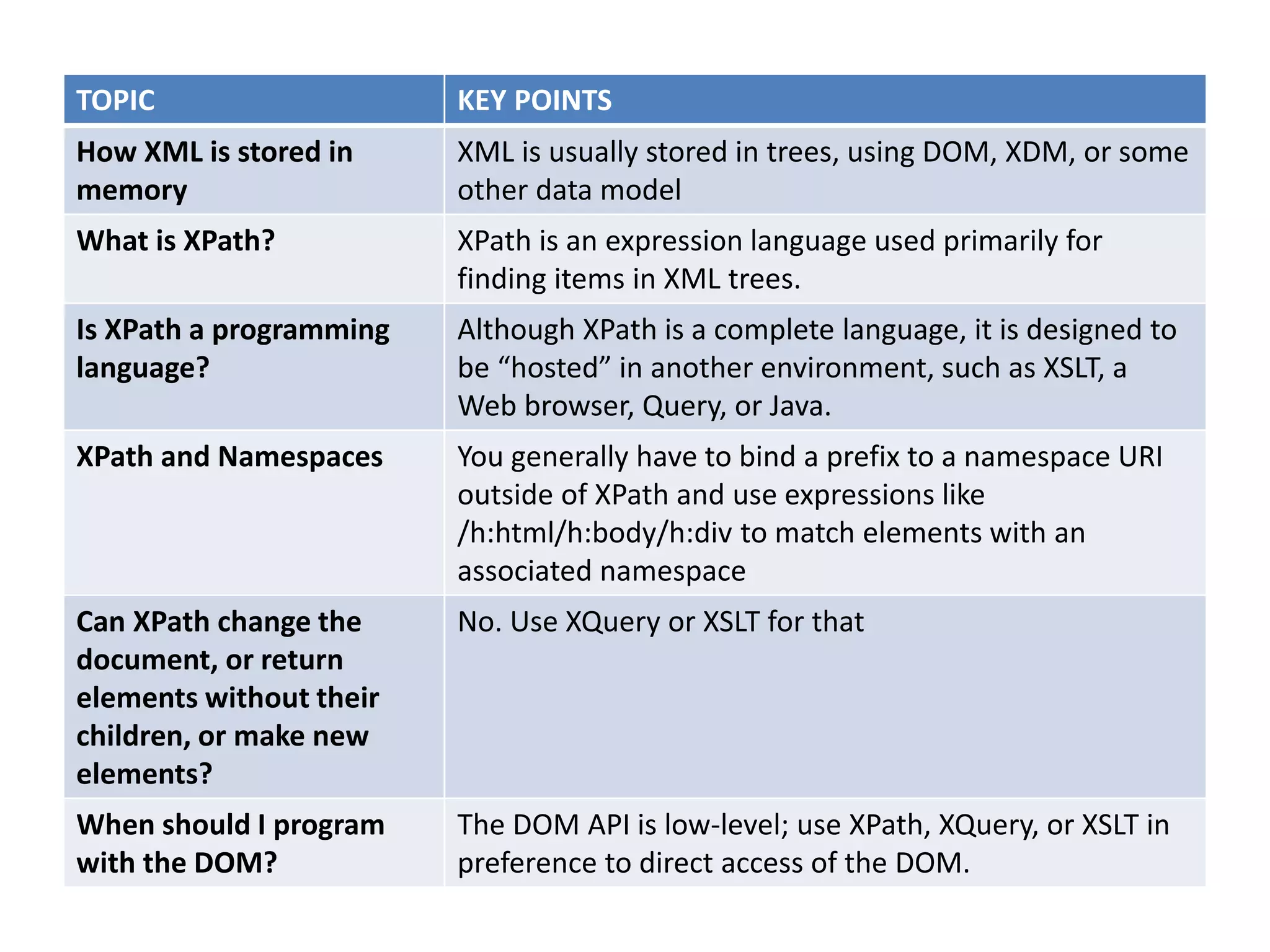
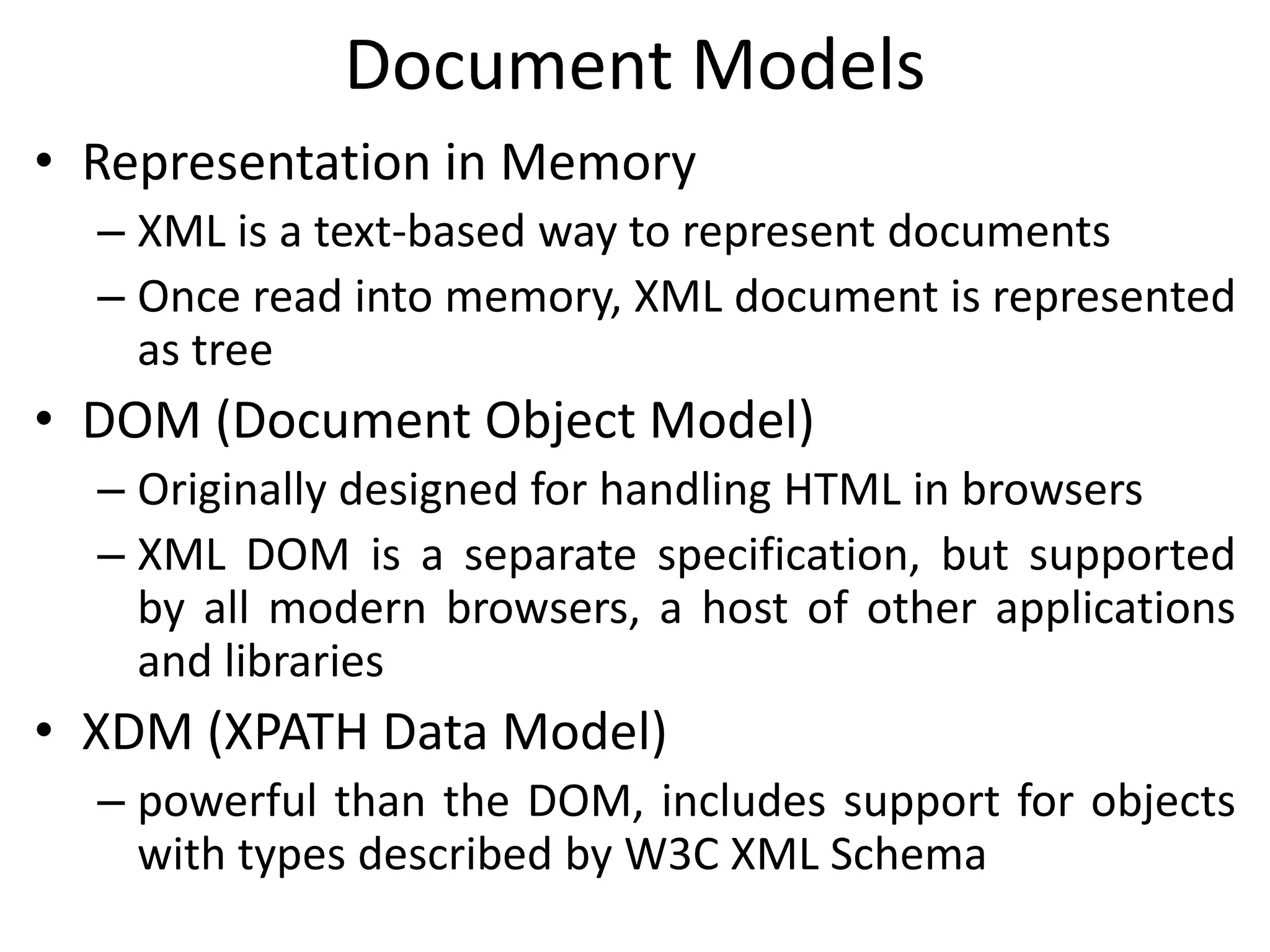
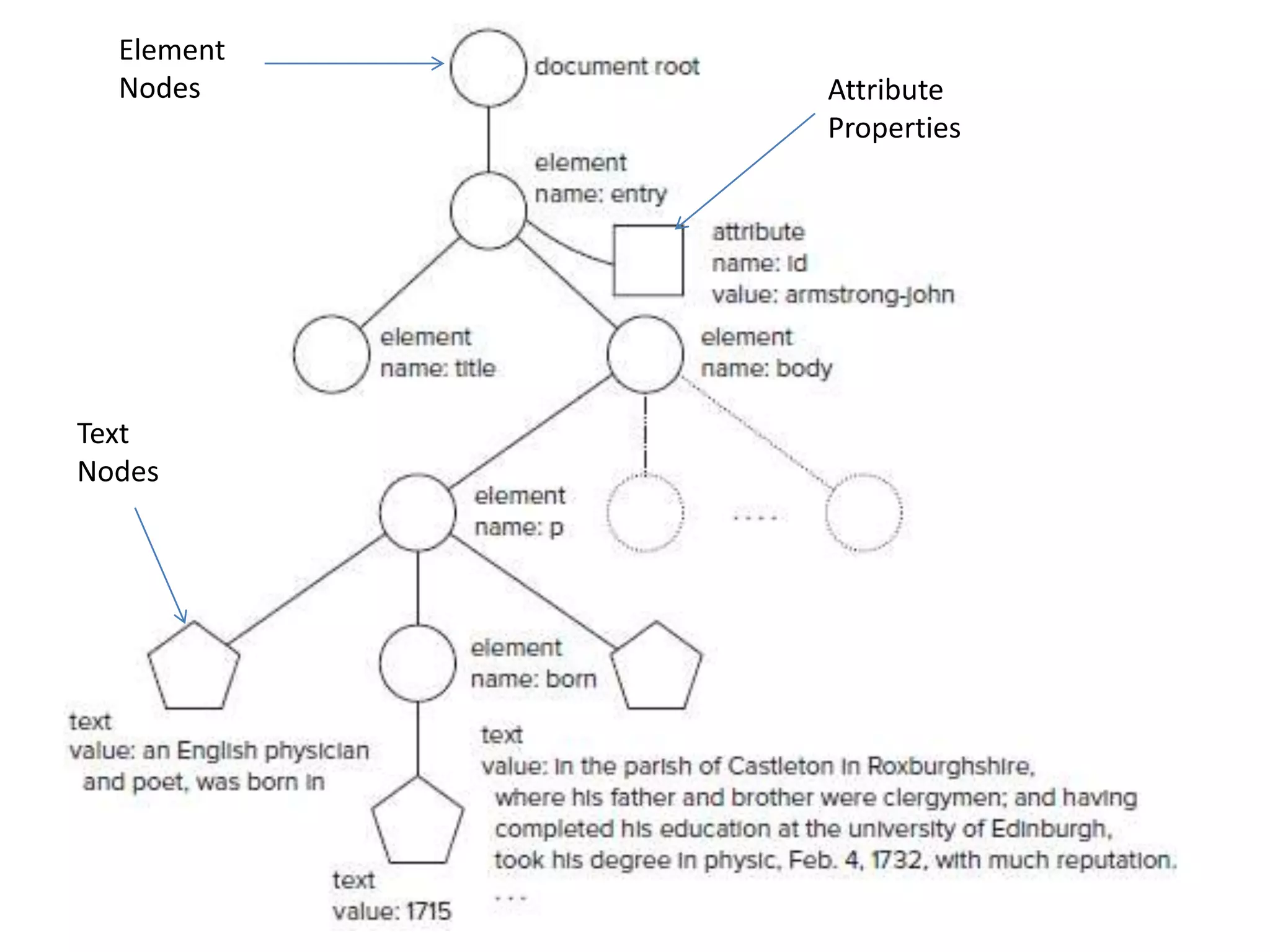
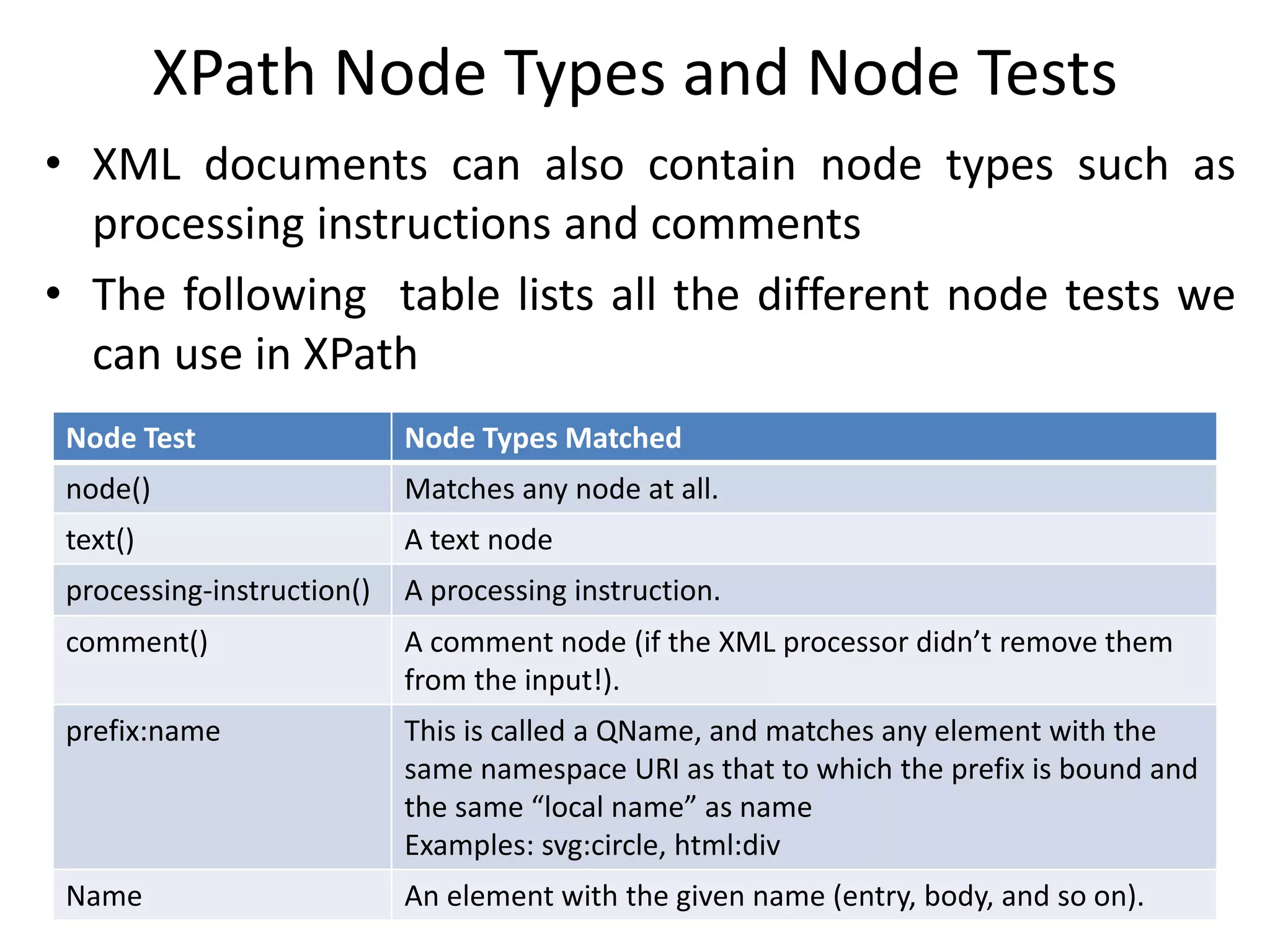
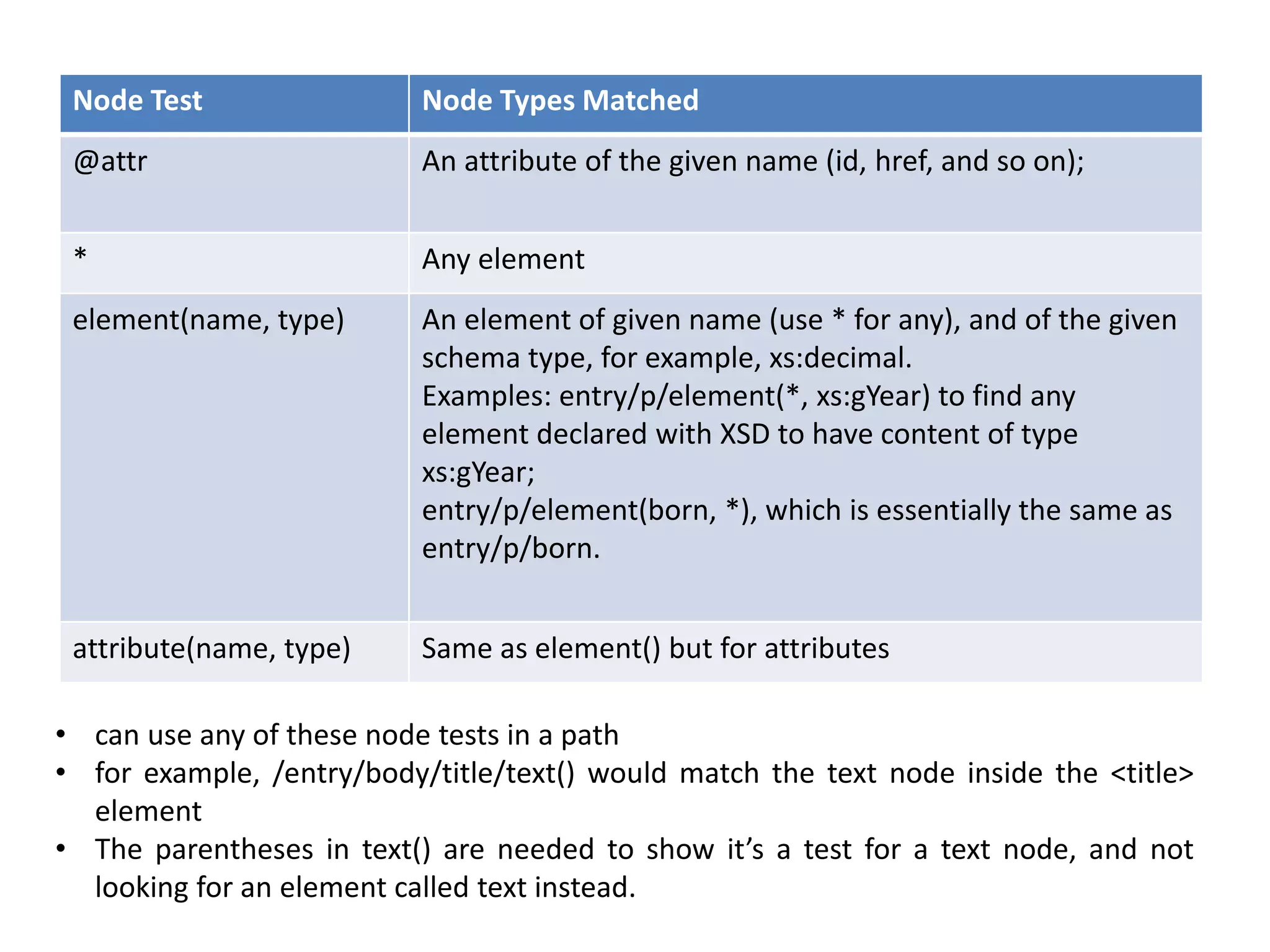
XML documents can be represented and stored in memory as tree structures using models like DOM and XDM. XPath is an expression language used to navigate and select parts of an XML tree. It allows traversing elements and their attributes, filtering nodes by properties or position, and evaluating paths relative to a context node. While XPath expressions cannot modify the document, they are commonly used with languages like XSLT and XQuery which can transform or extract data from XML trees.


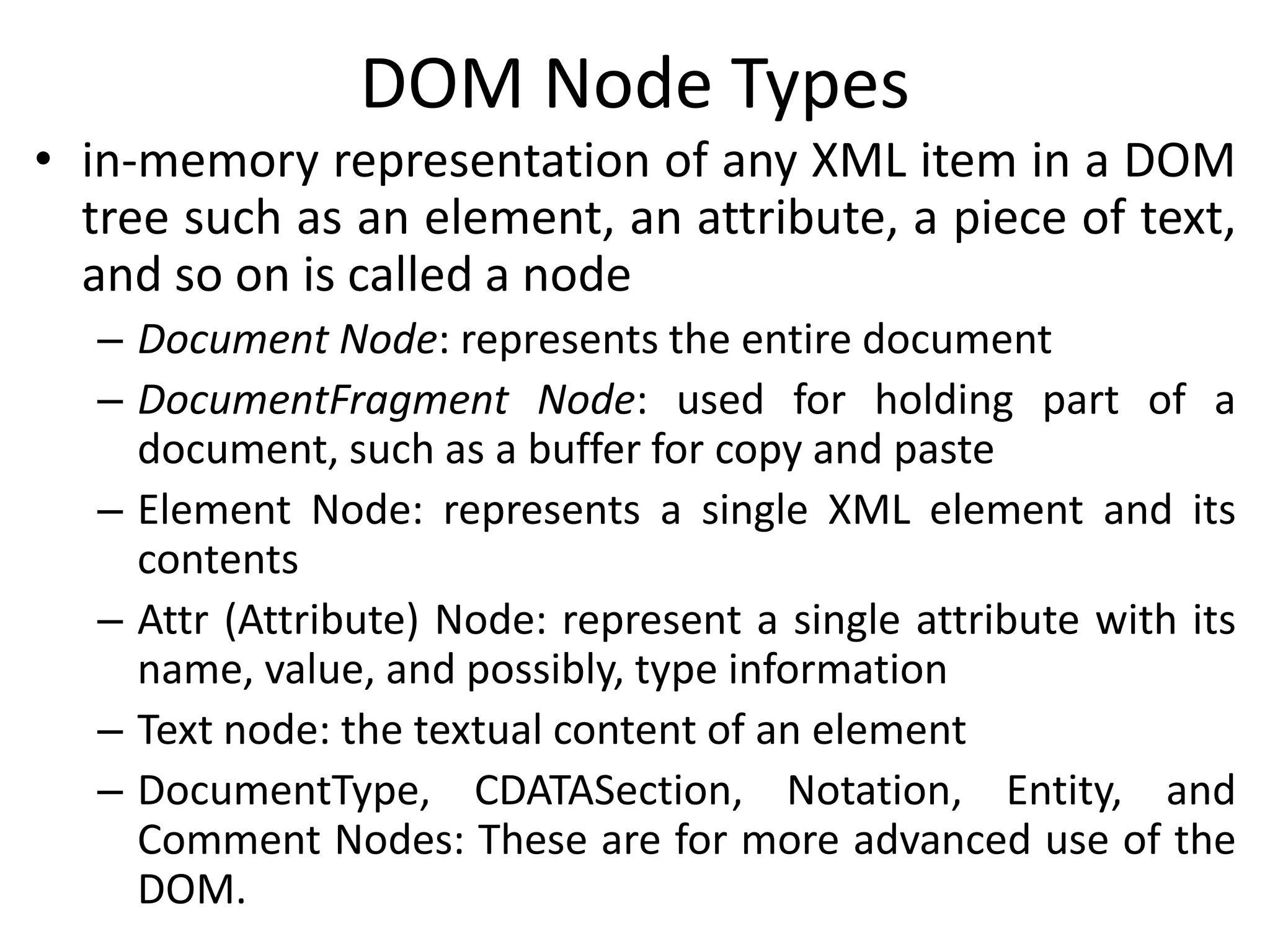
![DOM Node Lists
• Accessing the parts of a DOM tree from a program,
we get back a node list
• Simply a list of nodes
• Can iterate to march through the list one item at a
time
foreach (e in document.getelementsbytagname(“p”)) {
if (e.attributes[“role”] = “introduction”) {
document.delete(e);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/extractingdatafromxml-150603131902-lva1-app6891/75/Extracting-data-from-xml-6-2048.jpg)

![XPATH Basics
• How to use?
– pass an XPath expression and one or more XML documents to
an XPath engine
– the XPath engine evaluates the expression and gives you back
the result
– Can do it by including XPath in another language such as
XQuery or XSLT
• the result of evaluating an XPath expression is a node list
• Example: How to get at John Armstrong date of birth?
/entry/body/p/born
If there was a whole book with lots of entries, and you just
wanted the one for John Armstrong, then
/book/entry[@id = “armstrong-john”]/body/p/born](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/extractingdatafromxml-150603131902-lva1-app6891/75/Extracting-data-from-xml-8-2048.jpg)

![XPath Predicates
• can apply a predicate to any node list and the result is those
nodes for which the predicate evaluated to a true, or non-
zero value
• Can combine predicates like
/book/chapter[position() = 2]/p[@class = ‘footnote’][position() = 1]
– finds all <chapter> elements in a book, then uses a predicate to pick
out only those chapters that are the second child of the book
– then finds all the <p> children of that chapter, and uses a predicate
to filter out all except those <p> elements that have a class attribute
with the value footnote
– finally, it uses another predicate to choose only the first node in the
list i.e. the first <p> element
• expression inside the predicate can actually be any XPath
expression
/entries/entry[body/p/born = /entries/entry/@born]
– finds all the entry elements that contain a born element whose
value is equal to the born attribute on some entry element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/extractingdatafromxml-150603131902-lva1-app6891/75/Extracting-data-from-xml-12-2048.jpg)
![• Positional Predicates
– simplest predicate is just a number, like [17]: selects only the seventeenth
node
/book/ chapter[2] to select the second chapter and same as
/book/chapter[position() = 2]
– positional predicate is a filter with a Boolean expression inside
• The Context in Predicates
– every XPath expression is evaluated in a context
– The step (/) and the predicate change the context
– In the context of a <def> element in any document
//*[@use = current()/@id]
find every element with an attribute called use whose value is equal to
the id attribute on the current <def> element
//*[@use = @id]
find every element having use and id attributes with the same value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/extractingdatafromxml-150603131902-lva1-app6891/75/Extracting-data-from-xml-13-2048.jpg)