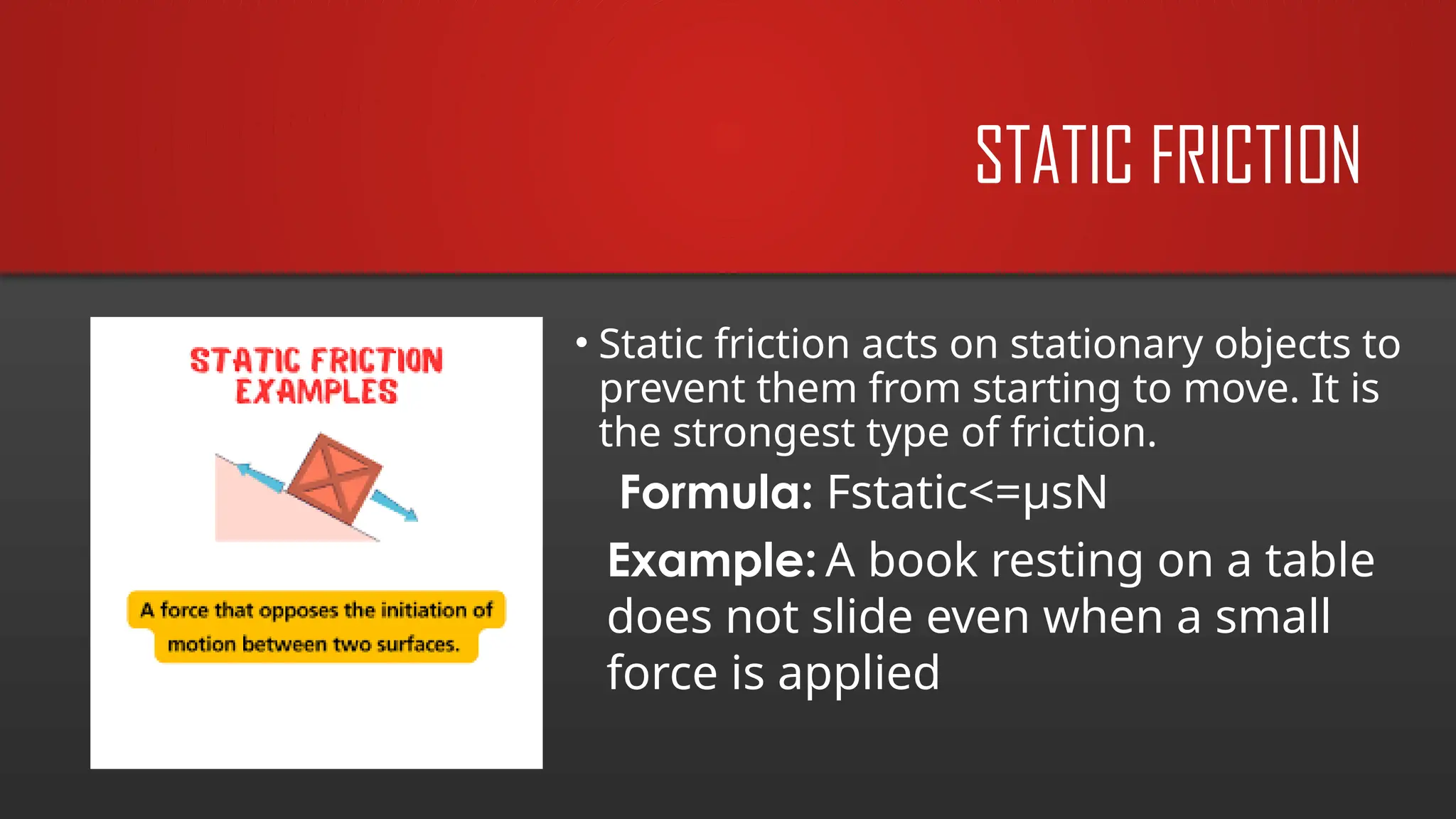
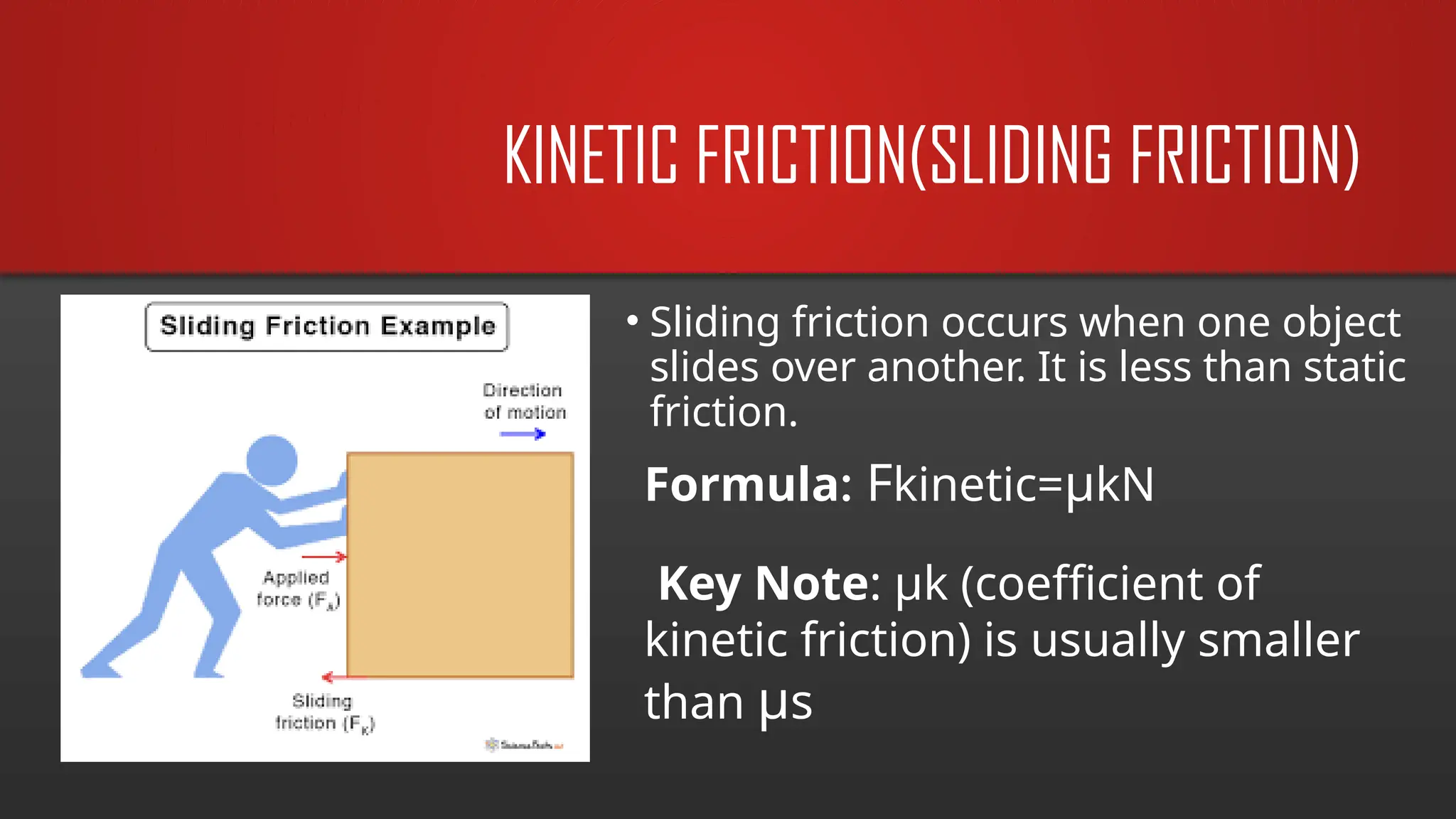
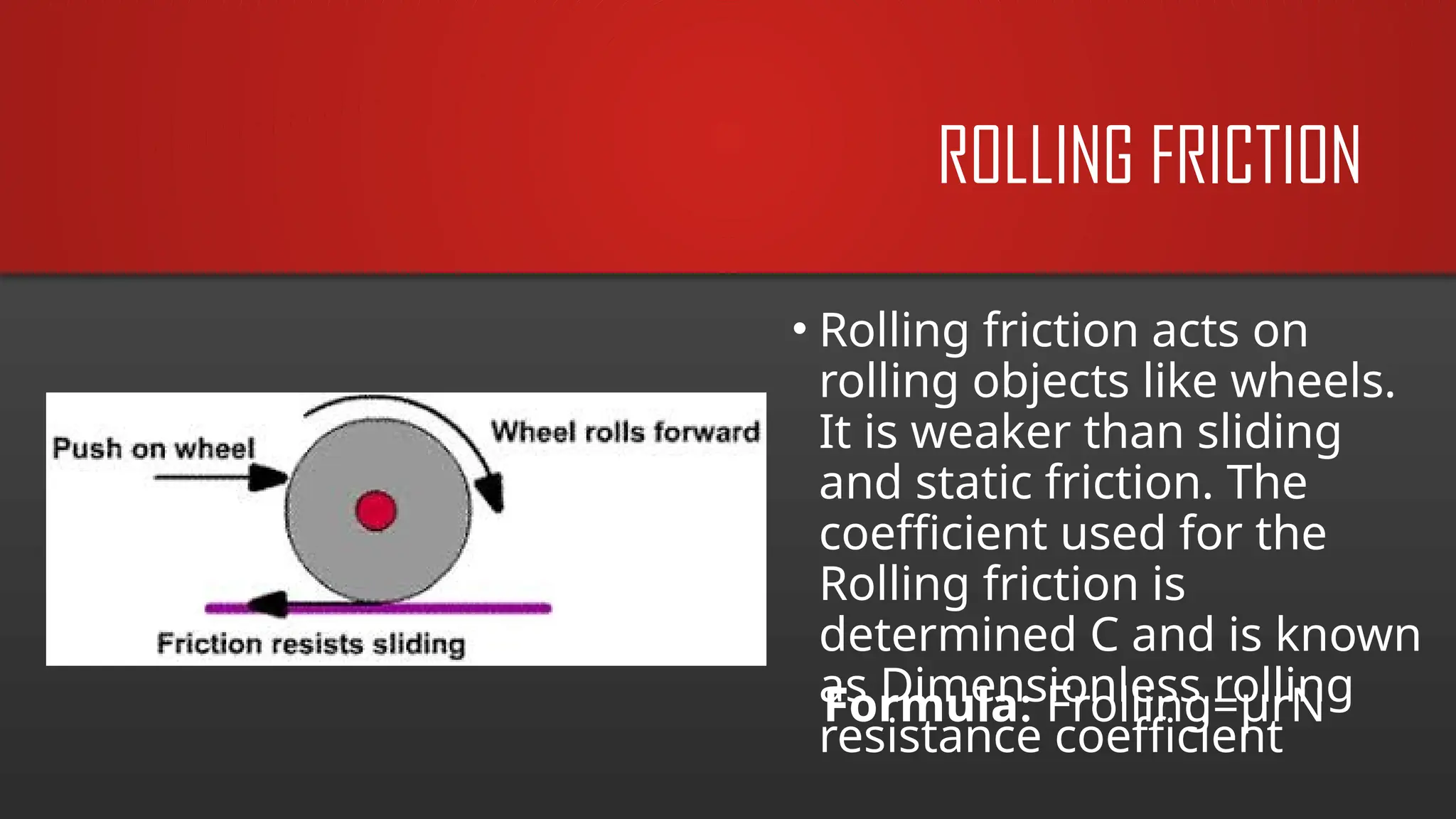
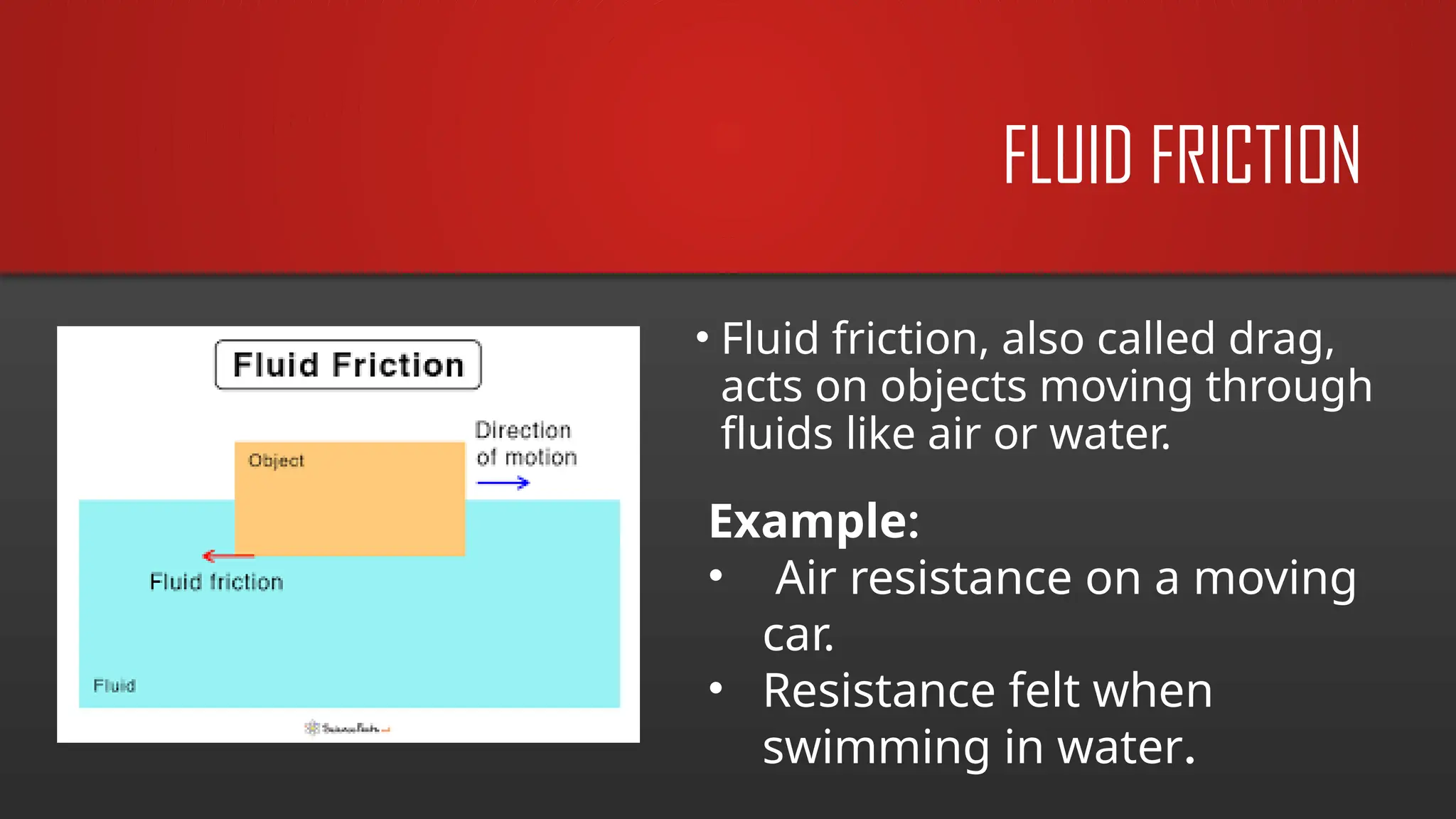
The document explains frictional force as a resistive force acting opposite to motion, emphasizing its importance in daily life, such as walking and driving. It discusses types of friction (static, kinetic, rolling, and fluid) and their applications in both nature and technology, along with key factors affecting friction. Additionally, it includes equations related to friction and practical problems that illustrate its role in motion control.