This document provides an overview of classical macroeconomic theory. It discusses how classical economics emerged as a revolution against mercantilism, emphasizing free markets and real factors of production over money and trade balances. Key aspects of classical theory covered include:
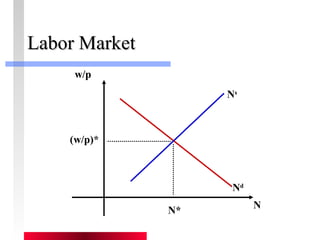
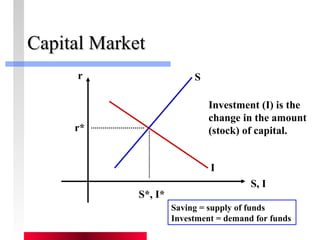
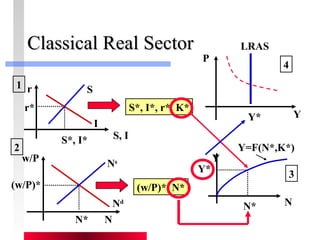
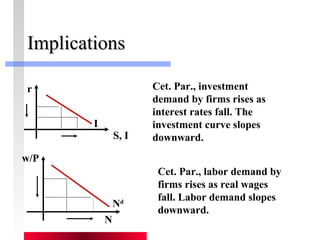
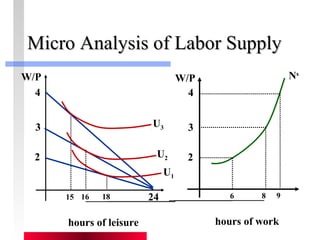
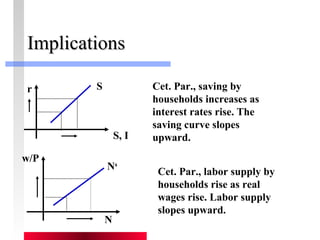
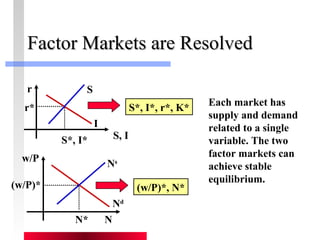
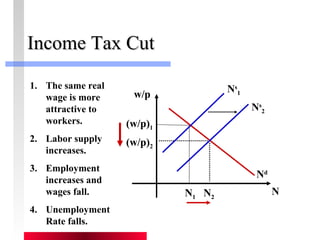
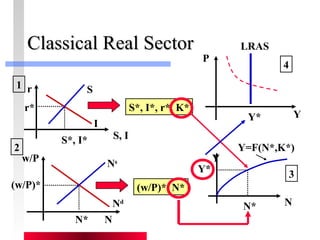
- Labor and capital markets clear through price adjustments to equilibrium.
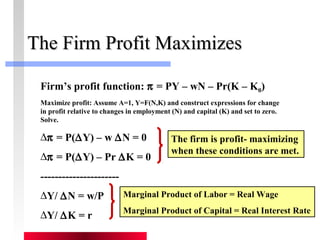
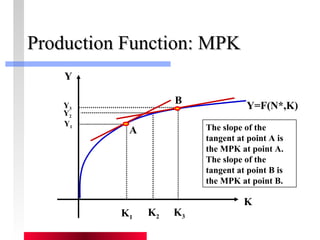
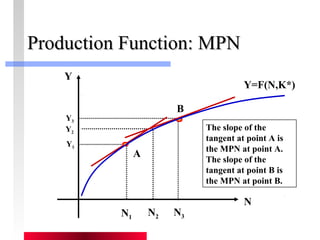
- Firms maximize profits by equaling marginal revenue product to factor prices.
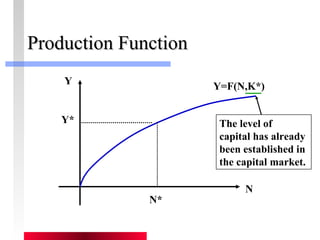
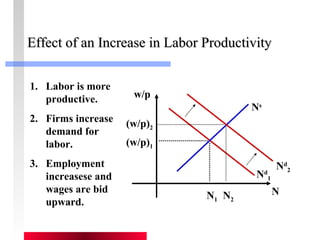
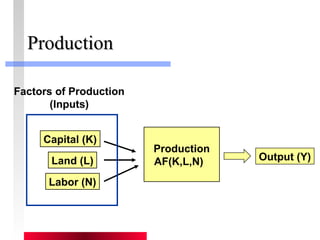
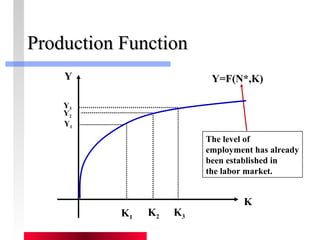
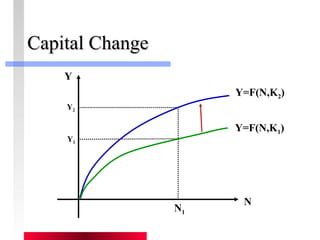
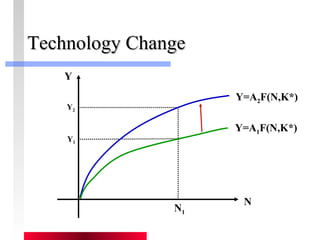
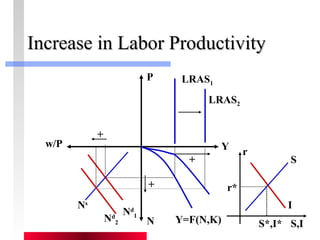
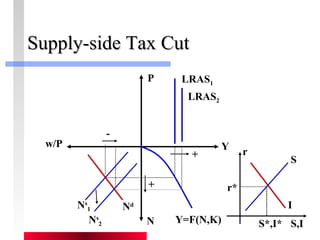
- Production depends on labor, capital and technology. Increases in these real factors of supply are what increase output.
- Money is neutral, having no long-run impact on real variables like output and employment.