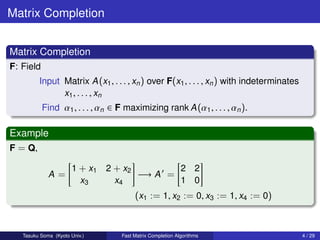
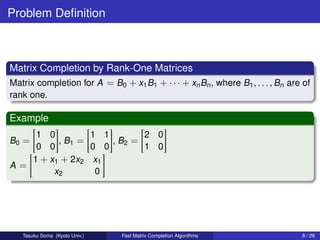
This document summarizes research on fast deterministic algorithms for matrix completion problems. It presents new algorithms for:
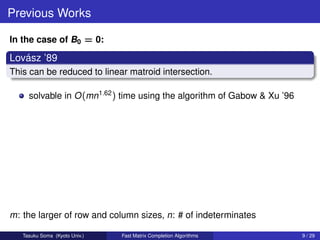
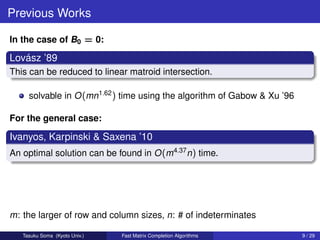
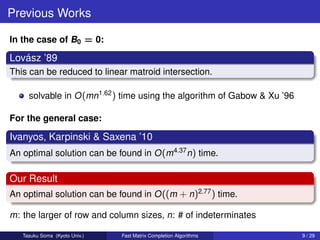
1) Matrix completion by rank-one matrices, solving it faster than previous work in O((m+n)2.77) time rather than O(m4.37n) time, where m is the larger matrix dimension and n is the number of indeterminates.
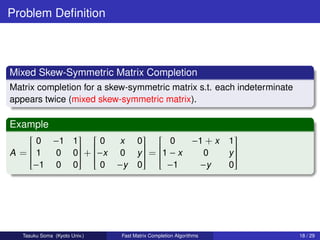
2) Mixed skew-symmetric matrix completion, the first deterministic polynomial time algorithm for this problem.
3) Skew-symmetric matrix completion by rank-two skew-symmetric matrices, the first deterministic polynomial time algorithm for this problem. The algorithms work over an arbitrary field.










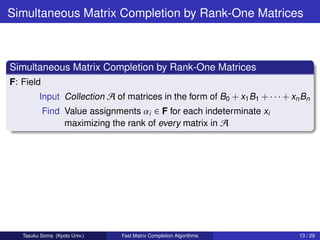
![Min-Max Theorem
Theorem
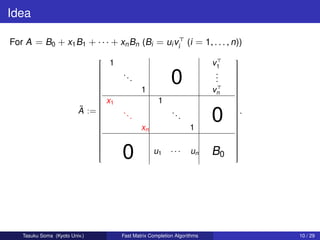
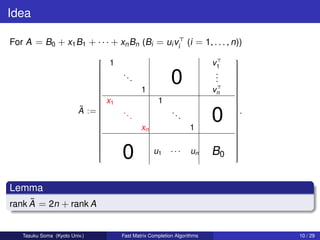
For A = B0 + x1 B1 + · · · + xn Bn ,
max{rank A : x1 , . . . , xn }
0 [vj : j J]
= min rank : J ⊆ {1, . . . , n} .
[uj : j ∈ J ] B0
Tasuku Soma (Kyoto Univ.) Fast Matrix Completion Algorithms 12 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-130326075741-phpapp02/85/Fast-Deterministic-Algorithms-for-Matrix-Completion-Problems-21-320.jpg)
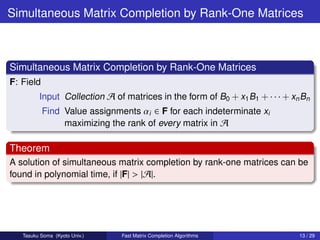
![Min-Max Theorem
Theorem
For A = B0 + x1 B1 + · · · + xn Bn ,
max{rank A : x1 , . . . , xn }
0 [vj : j J]
= min rank : J ⊆ {1, . . . , n} .
[uj : j ∈ J ] B0
´
Corollary (Lovasz ’89)
If B0 = 0, then
max{rank A : x1 , . . . , xn }
= min{dim uj : j ∈ J + dim vj : j J : J ⊆ {1, . . . , n}}
Tasuku Soma (Kyoto Univ.) Fast Matrix Completion Algorithms 12 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-130326075741-phpapp02/85/Fast-Deterministic-Algorithms-for-Matrix-Completion-Problems-22-320.jpg)




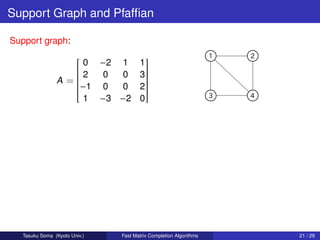
![Rank of Mixed Skew-Symmetric Matrix
Lemma (Murota ’03)
For an m × m mixed skew-symmetric matrix A = Q + T
(Q: constant part, T : indeterminates part),
rank A = max |FQ FT | : both Q [FQ ], T [FT ] are nonsingular
RHS is linear delta-covering.
Optimal FQ and FT can be found in O (m4 )
time (Geelen, Iwata & Murota ’03).
Tasuku Soma (Kyoto Univ.) Fast Matrix Completion Algorithms 20 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-130326075741-phpapp02/85/Fast-Deterministic-Algorithms-for-Matrix-Completion-Problems-32-320.jpg)
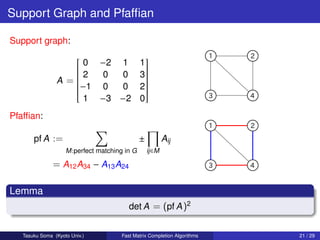
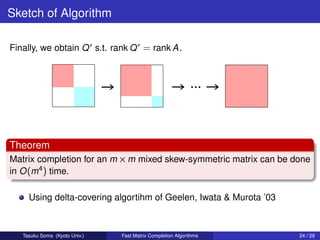
![Sketch of Algorithm
Algorithm
1: Find an optimal solution FQ and FT for linear delta-covering.
2: Find a perfect matching M in the support graph of T [FT ].
Tasuku Soma (Kyoto Univ.) Fast Matrix Completion Algorithms 22 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-130326075741-phpapp02/85/Fast-Deterministic-Algorithms-for-Matrix-Completion-Problems-35-320.jpg)
![Sketch of Algorithm
Algorithm
1: Find an optimal solution FQ and FT for linear delta-covering.
2: Find a perfect matching M in the support graph of T [FT ].
3: for each ij ∈ M do
4: Substitute α to Tij so that Q [FQ ∪ {i , j }] will be nonsingular after
substitution.
5: FQ := FQ ∪ {i , j }
6: end for
Tasuku Soma (Kyoto Univ.) Fast Matrix Completion Algorithms 22 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-130326075741-phpapp02/85/Fast-Deterministic-Algorithms-for-Matrix-Completion-Problems-36-320.jpg)
![Sketch of Algorithm
Algorithm
1: Find an optimal solution FQ and FT for linear delta-covering.
2: Find a perfect matching M in the support graph of T [FT ].
3: for each ij ∈ M do
4: Substitute α to Tij so that Q [FQ ∪ {i , j }] will be nonsingular after
substitution.
5: FQ := FQ ∪ {i , j }
6: end for
7: Substitute 0 to the rest of indeterminates
8: return the resulting matrix
Tasuku Soma (Kyoto Univ.) Fast Matrix Completion Algorithms 22 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-130326075741-phpapp02/85/Fast-Deterministic-Algorithms-for-Matrix-Completion-Problems-37-320.jpg)
![Sketch of Algorithm
How can we find α s.t. Q [FQ ∪ {i , j }] will be nonsingular?
A =Q +T
Tasuku Soma (Kyoto Univ.) Fast Matrix Completion Algorithms 23 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-130326075741-phpapp02/85/Fast-Deterministic-Algorithms-for-Matrix-Completion-Problems-38-320.jpg)
![Sketch of Algorithm
How can we find α s.t. Q [FQ ∪ {i , j }] will be nonsingular?
A =Q +T A =Q +T
Tasuku Soma (Kyoto Univ.) Fast Matrix Completion Algorithms 23 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-130326075741-phpapp02/85/Fast-Deterministic-Algorithms-for-Matrix-Completion-Problems-39-320.jpg)
![Sketch of Algorithm
How can we find α s.t. Q [FQ ∪ {i , j }] will be nonsingular?
A =Q +T A =Q +T
Lemma
Q : modified matrix of Q as Qij := Qij + α, Qji := Qji − α
pf Q [FQ ∪ {i , j }] = pf Q [FQ ∪ {i , j }] ± α · pf Q [FQ ]
Tasuku Soma (Kyoto Univ.) Fast Matrix Completion Algorithms 23 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-130326075741-phpapp02/85/Fast-Deterministic-Algorithms-for-Matrix-Completion-Problems-40-320.jpg)