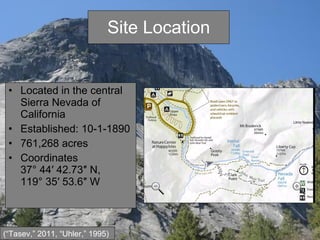
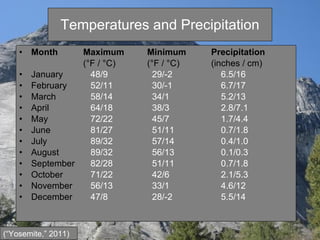
This document summarizes a field report about a hike on the Mist Trail in Yosemite National Park. It describes the location and climate of the park, details of the Mist Trail including landmarks along the way, examples of the types of trees and rocks seen, and some wildlife that inhabits the park's various habitats. References used in compiling the report are also cited.