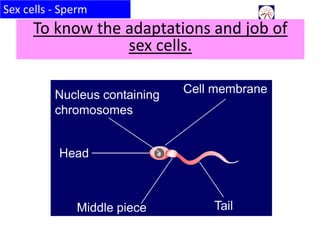
The document discusses a lesson on sex cells. It will cover the basic features and adaptations of sperm and eggs, how fertilization takes place, and the process of fertilization in detail. Students will label diagrams of sperm and eggs and discuss their structures and where they are produced. The lesson will also cover the roles of sperm and eggs in fertilization through activities like describing a "Situations Vacant" job posting for a sperm or egg.