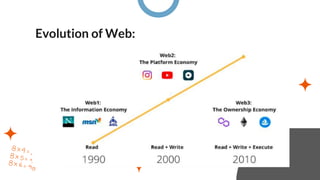
The document discusses the evolution of the World Wide Web through four stages:
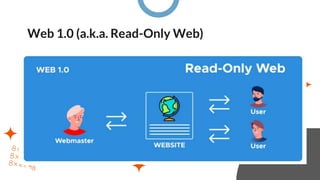
Web 1.0 (1991-2004) was the "read-only web" characterized by static websites where users could only consume information.
Web 2.0 (2005-2010) was the "read-write web" where users could interact with dynamic content and contribute their own content through blogs, social media, and user-generated content.
Web 3.0 (2010-present) aims to be a more open and decentralized "intelligent web" through technologies like semantic web and artificial intelligence.
Emerging technologies like internet of things, artificial intelligence, 5G networks, and big data are fueling further developments and