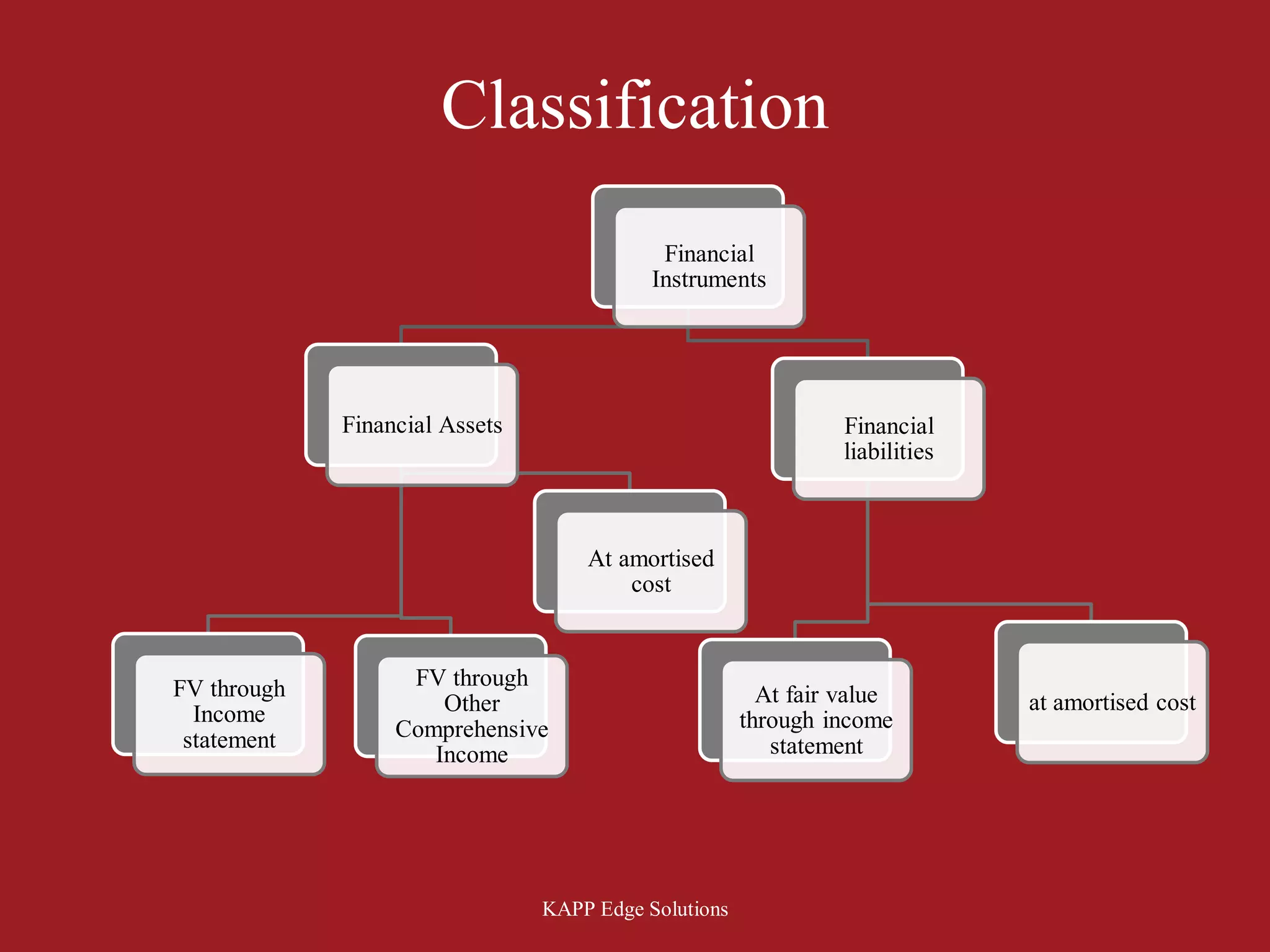
The document discusses key concepts related to accounting for financial instruments under IAS 32, IAS 39 and IFRS 9 such as definition of financial instruments, classification of financial assets and liabilities, initial measurement, amortized cost method, fair value accounting, transaction costs, compound instruments and other requirements. It provides examples to explain concepts such as business model, classification of instruments as amortized cost or fair value, treatment of transaction costs, calculation of amortized cost and separation of compound instruments into liability and equity components.