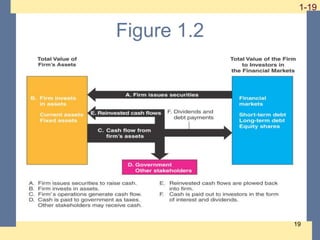
This document provides an introduction to financial management. It discusses key concepts including the roles and goals of financial managers. The different forms of business organization like sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations are outlined. The document also introduces basic areas of finance like corporate finance, investments, financial institutions, and international finance. It explains what financial management decisions entail and the potential agency problem between owners and managers.