Embed presentation
Download to read offline

![The form is:f[g(x)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtogetfgx-110106165803-phpapp01/85/Form-of-a-Composite-Function-2-320.jpg)




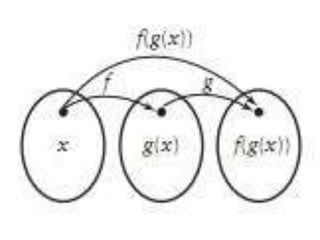
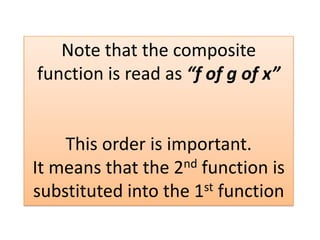

The form of a composite function is f[g(x)], which is read as "f of g of x" and means that the output of the inner function g(x) is substituted into the outer function f. This order is important as it indicates that g(x) is evaluated first before the result is input into f.

![The form is:f[g(x)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtogetfgx-110106165803-phpapp01/85/Form-of-a-Composite-Function-2-320.jpg)






