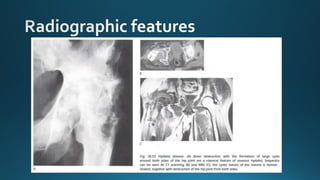
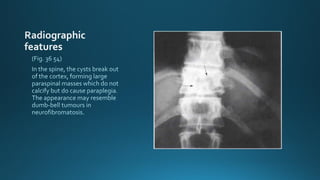
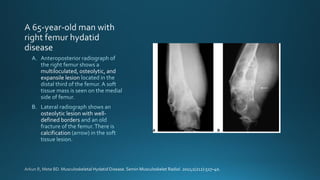
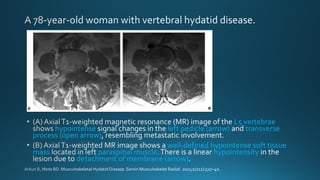
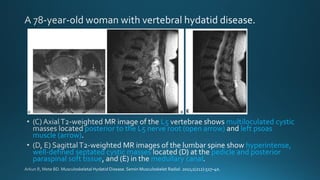
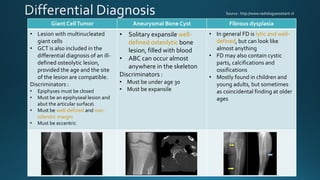
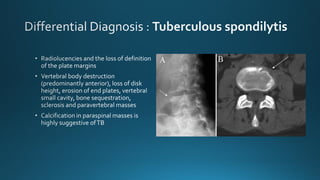
This document summarizes key information about hydatid disease from a medical textbook chapter on bone and joint infections. Hydatid disease, also known as echinococcosis, involves infection by the larval stage of the tapeworm Echinococcus. It most commonly affects the liver and lungs. Rarely, it can spread to bones, preferentially infecting the spine, long bones, and vertebrae. In bones, the enlarging cysts absorb bone and spread along the medulla, causing osteolytic lesions that become well-defined over time. Imaging plays an important role in diagnosis, showing characteristic multiloculated, osteolytic lesions with well-defined borders and possible calcification. Differential diagnosis includes aneurysmal