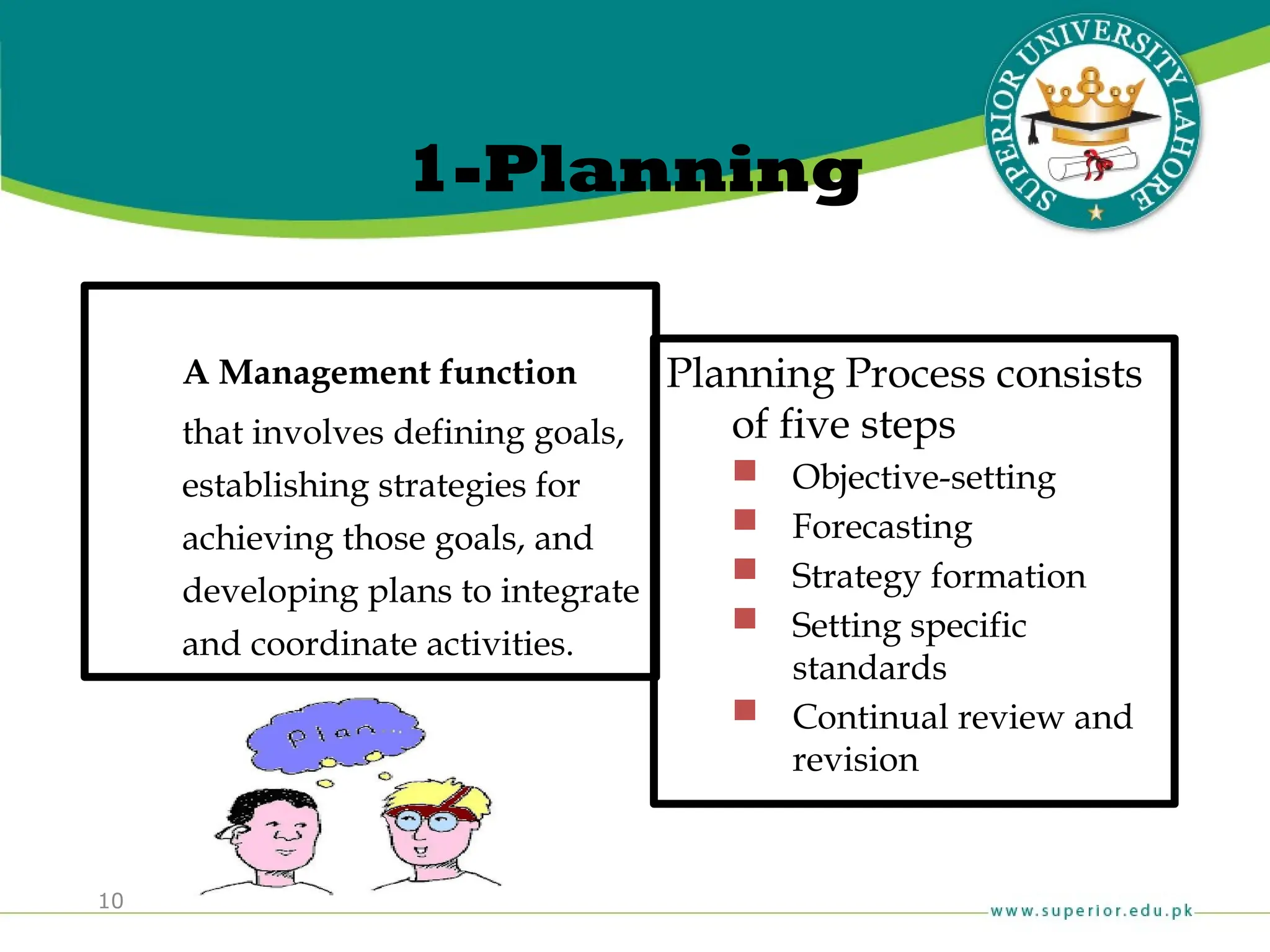
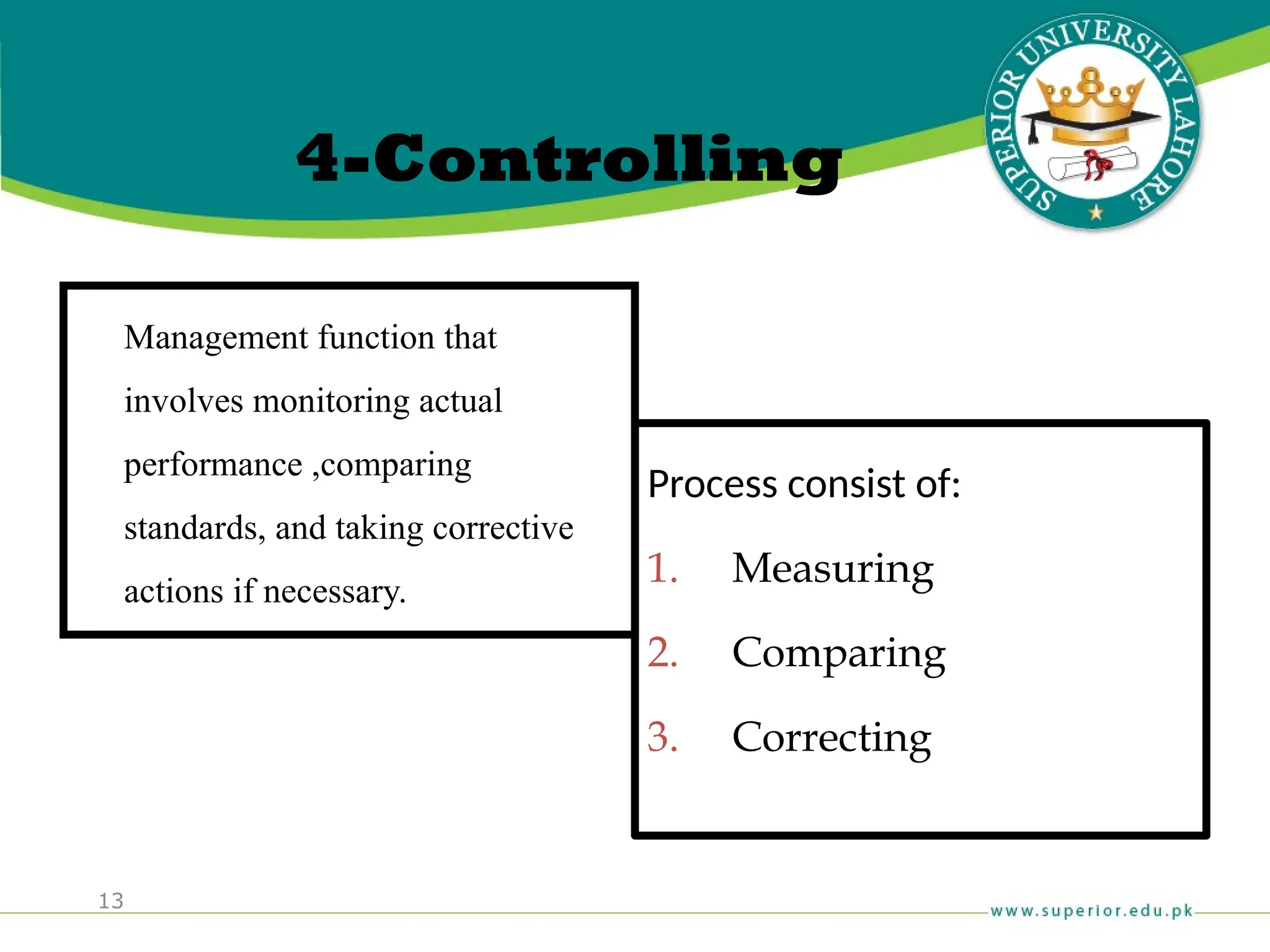
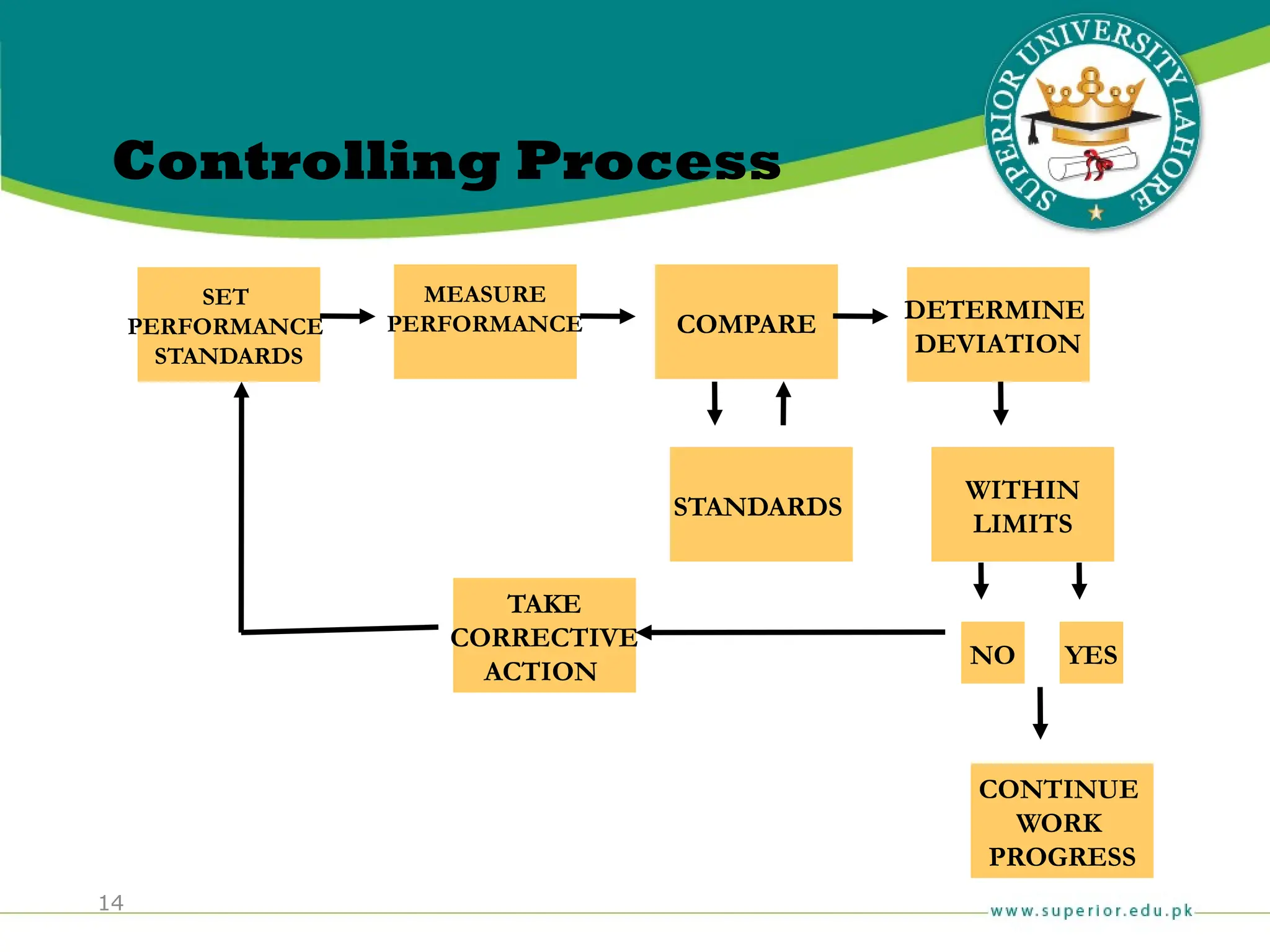
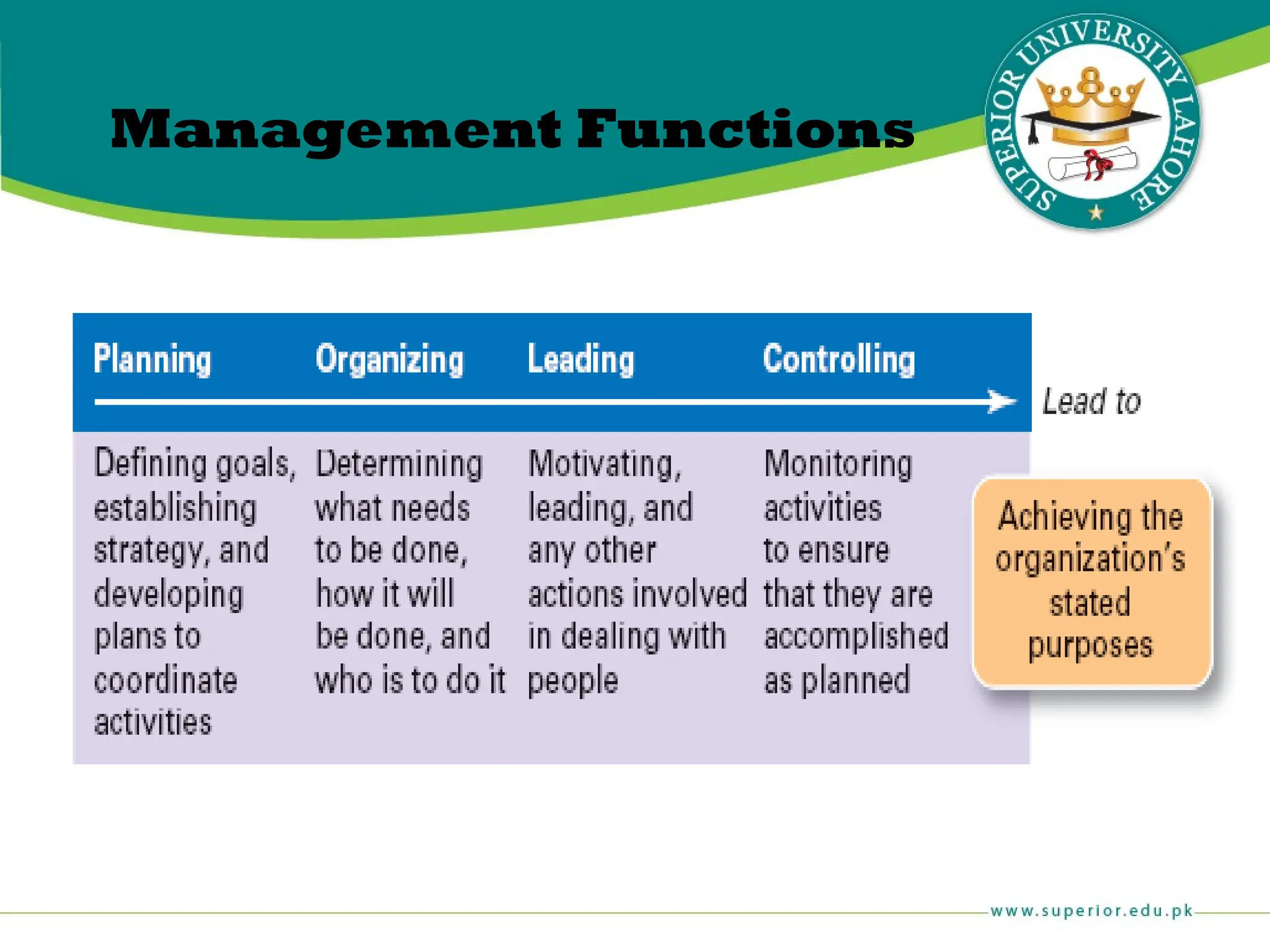
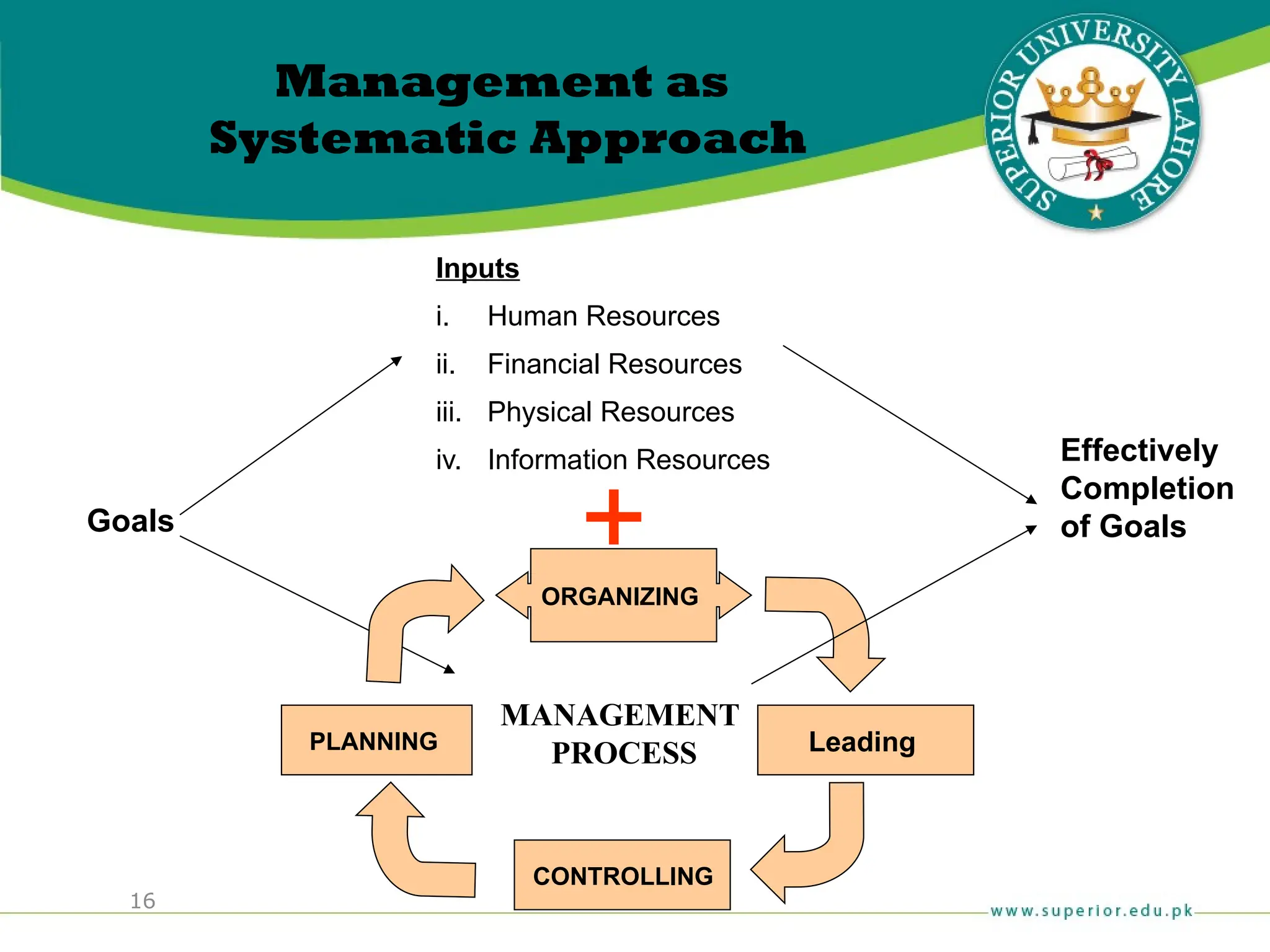
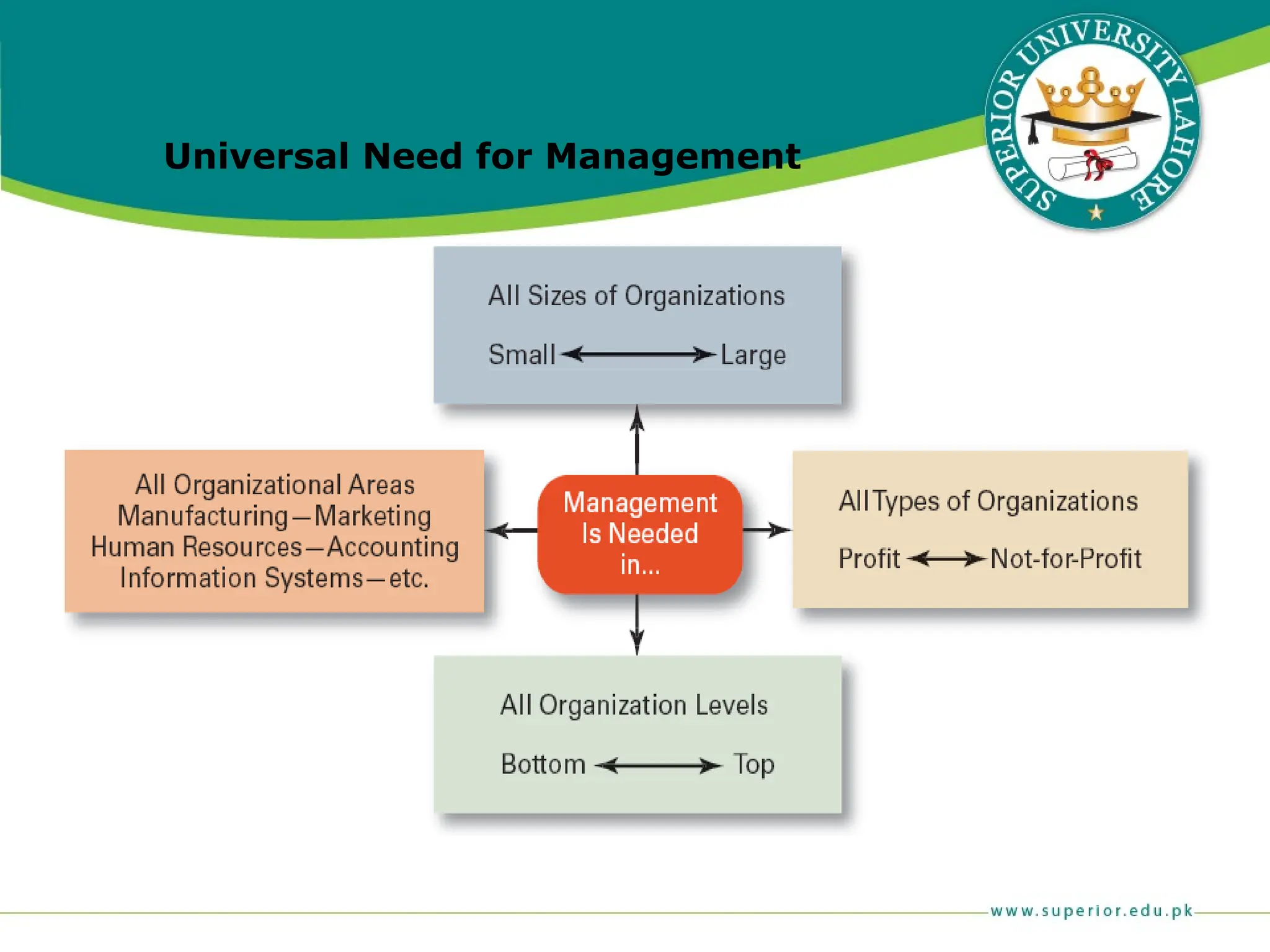
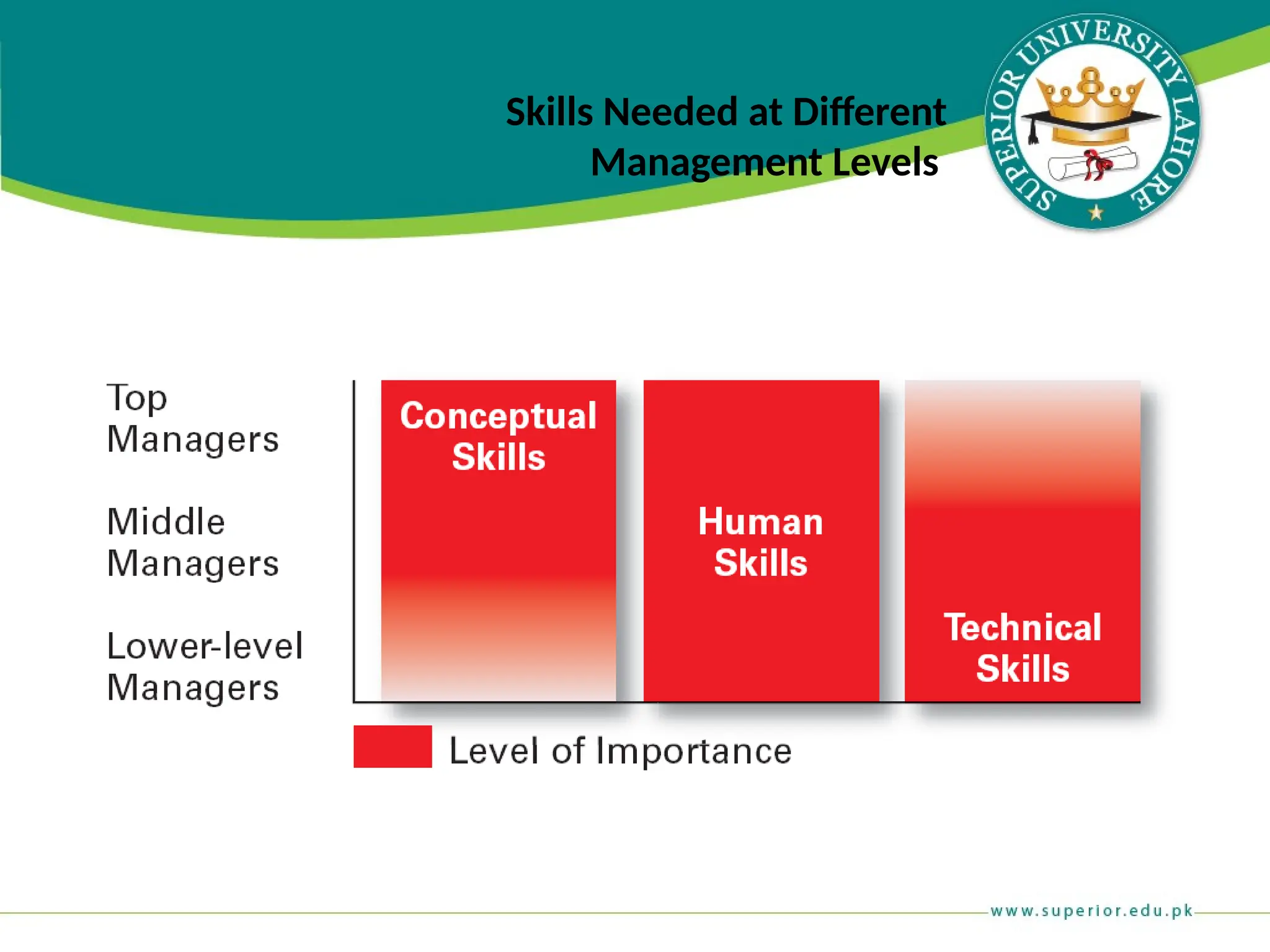
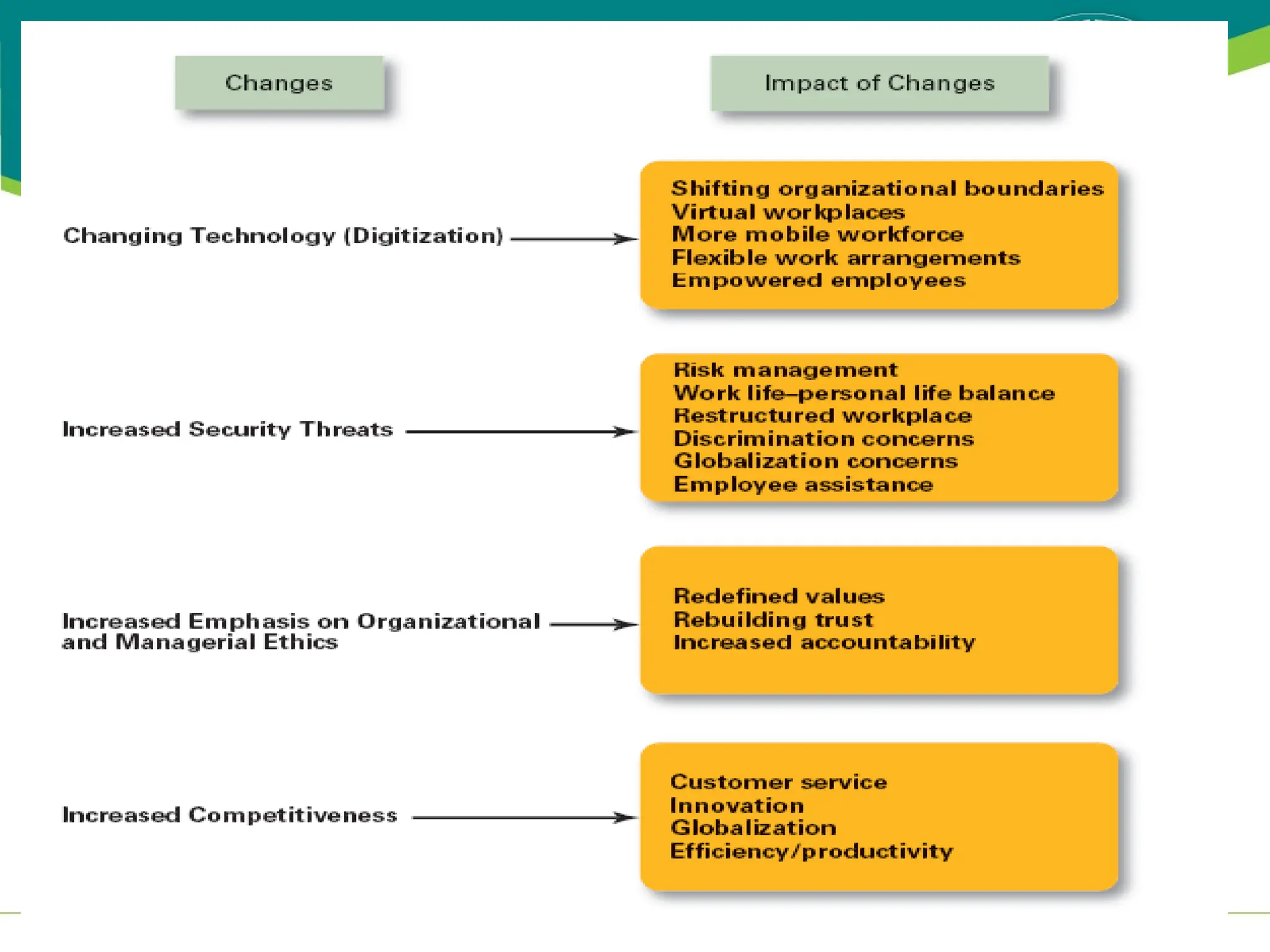
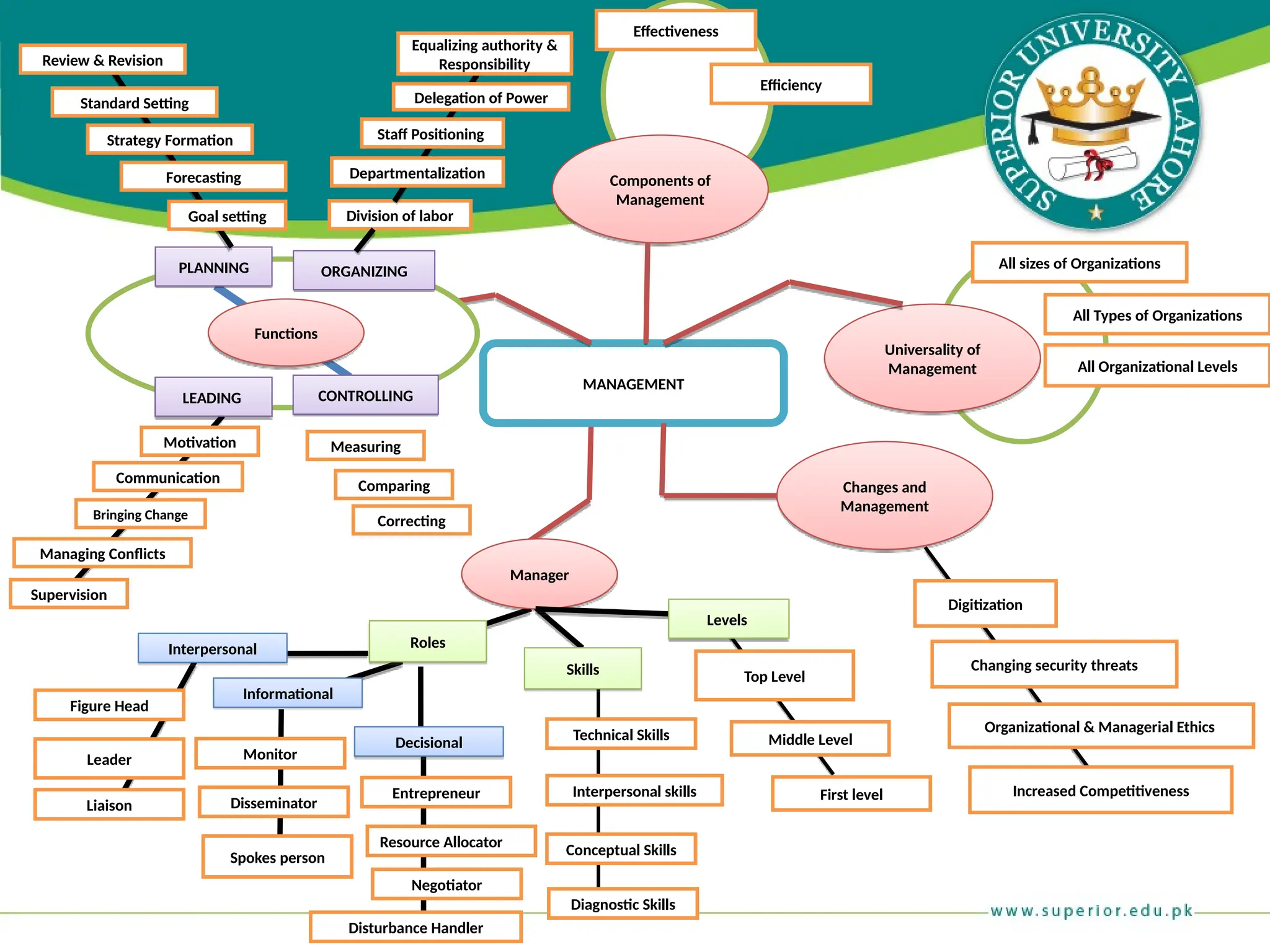
The document provides an overview of management principles, defining business and organizations, and outlining the roles and functions of managers. Key management functions include planning, organizing, leading, and controlling, with an emphasis on efficiency and effectiveness in achieving organizational goals. It also distinguishes between managerial and non-managerial roles, highlighting the importance of various managerial skills and the universality of management across different types of organizations.