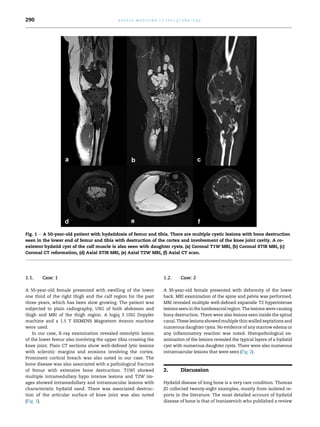
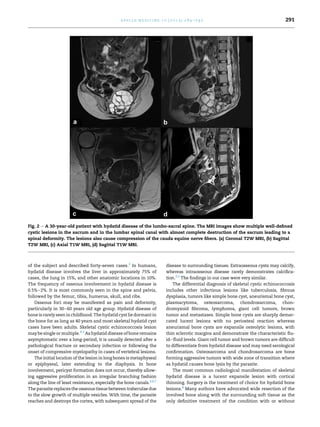
Hydatid disease of bones, caused by Echinococcus granulosus, is a rare condition affecting the skeletal system, occurring in only 0.5% to 2% of cases, primarily in long bones like the femur and tibia. Imaging findings reveal osteolytic lesions, and the diagnosis can often be misunderstood unless specifically considered, with histopathological confirmation being essential. Treatment is primarily surgical, with wide resection of affected bones being the definitive method of management.