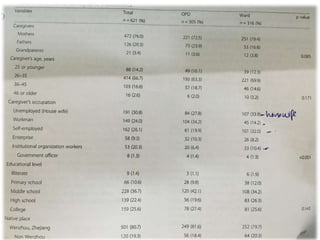
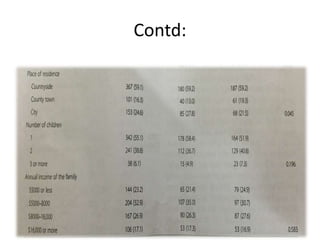
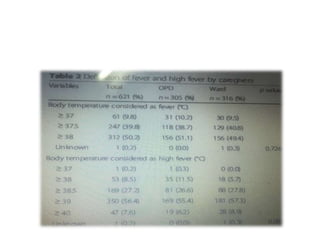
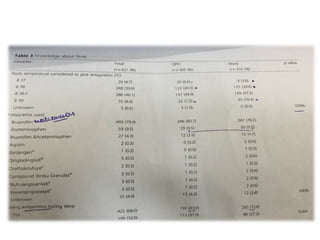
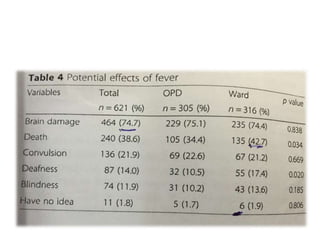
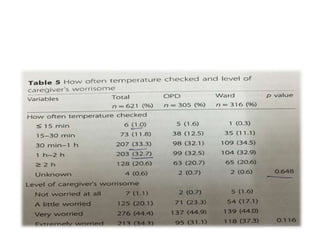
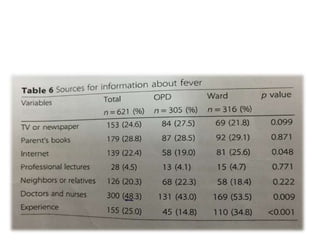
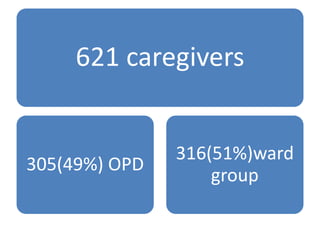
The study explores caregivers' attitudes towards fever in children, comparing those in outpatient and inpatient settings at a children's hospital in China. It found widespread 'fever phobia,' with many caregivers believing fevers cause serious harm, despite education efforts proving largely ineffective. The study underscores the need for accurate information from healthcare providers to better manage caregiver concerns about fever.