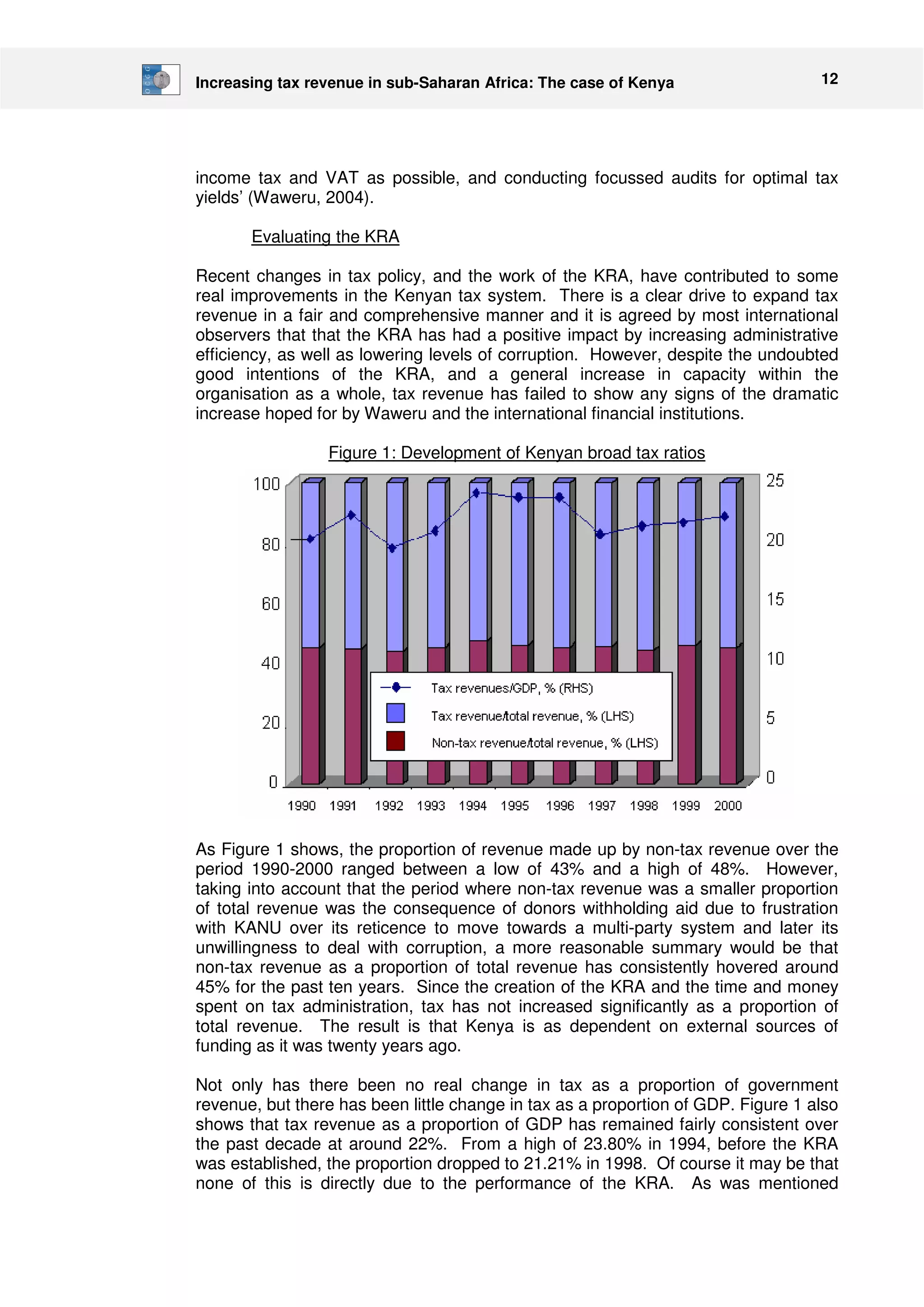
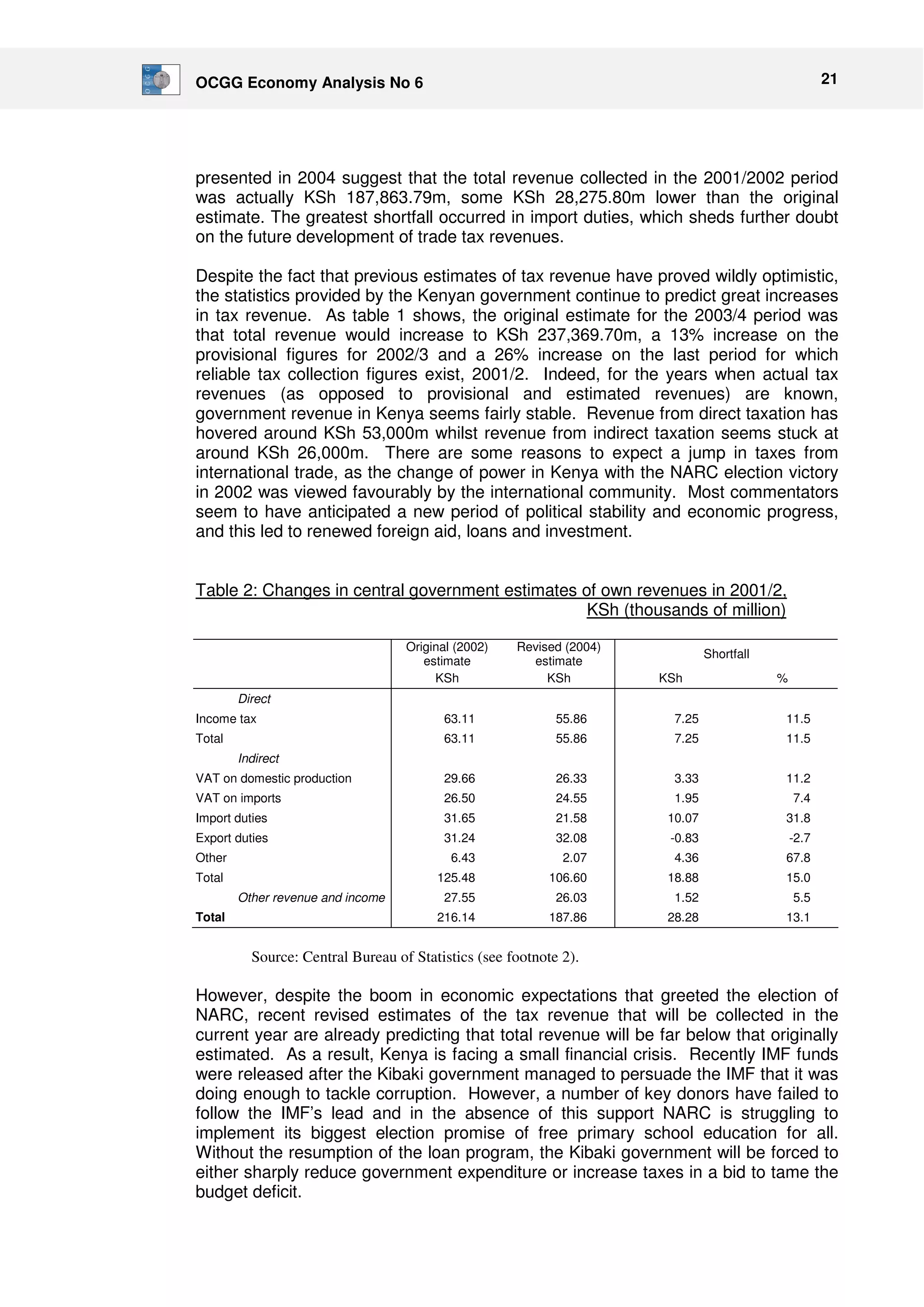
This document discusses tax reforms in Kenya that were recommended by the IMF to increase tax revenue. It finds that while trade liberalization increased tax revenues from imports in the short term, domestic tax reforms like VAT and income taxes have not increased revenue as much as hoped due to structural economic limitations. Further trade liberalization proposed by the IMF risks reducing tax revenues, which could undermine development programs given constraints on expanding domestic taxation. The document argues Kenya should maintain some tariffs in the short term to fund expanding the tax base long term through projects like increasing wages.