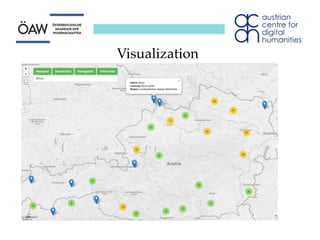
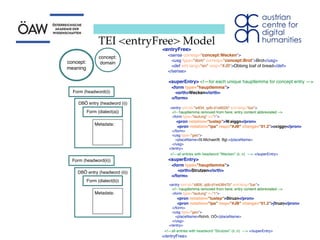
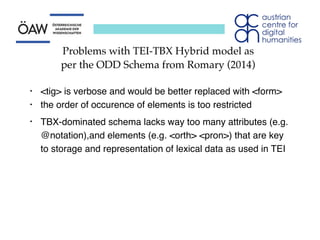
The document discusses representing heterogeneous dialect data from the DBÖ collection in a standardized way. It considers using XML-based standards like TEI to encode the data onomasiologically rather than just semasiologically. Two options - modifying TEI's <entryFree> element or using a TBX-TEI hybrid - are presented but have problems in fully and legitimately representing the data. The conclusion is that TEI needs a dedicated means of encoding onomasiological entries with an appropriate set of elements and attributes to fully capture the lexical information.