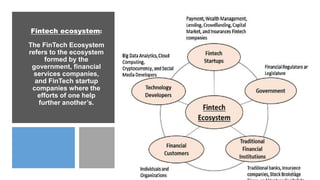
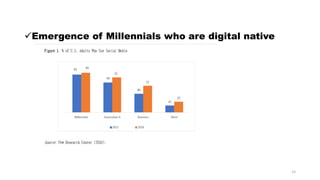
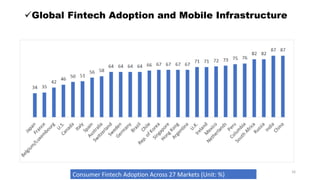
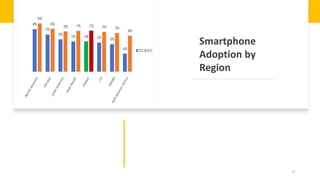
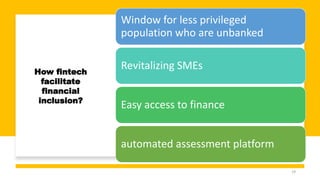
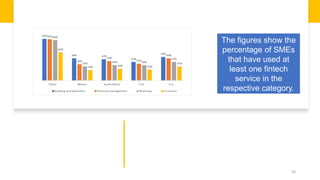
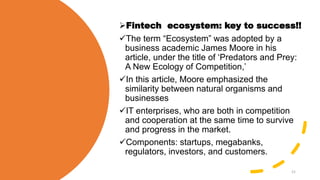
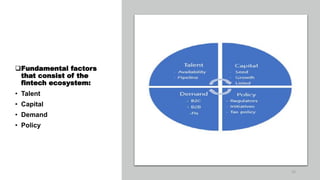
Fintech has the potential to promote greater financial inclusion through convenience, lower costs, and accessibility. An integrated fintech ecosystem is key, with cooperation between startups, traditional financial institutions, investors, and regulators. When properly developed, fintech can help bridge the gap to banking services for the unbanked, facilitate lending to SMEs, and revitalize economic growth across APEC nations in the digital age.