Embed presentation
Download to read offline




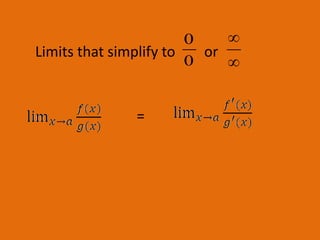


![If f is continuous on [a,b] a value c exists such that](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalprojectflashcards-110525090259-phpapp02/85/Final-project-flashcards-11-320.jpg)
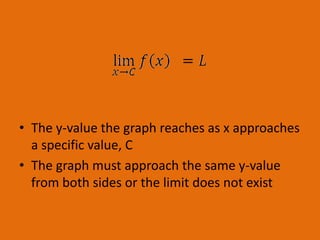
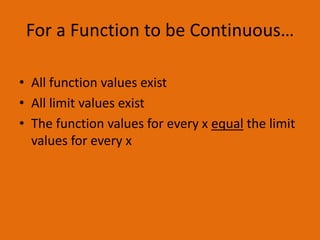
Limits describe the y-value a graph approaches as x approaches a specific value. For a limit to exist, the graph must approach the same y-value from both sides. The squeeze theorem states that if f(x) is squeezed between g(x) and h(x) near a value except at a, and the limits of g(x) and h(x) exist and are equal, then the limit of f(x) is the same as those limits. L'Hopital's rule is used to evaluate limits that result in indeterminate forms like 0/0 or ∞/∞. For a function to be continuous, its function values and limit values must all exist and be equal for





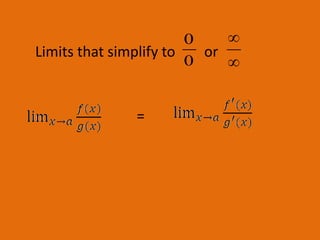



![If f is continuous on [a,b] a value c exists such that](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalprojectflashcards-110525090259-phpapp02/85/Final-project-flashcards-11-320.jpg)