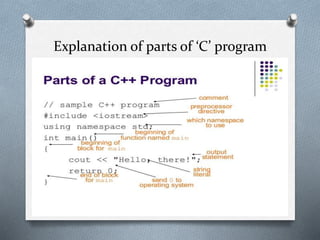
The document discusses the features and structure of the C programming language, developed by Dennis Ritchie as an evolution from the B language. Key characteristics include portability, modularity, and support for bit-wise operations, making C a middle-level structured programming language. It explains the basic structure of a C program, which must include the main() function and emphasizes that all statements end with a semicolon.