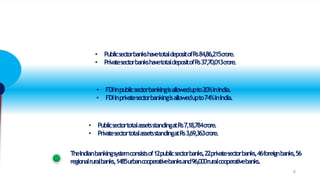
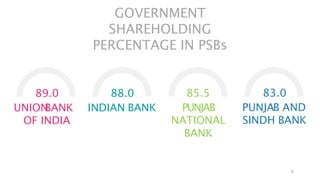
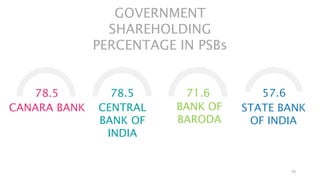
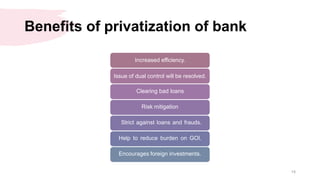
Privatization of public sector banks in India could provide benefits but also risks. It may increase efficiency and reduce the financial burden on the government, but it could also reduce services to rural areas and priority sectors. Two public sector banks are proposed for privatization to increase capital and implement best practices, but the final decision has not been made. Both public and private banking structures are important for the economy, so policies aim to improve governance and reduce political interference for public sector banks while allowing all to thrive.