The document discusses file handling in C and data structures. It provides objectives of the training which include facilitating placement exams and tests, developing problem solving abilities, and enhancing knowledge. It then describes how the training is different from routine classes by discussing MCQs, assessment problems, emphasis on additional concepts, and preparation of a question bank. The topics to be covered are listed as file handling, file operations in C, modes, and file I/O functions. Various file operations like opening, closing, reading and writing files are explained along with code examples. Multiple choice questions related to file handling concepts in C are also provided.



























![C & DATA STRUCTURE (FILE HANDLING)
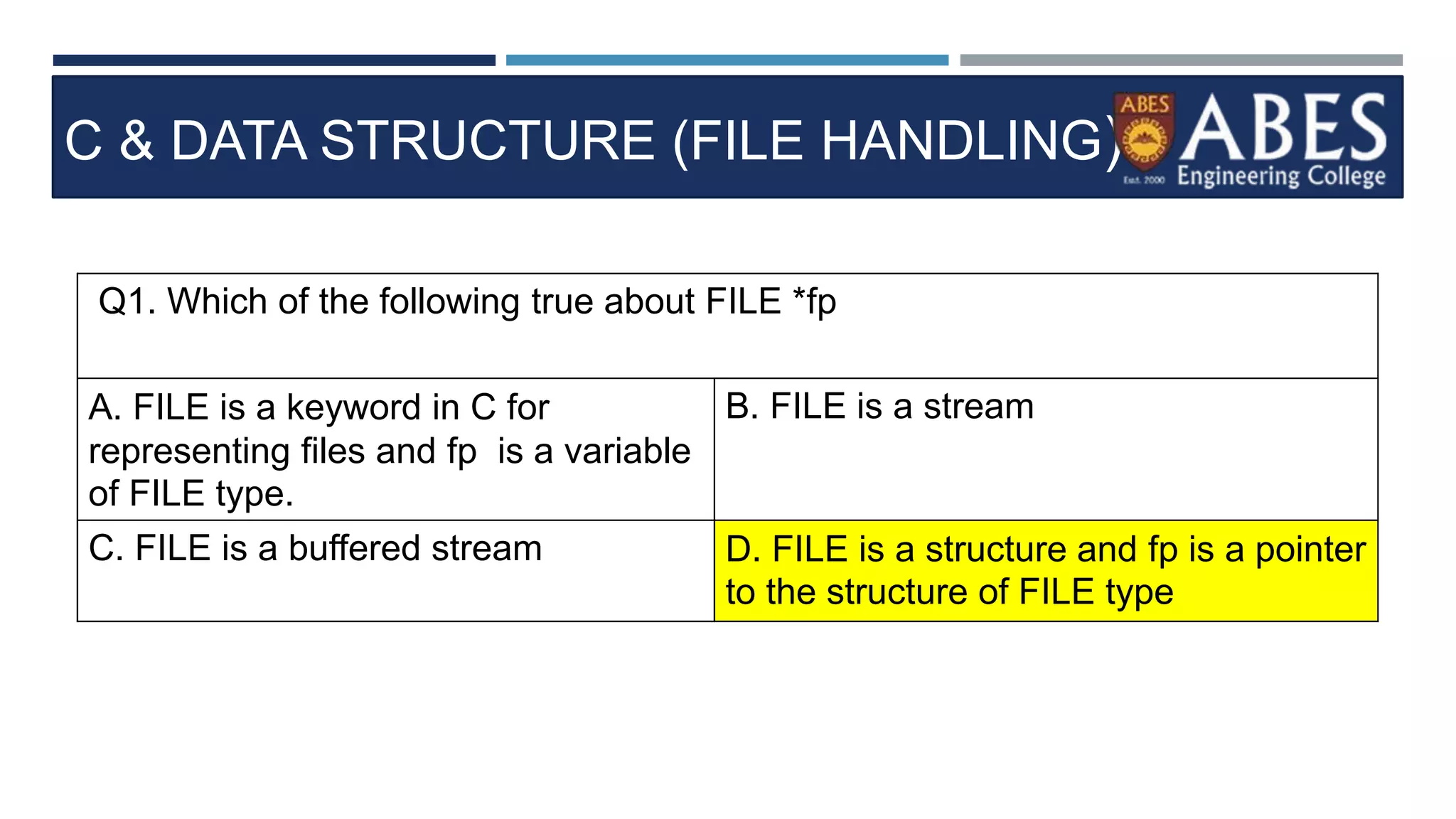
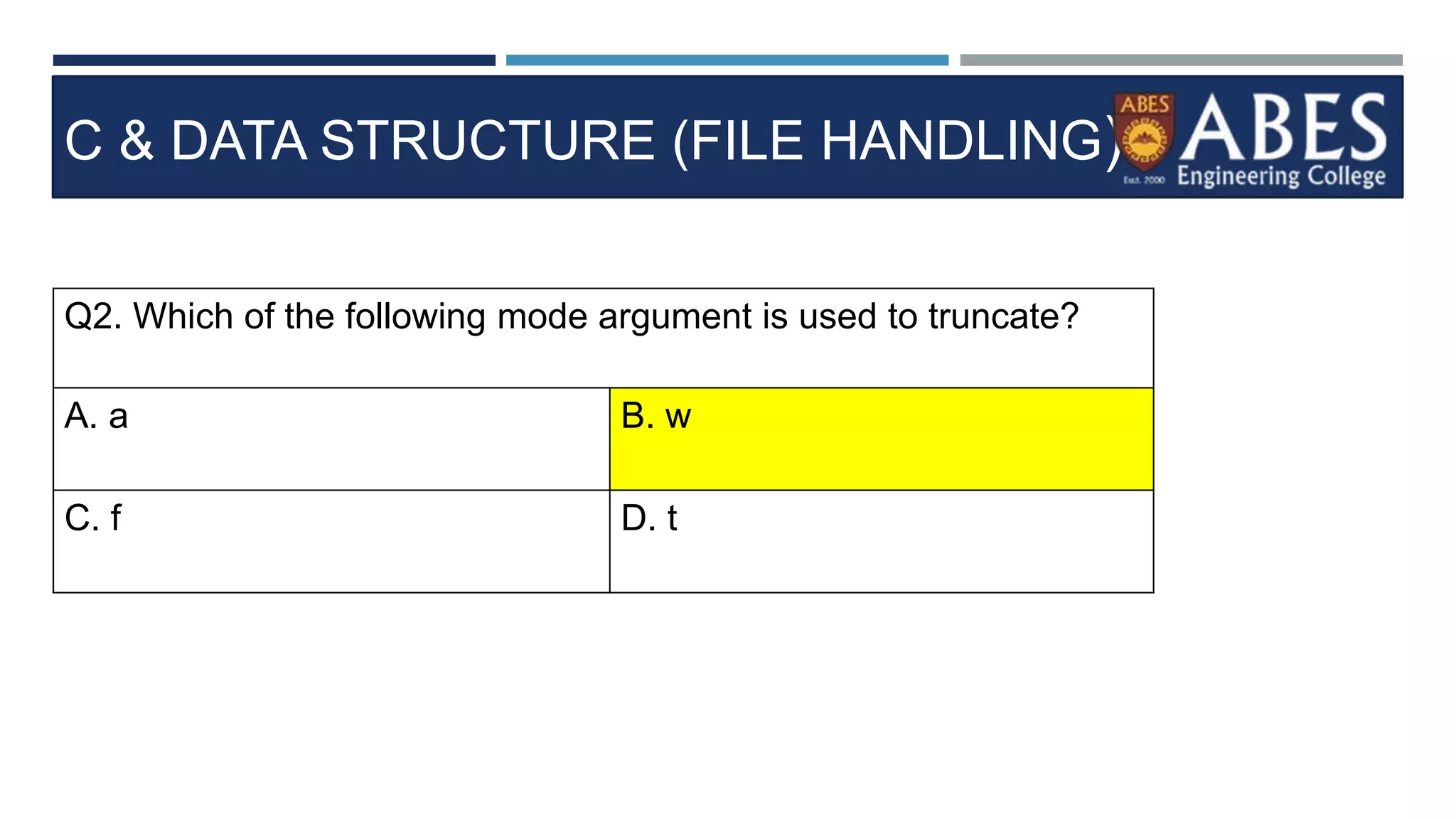
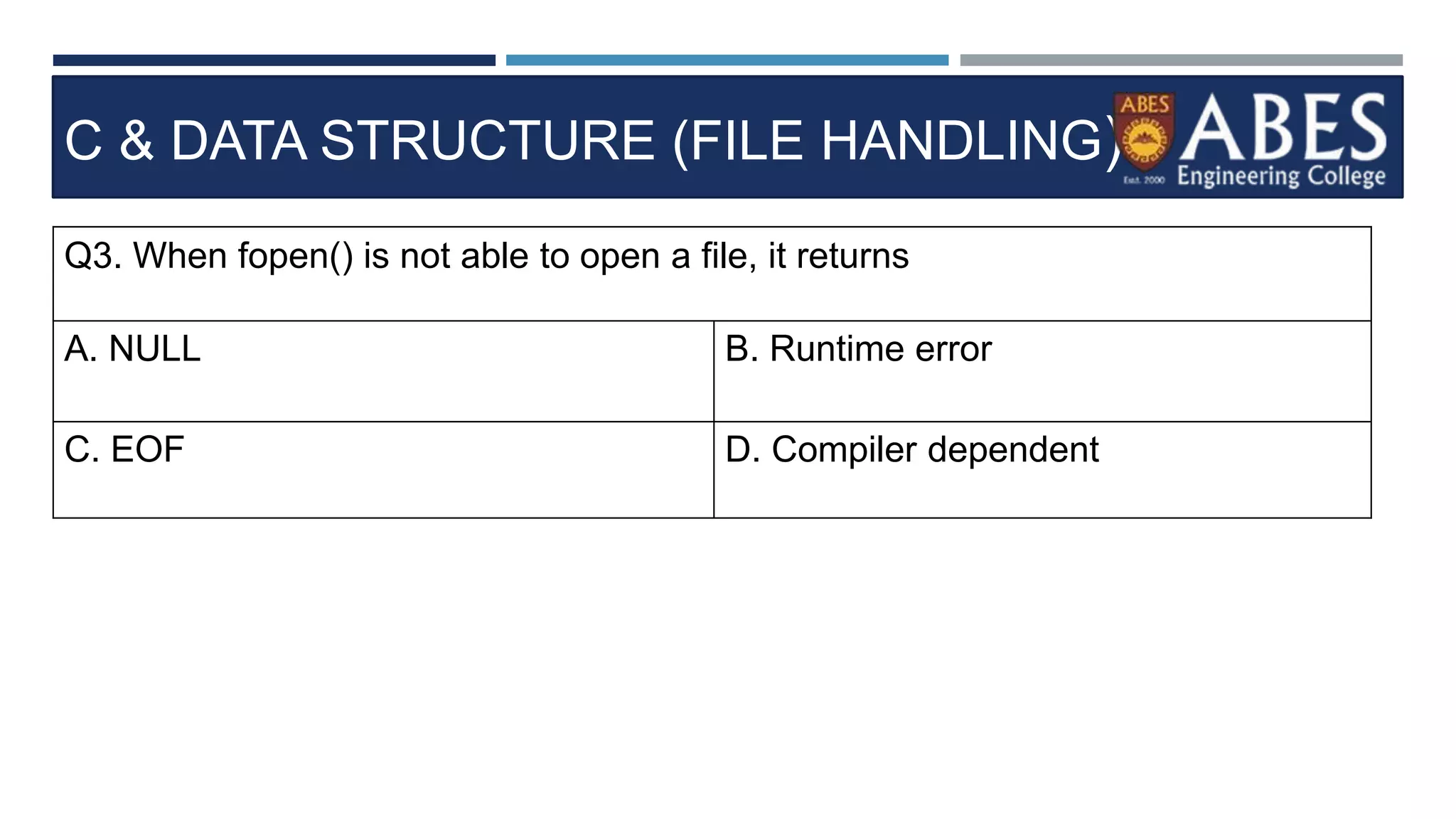
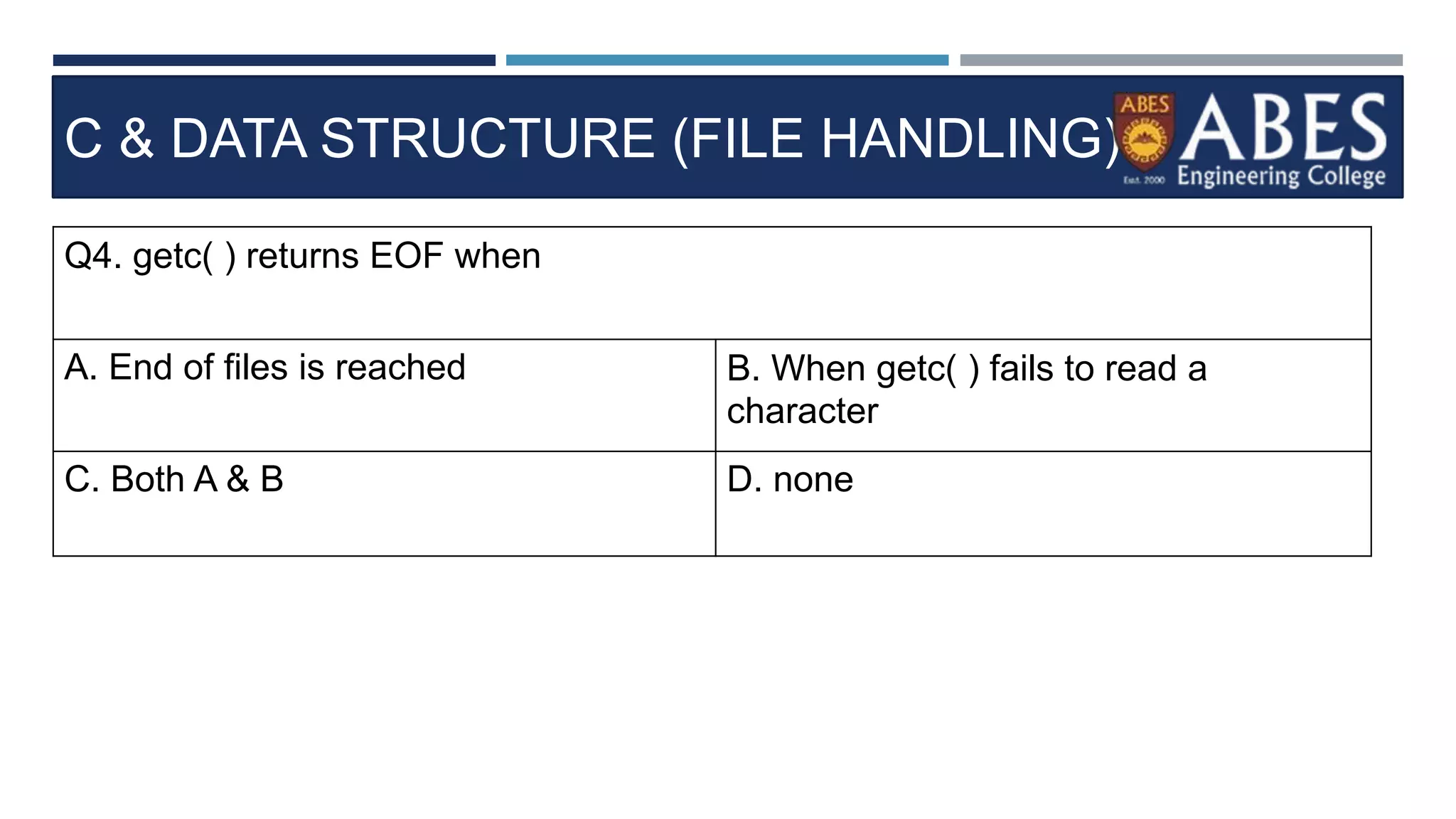
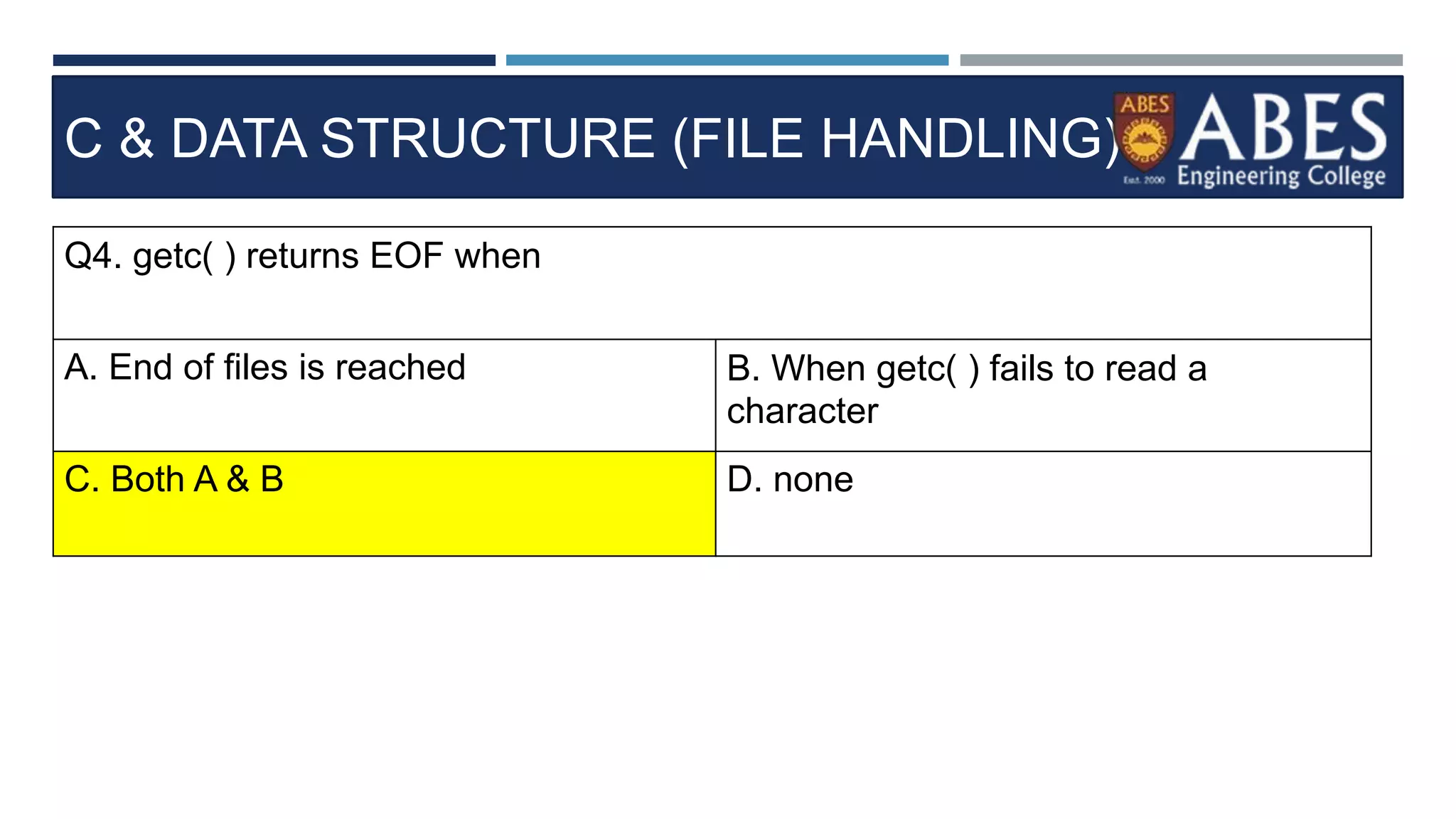
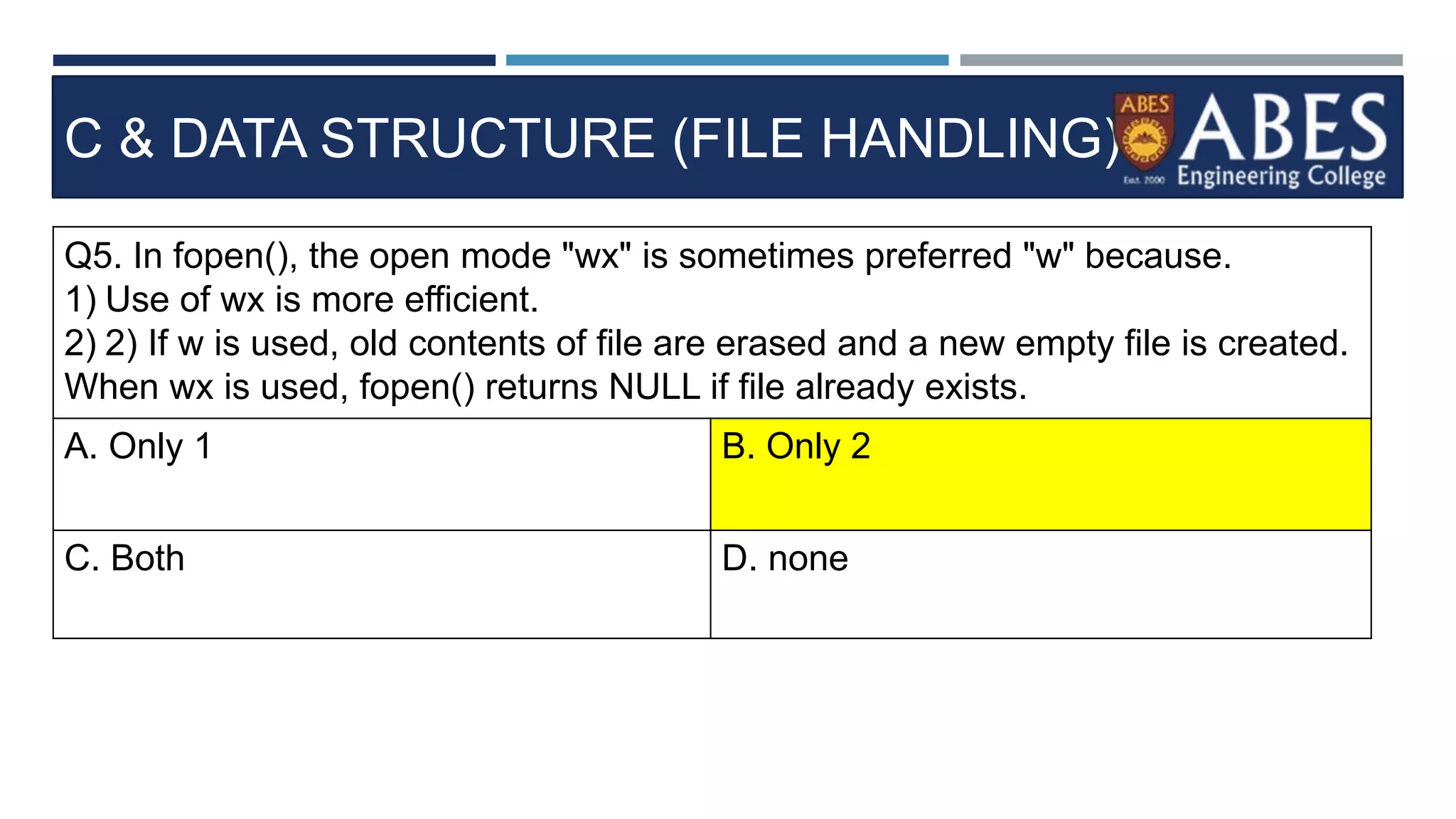
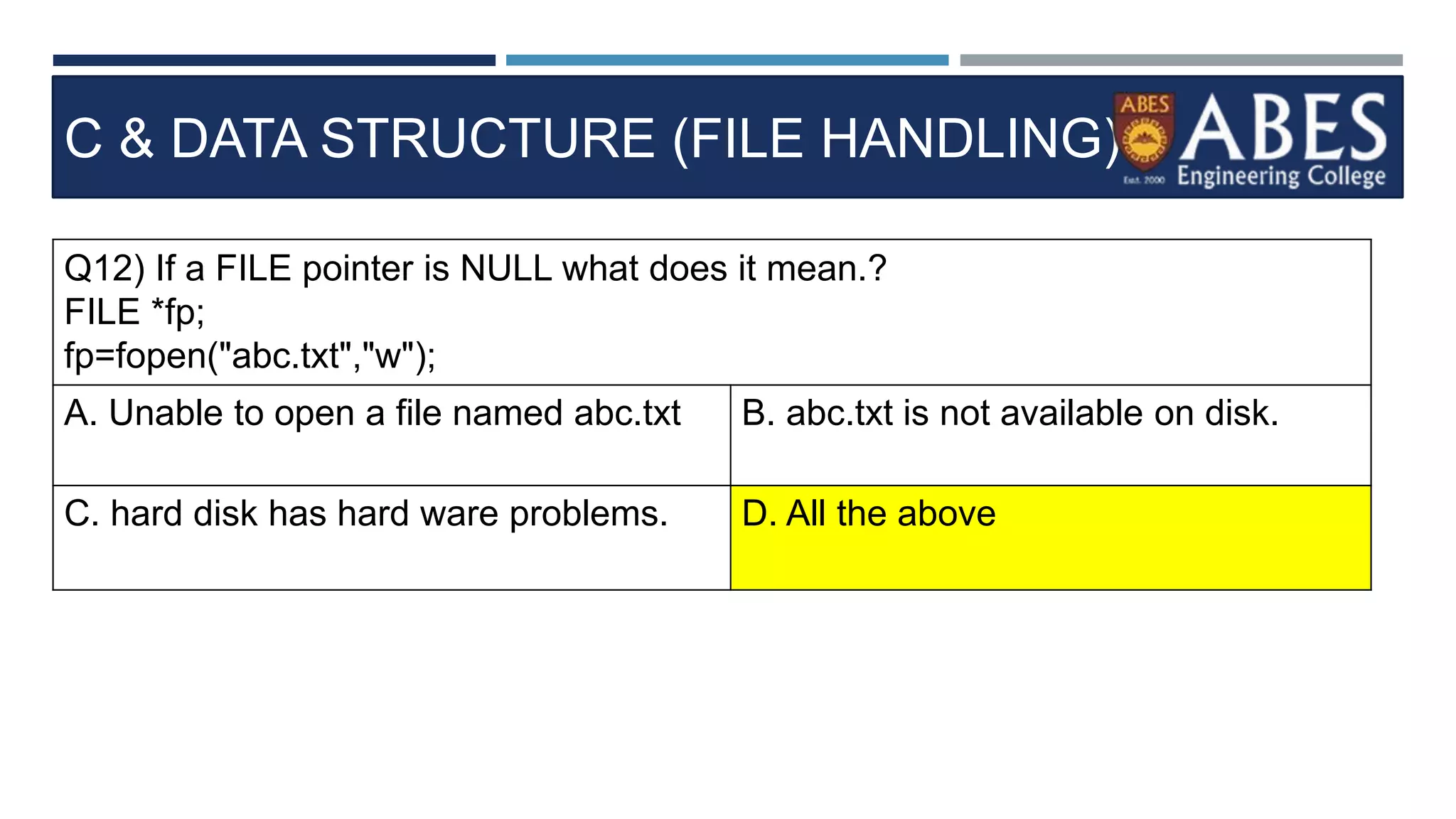
Q13) Choose a correct stateme
nt about FGETS in C program.?
int main()
{
FILE *fp;
char str[80];
fp=fopen("readme.txt","r");
while(fgets(str,80,fp) != NULL)
{
printf("%s",str);
}
fclose(fp);
A. str in fgets() is a like
a user buffer that can
store 80 characters
each time
B. FGETS returns null
if no characters are left
C. fgets() reads content
from File. FPUS writes
content back to File..
D. All the above](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filehandling-230824103041-575063cf/75/filehandling-pptx-36-2048.jpg)
![C & DATA STRUCTURE (FILE HANDLING)
Q13) Choose a correct stateme
nt about FGETS in C program.?
int main()
{
FILE *fp;
char str[80];
fp=fopen("readme.txt","r");
while(fgets(str,80,fp) != NULL)
{
printf("%s",str);
}
fclose(fp);
A. str in fgets() is a like
a user buffer that can
store 80 characters
each time
B. FGETS returns null
if no characters are left
C. fgets() reads content
from File. FPUS writes
content back to File..
D. All the above](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filehandling-230824103041-575063cf/75/filehandling-pptx-37-2048.jpg)