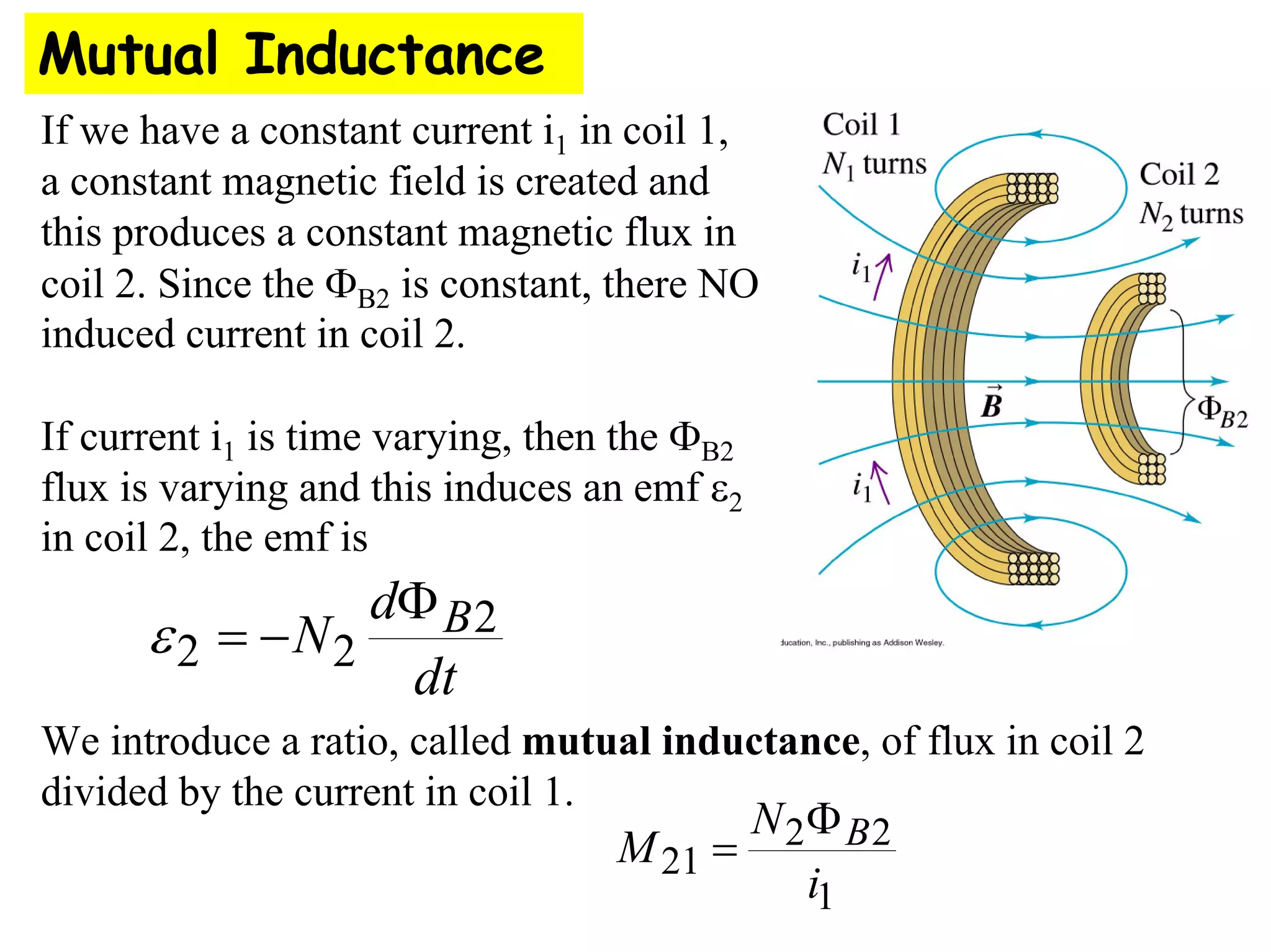
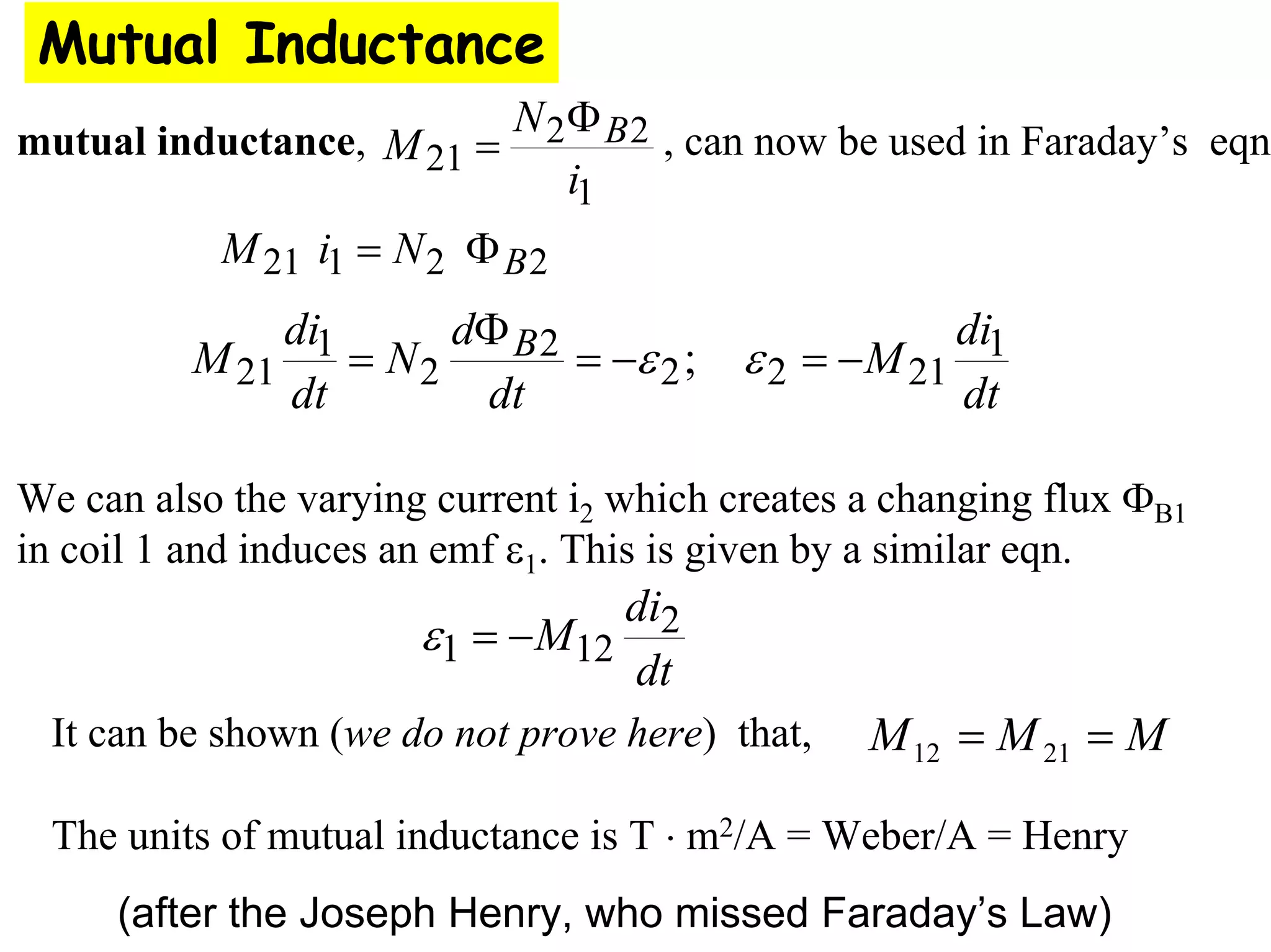
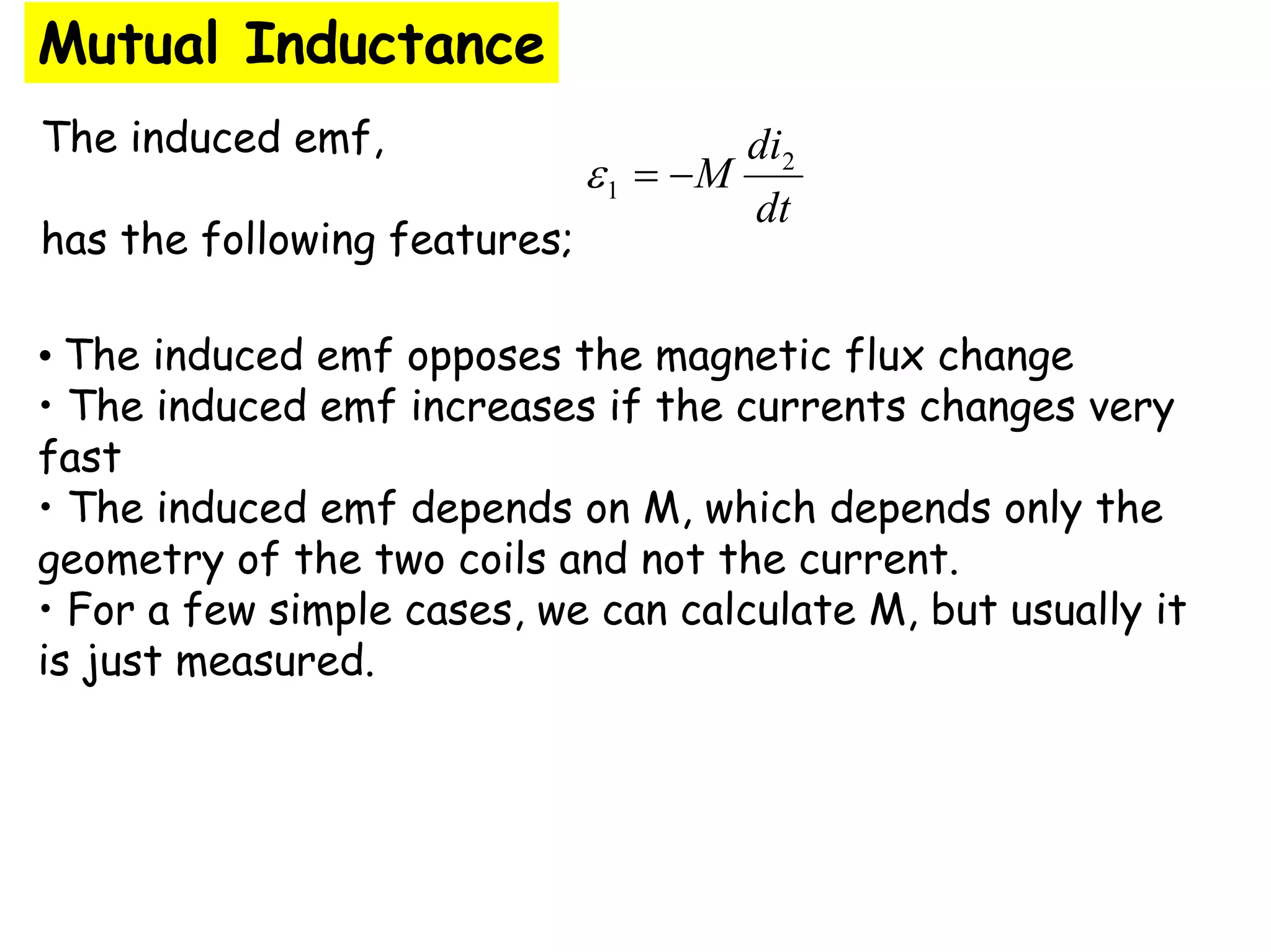
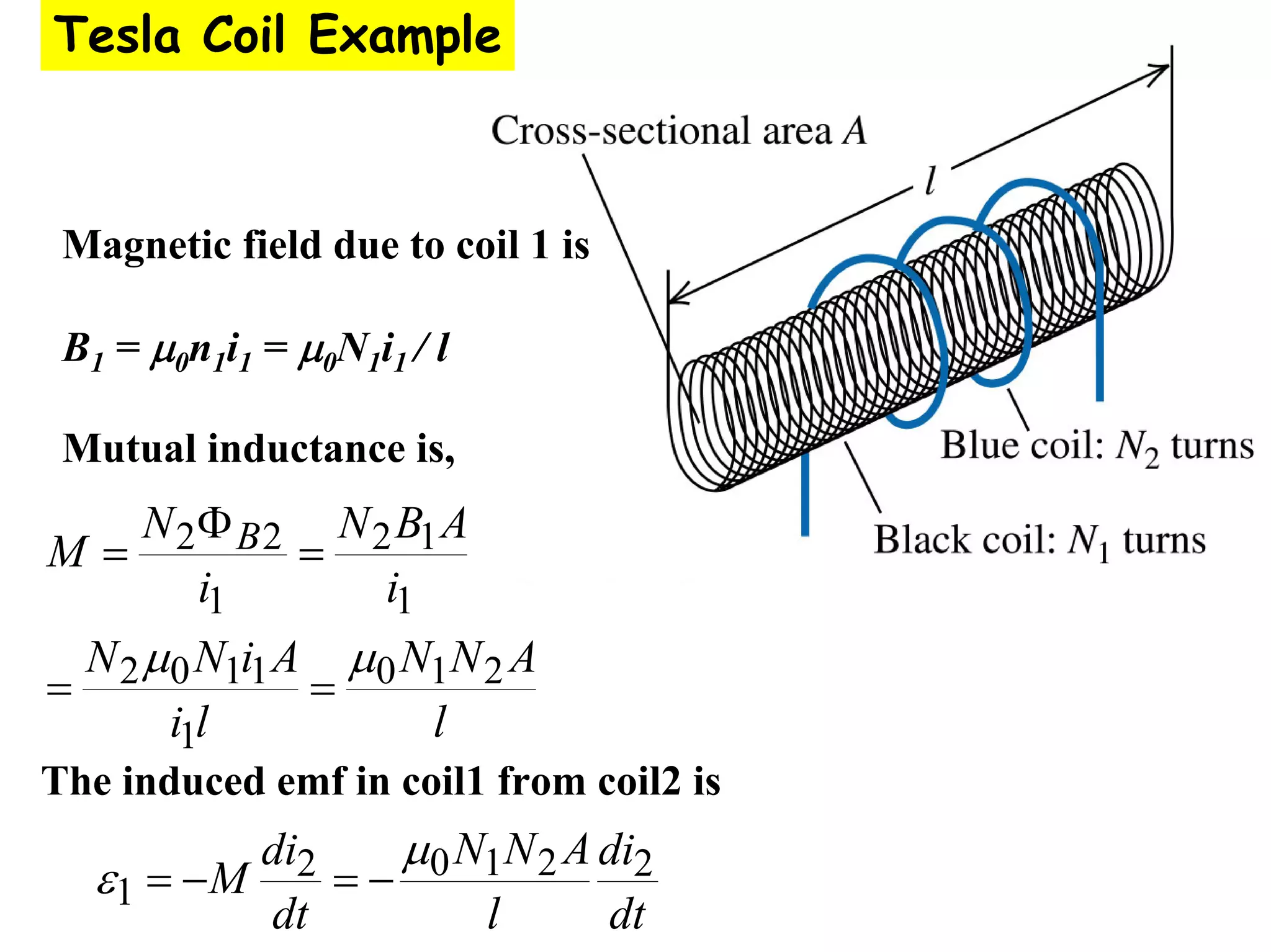
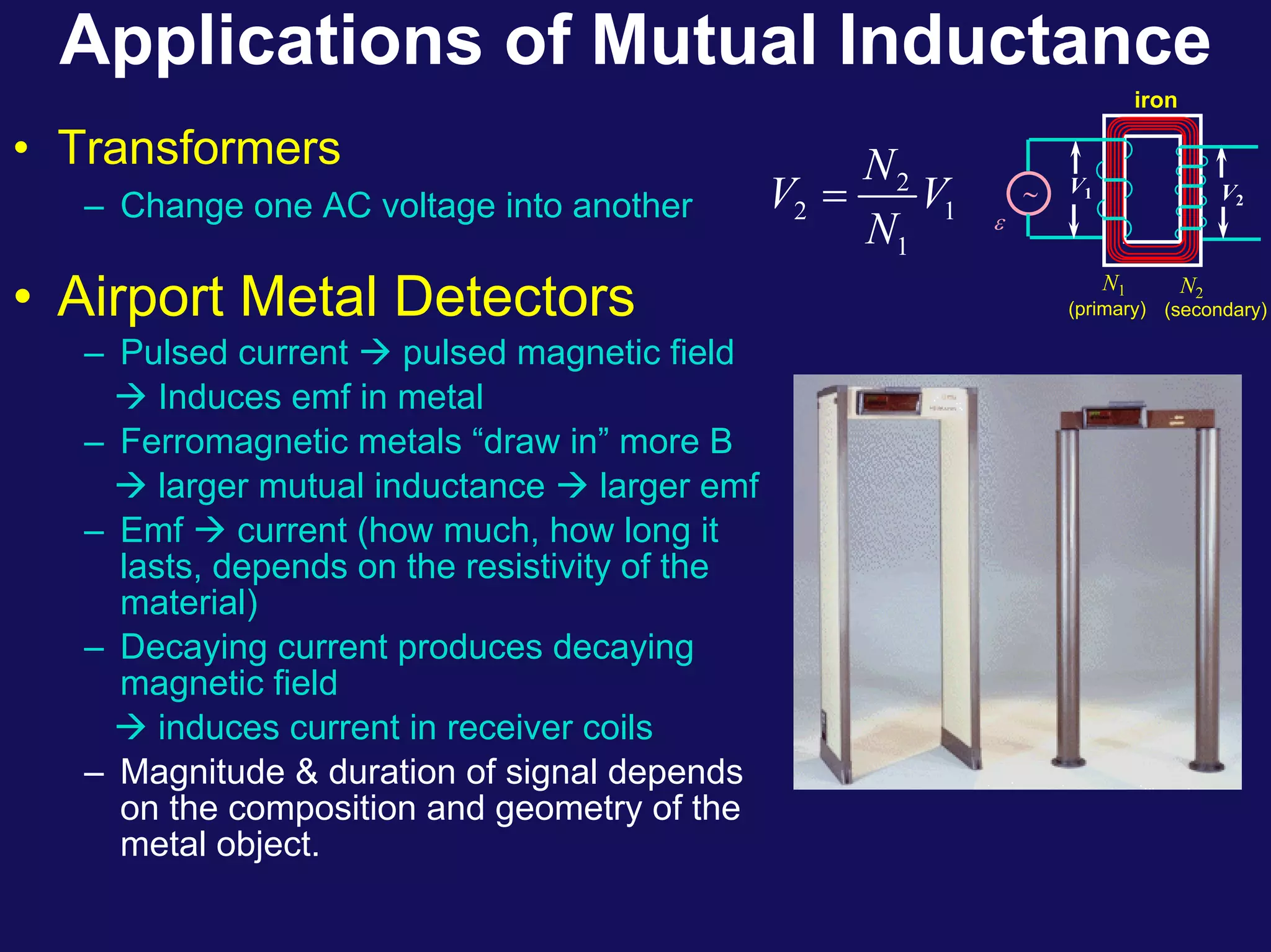
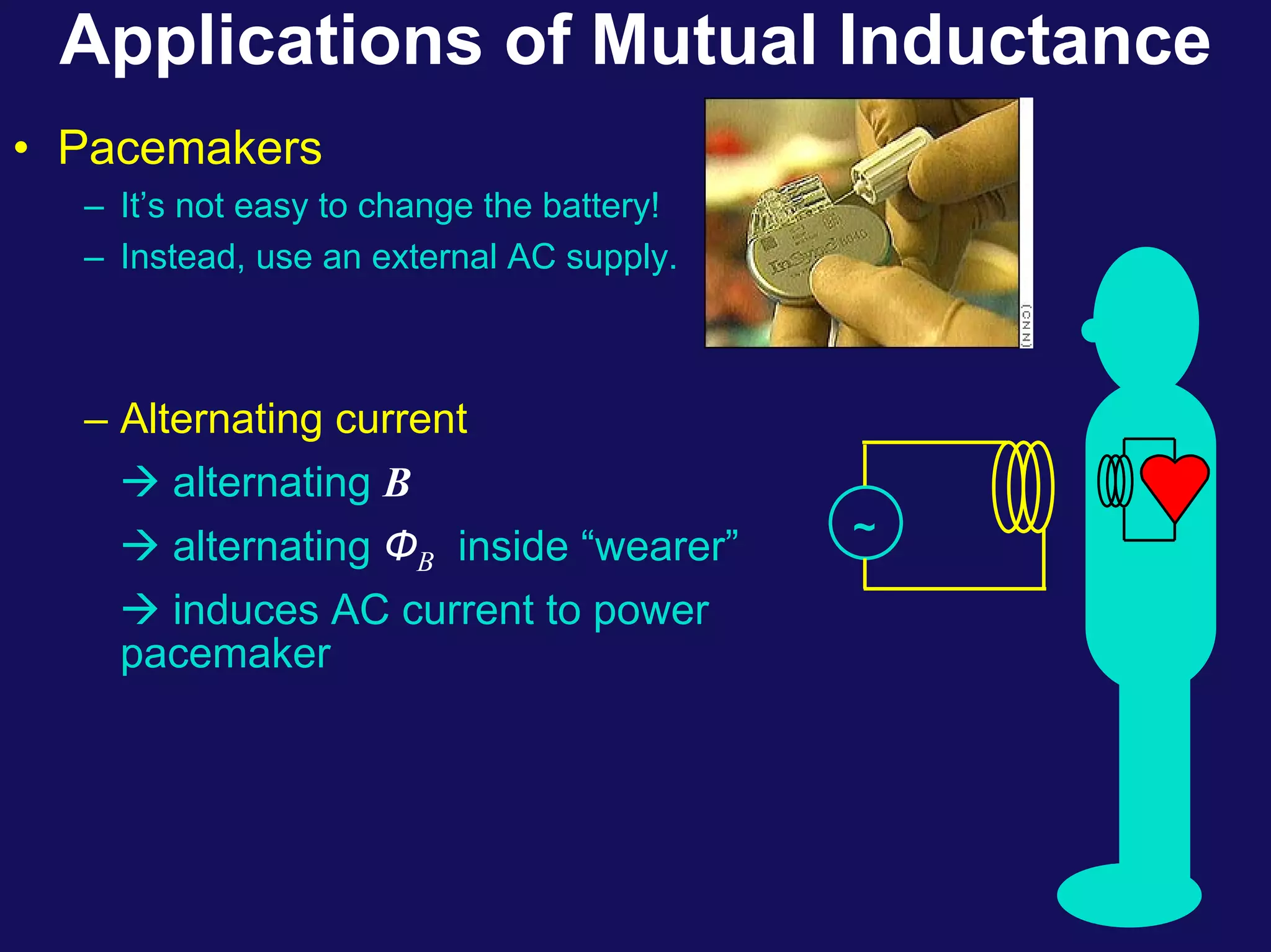
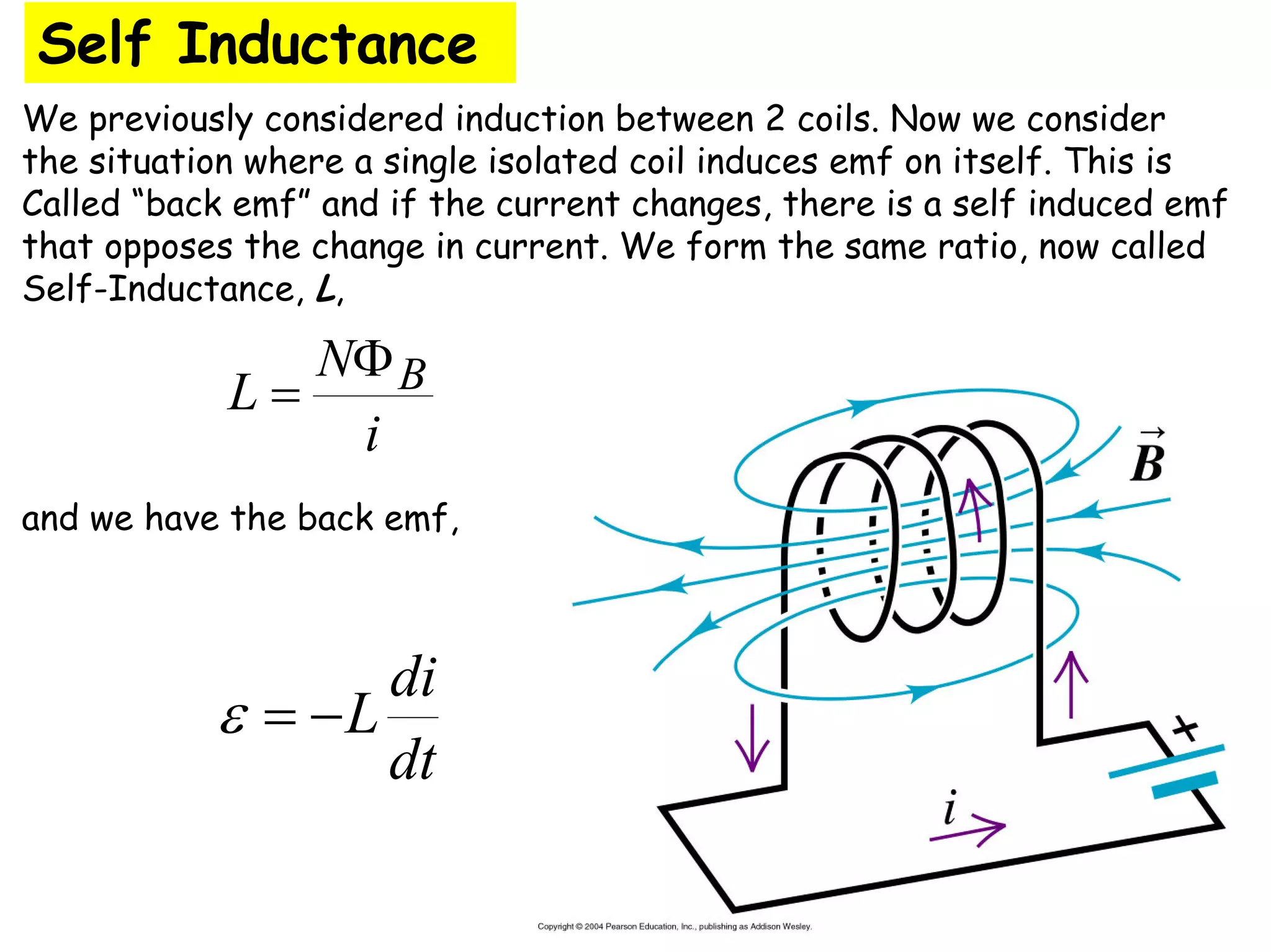
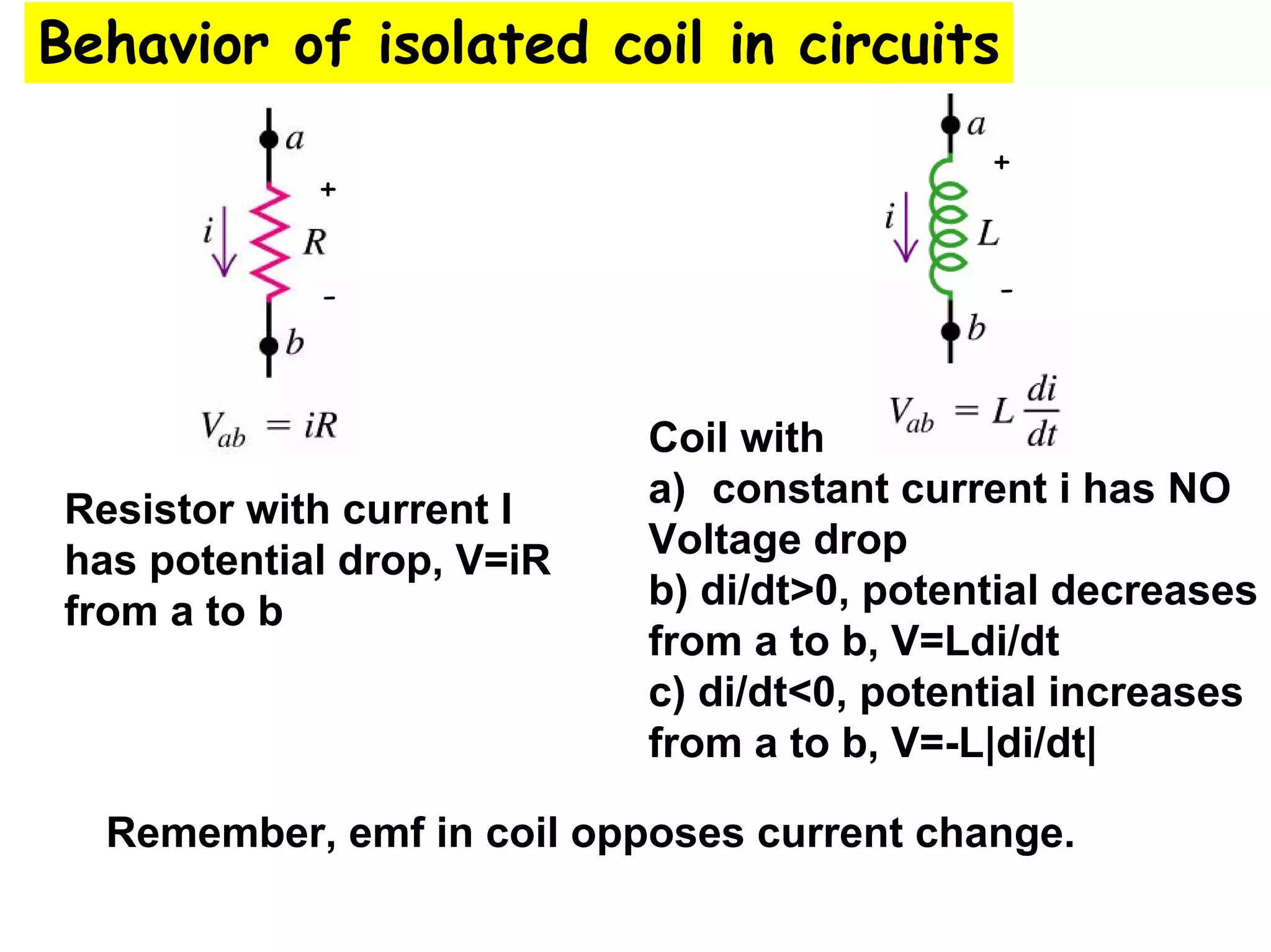
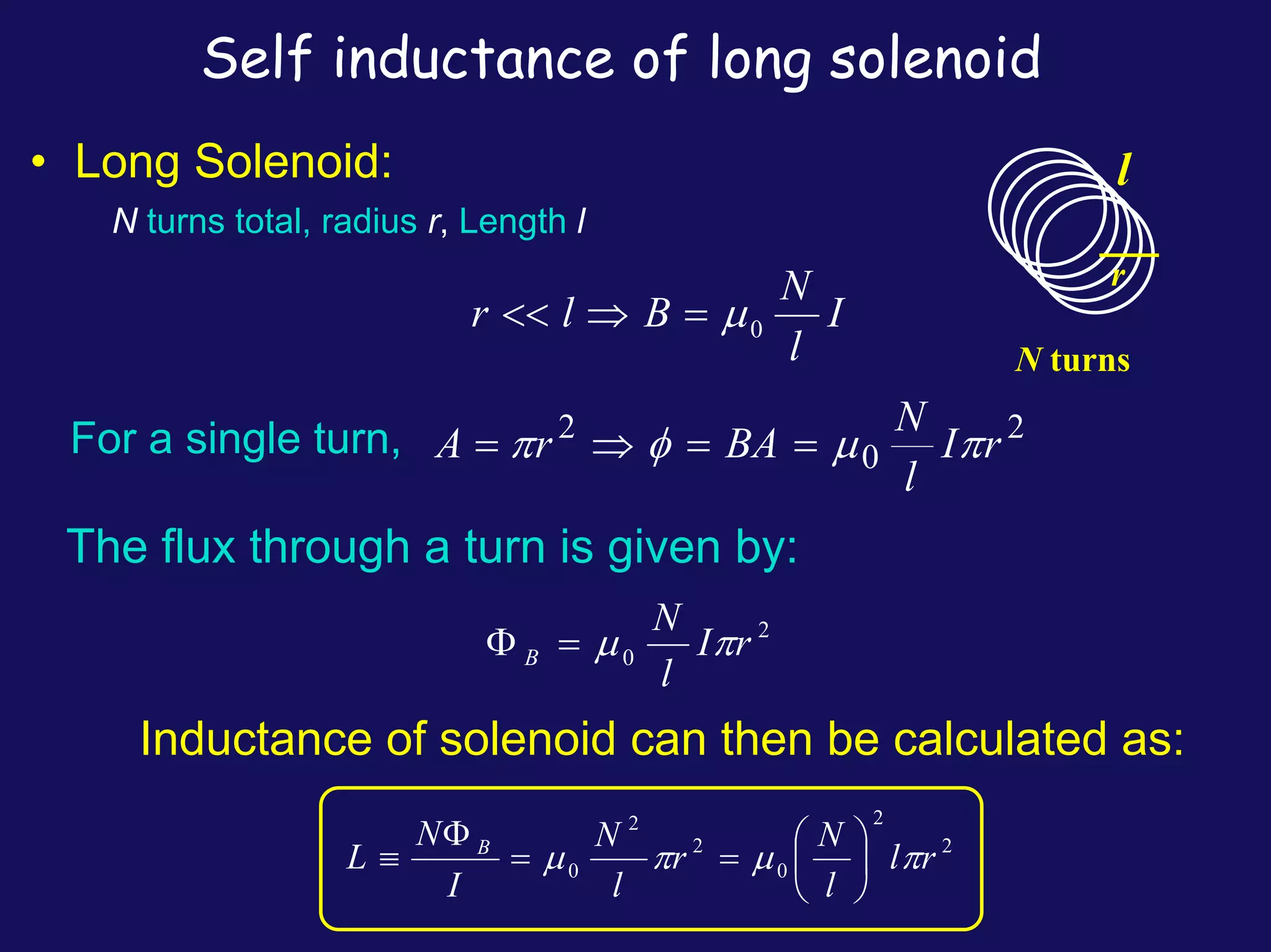
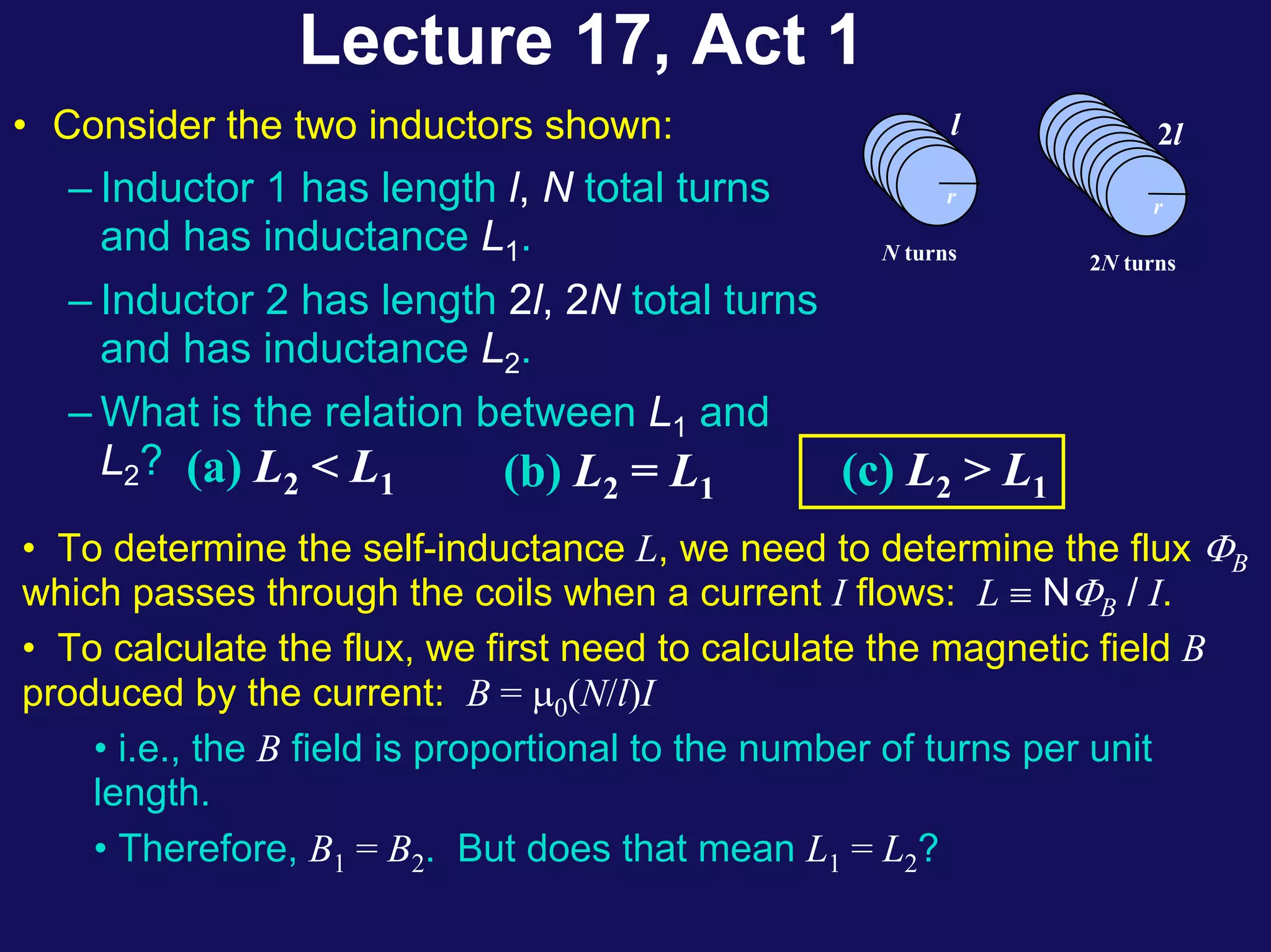
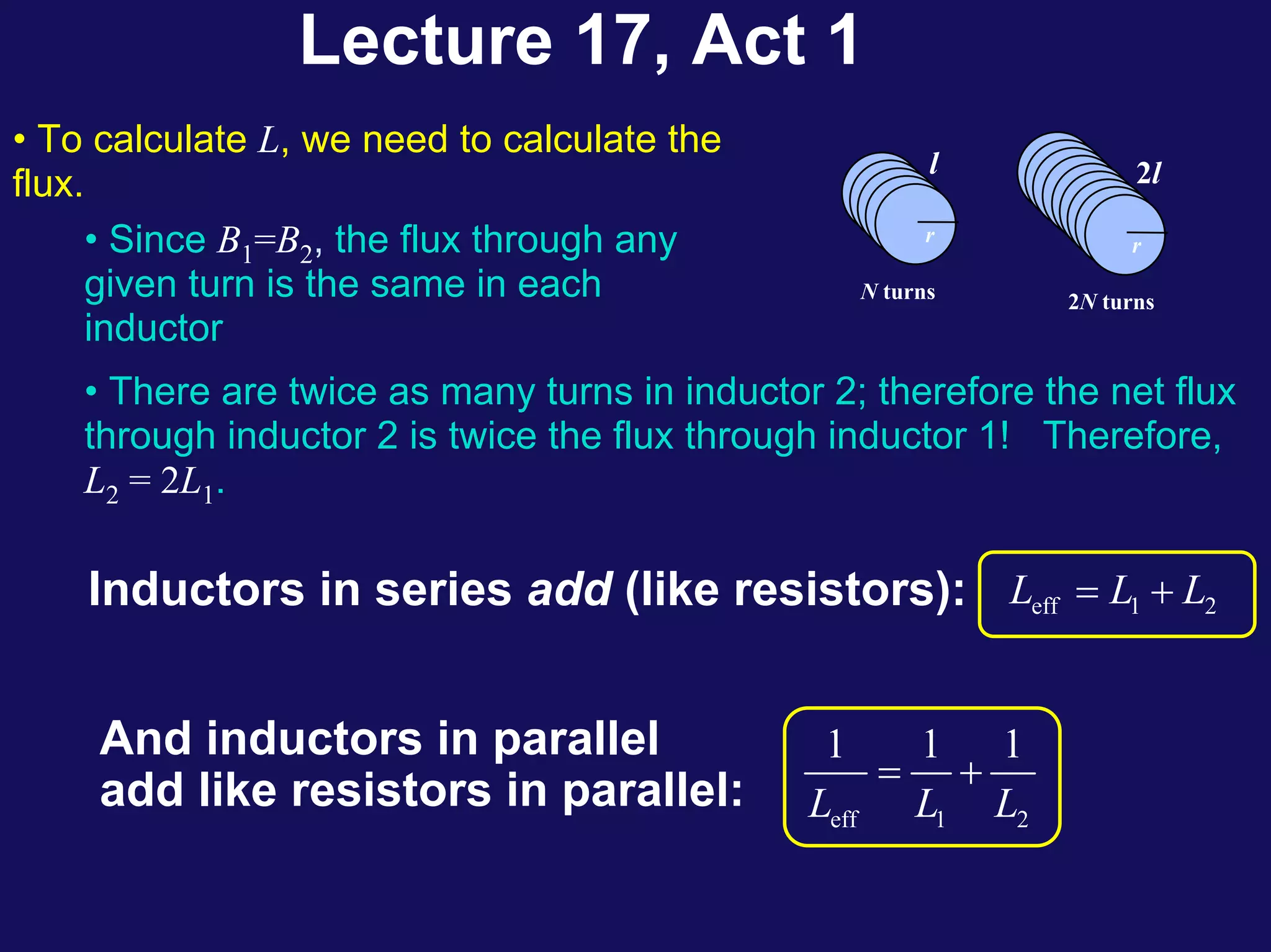
Two coils have a mutual inductance of 3.25×10−4 H. If the current in the first coil increases at a rate of 830 A/s, the induced emf in the second coil will be -27 V. If the current was instead increasing in the second coil, the induced emf in the first coil would also be -27 V. Mutual inductance describes the relationship between the magnetic flux in one coil produced by the current in the other, and can be used to calculate induced emfs using Faraday's law.