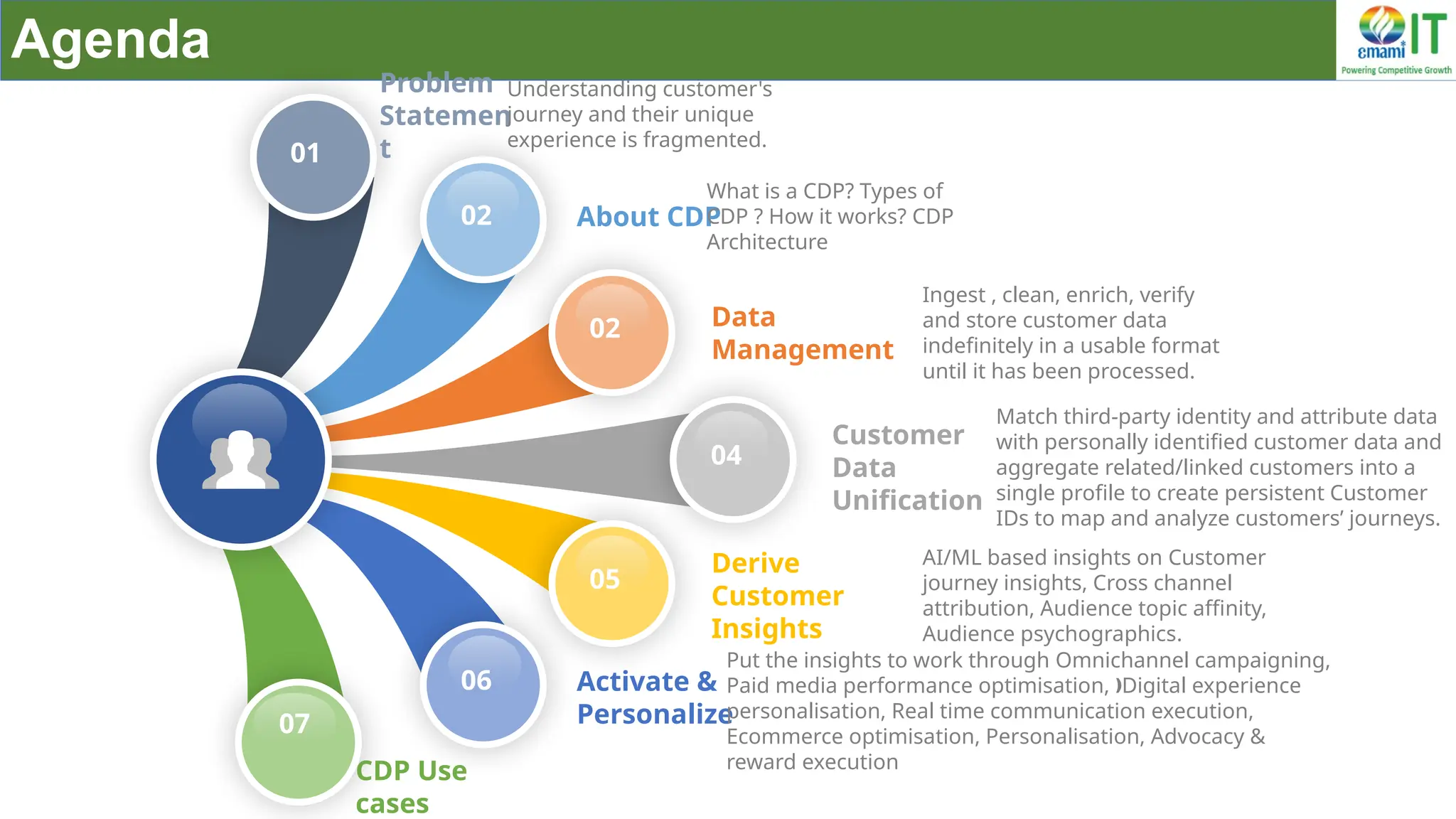
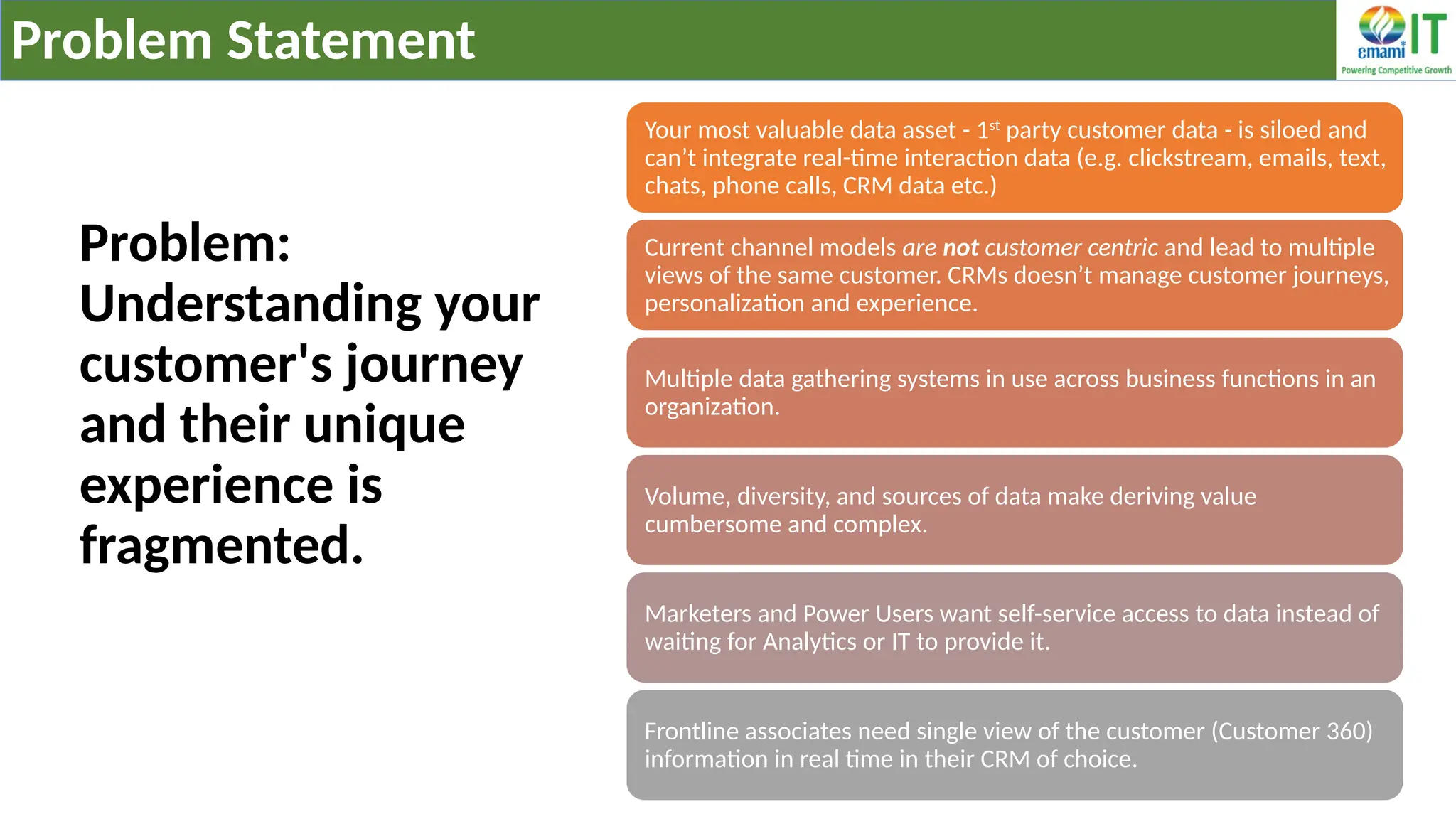
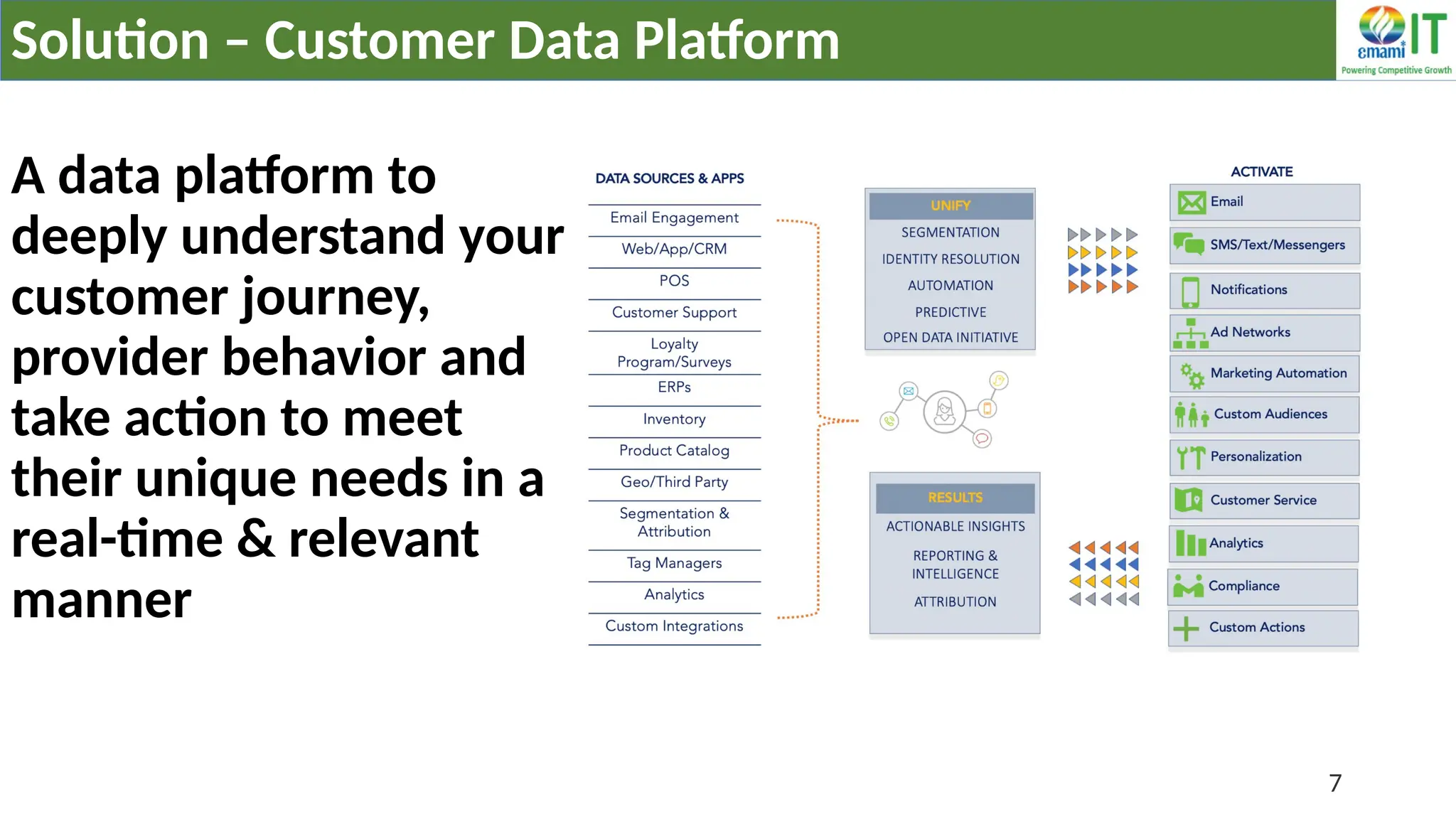
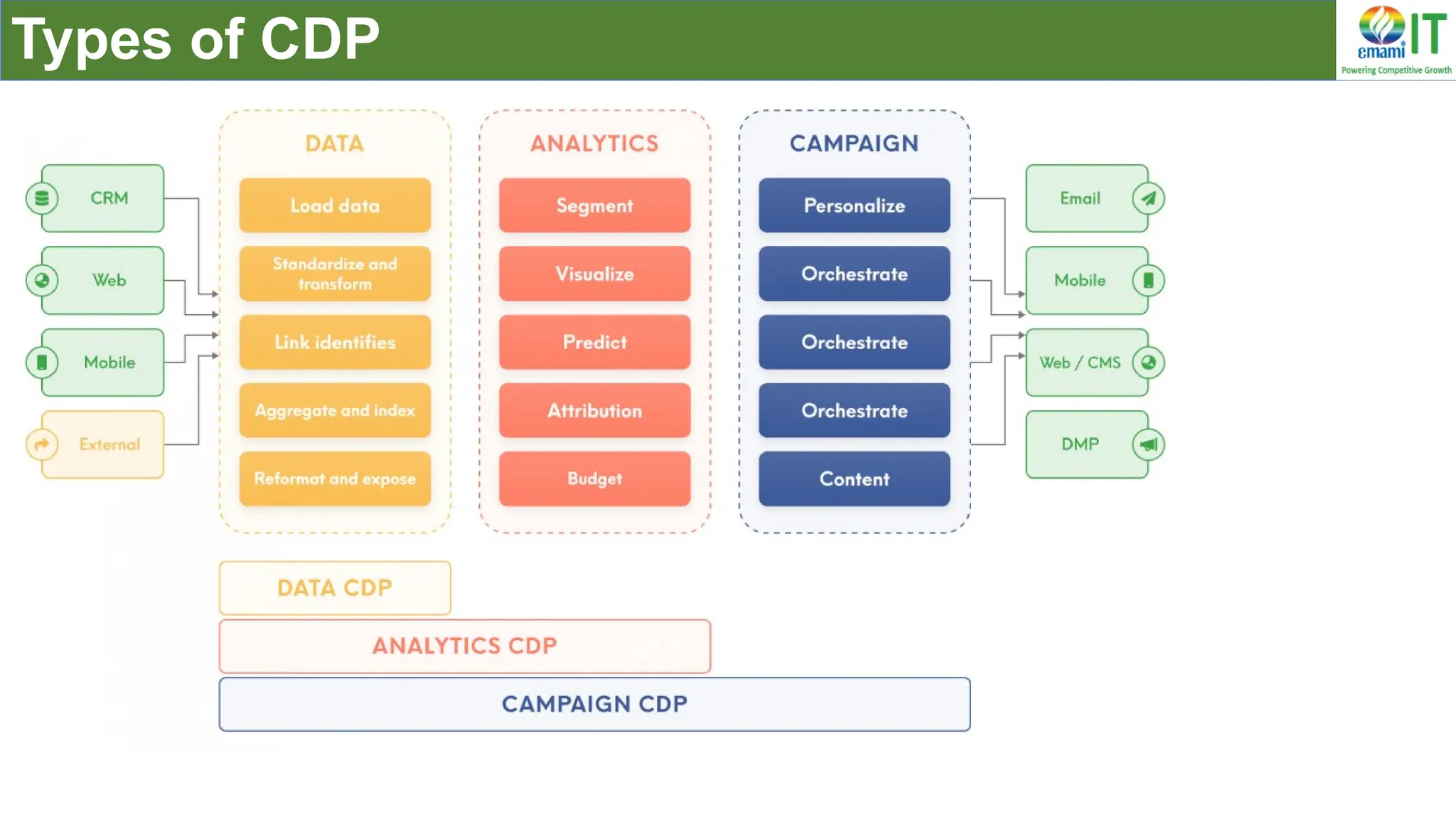
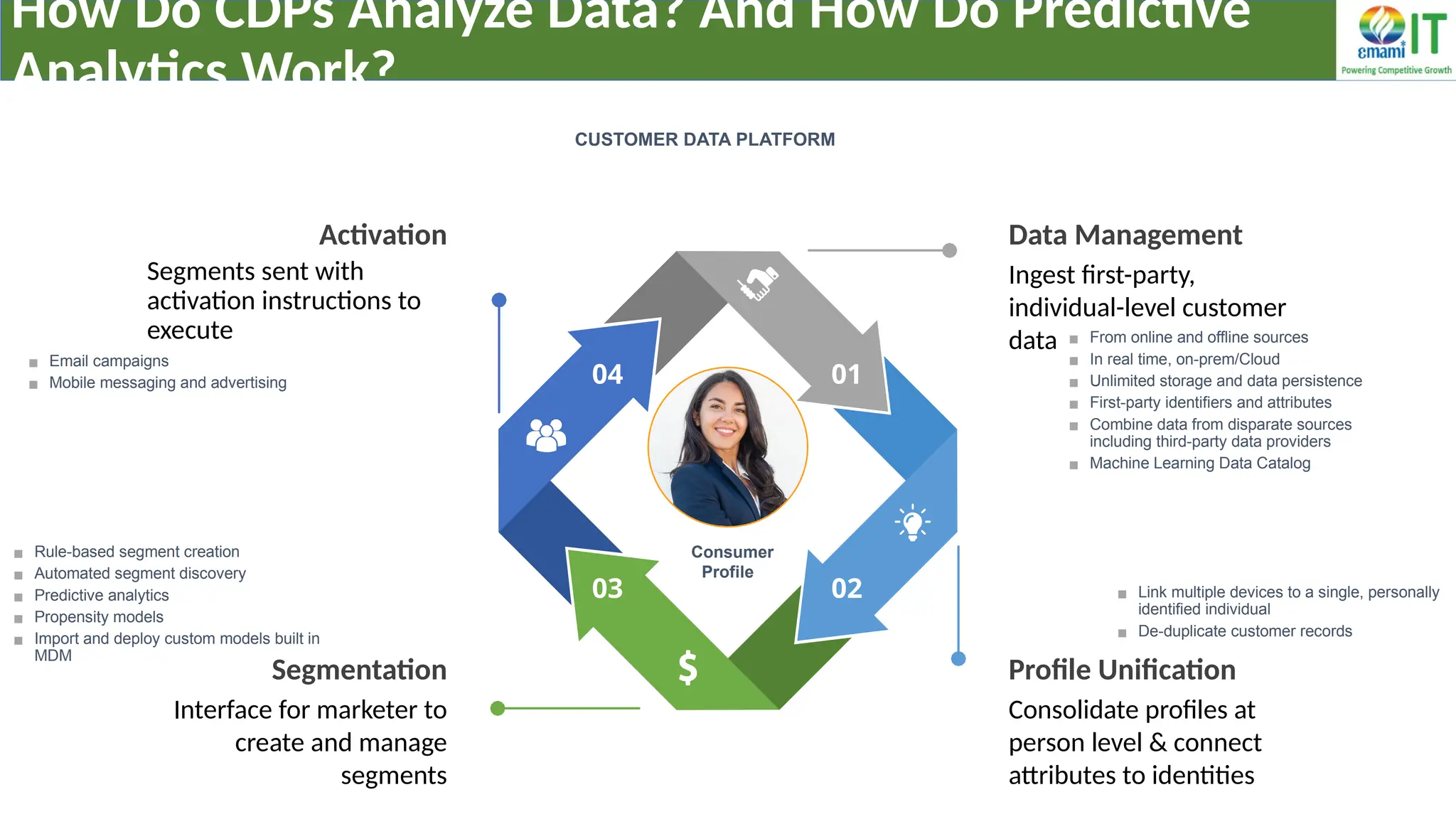
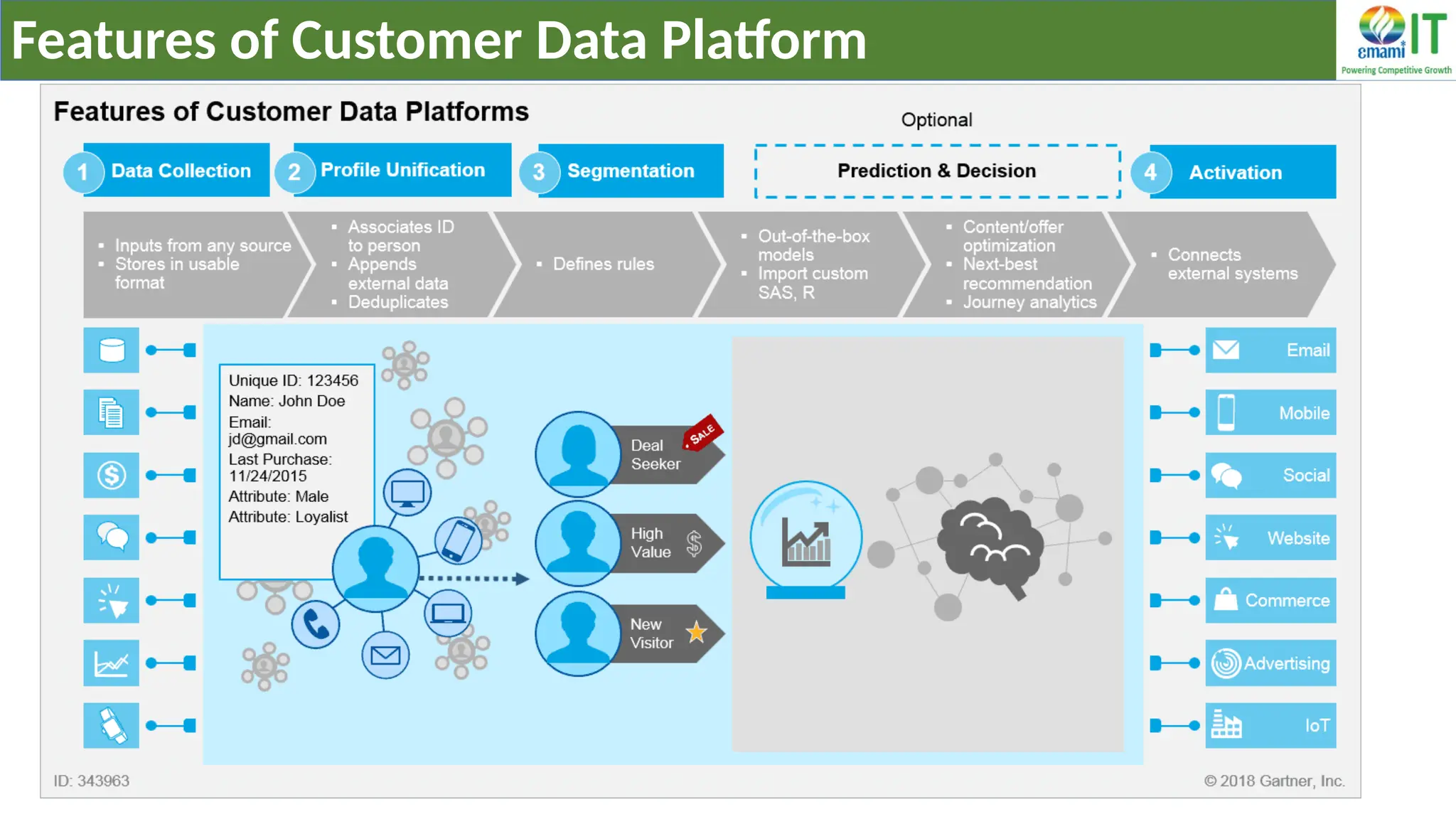
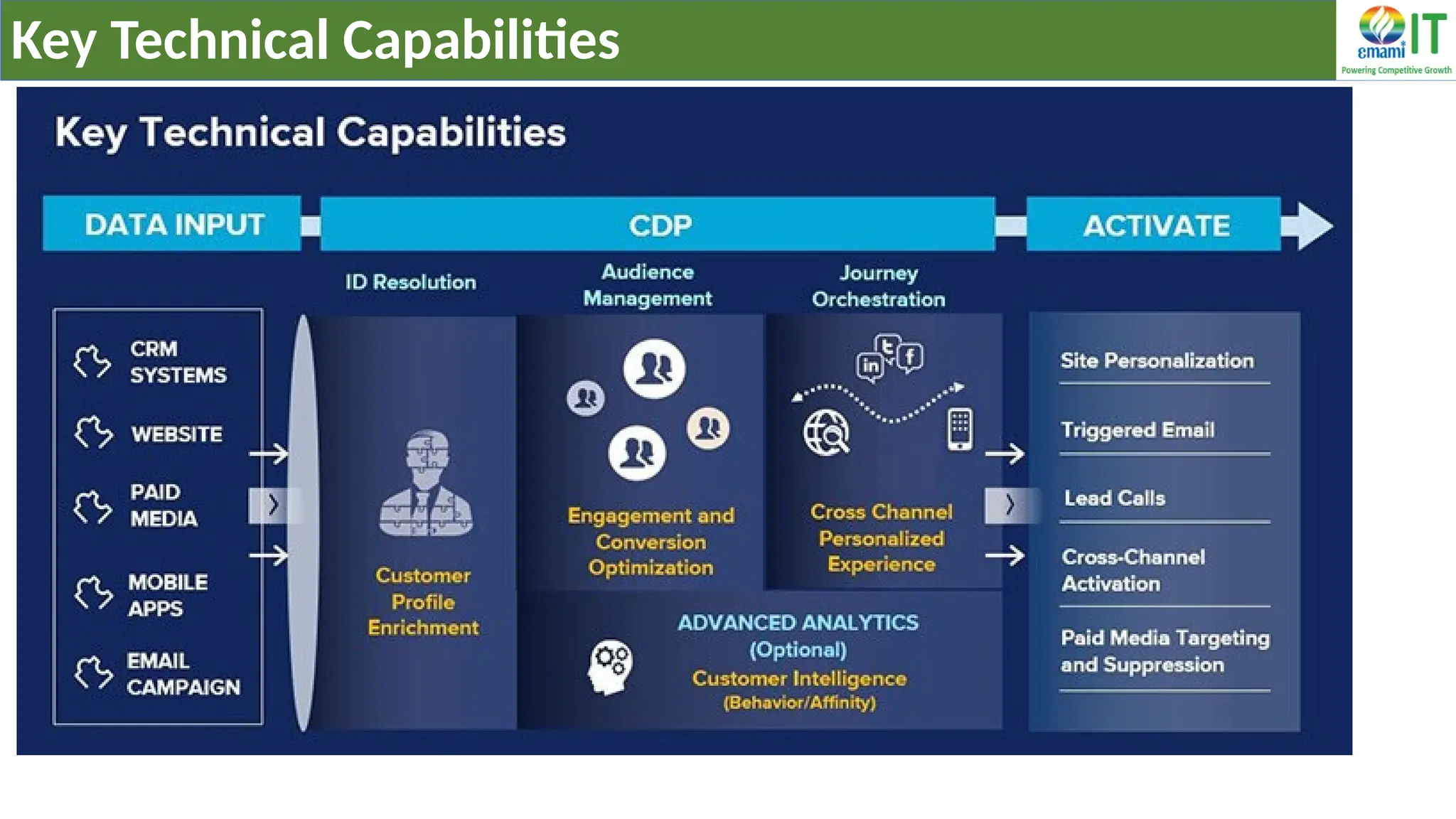
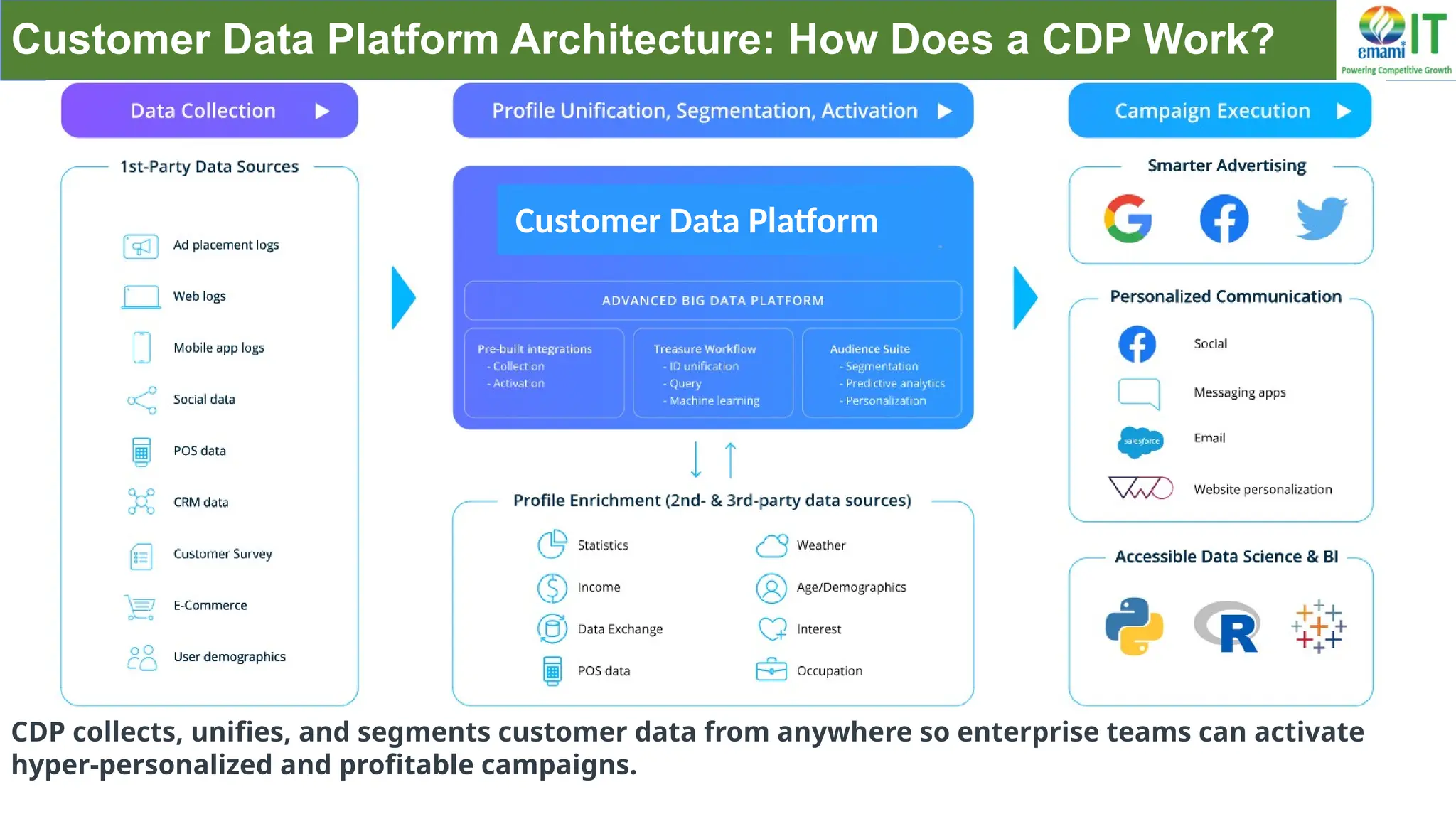
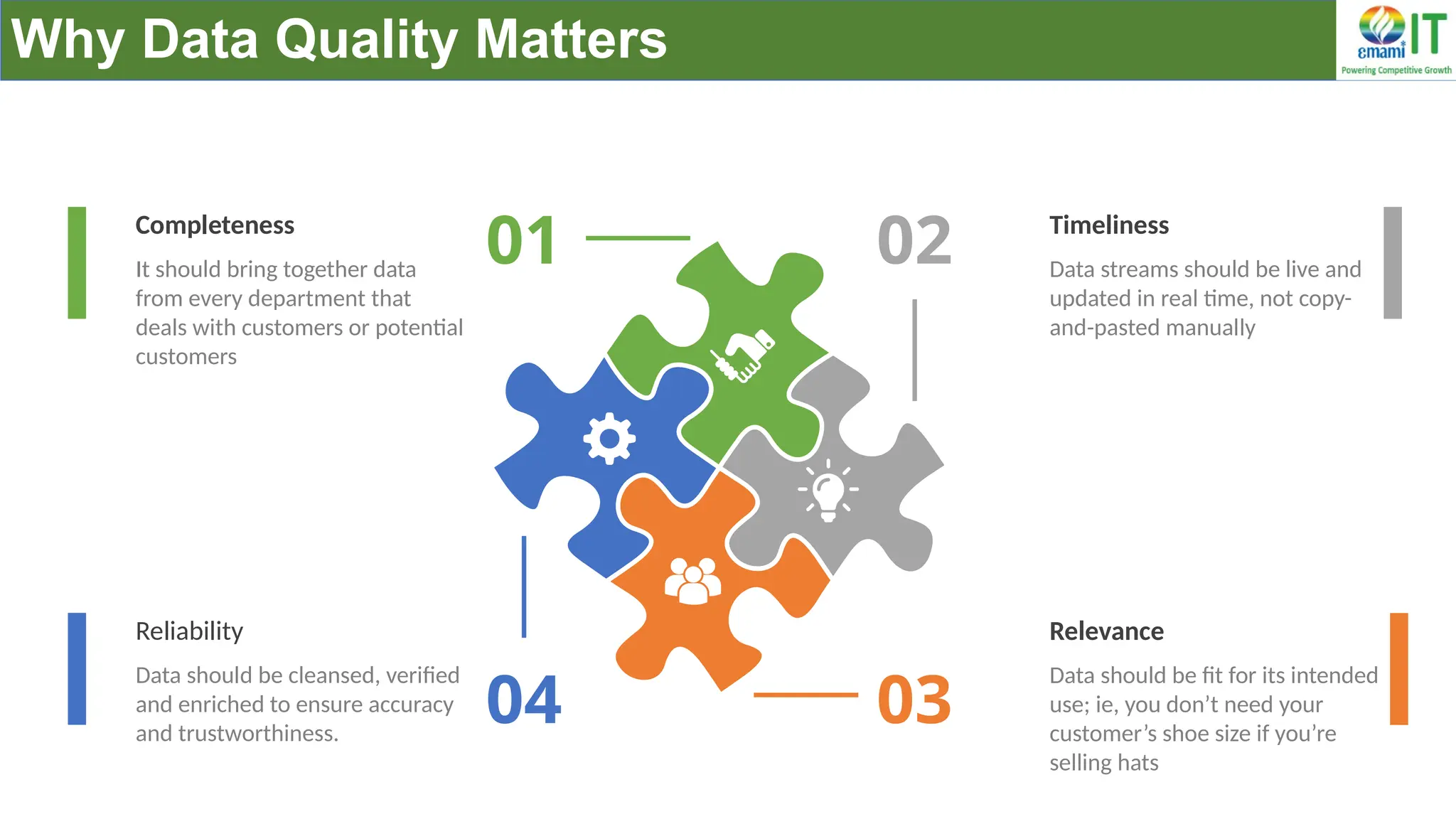
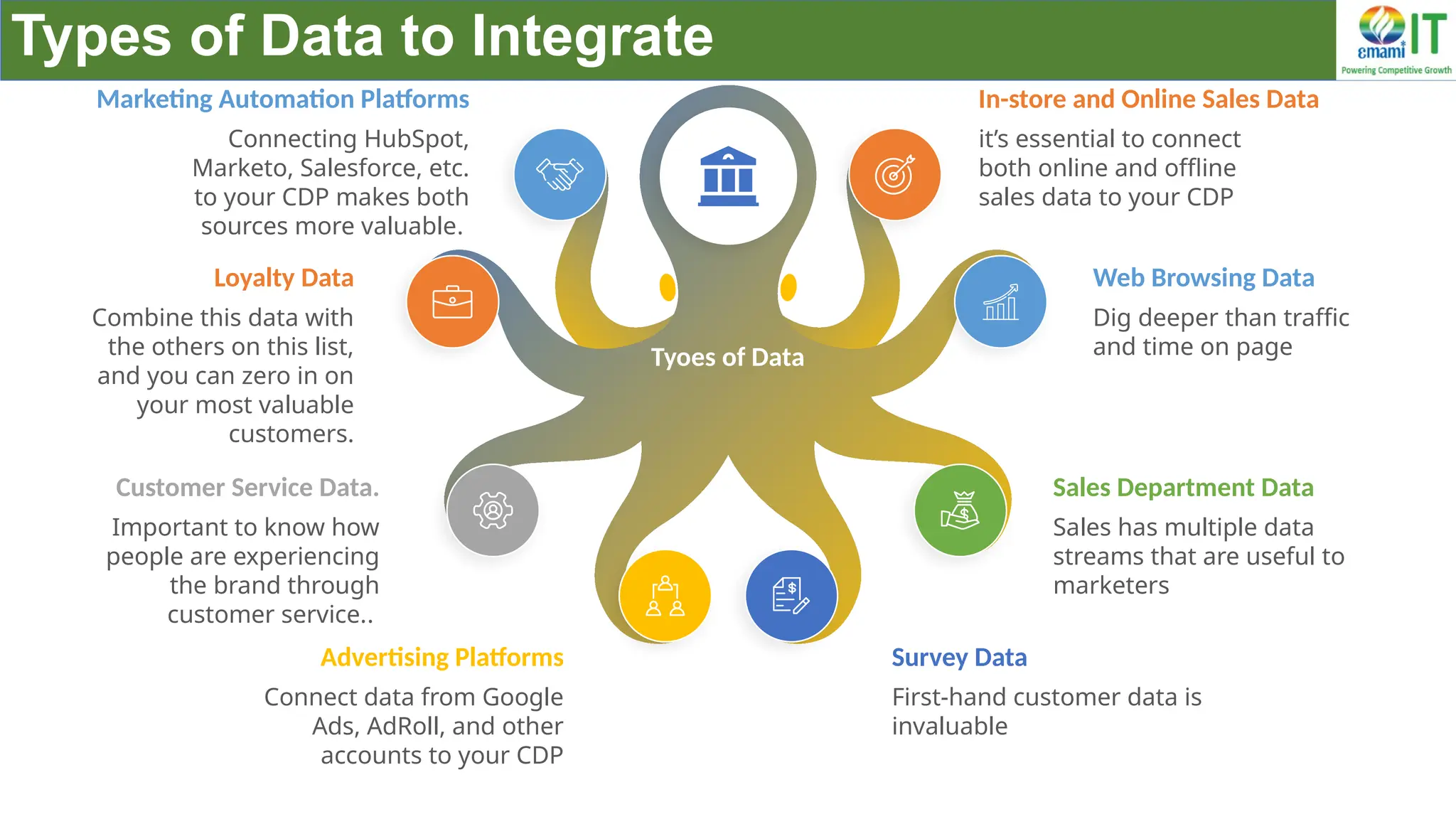
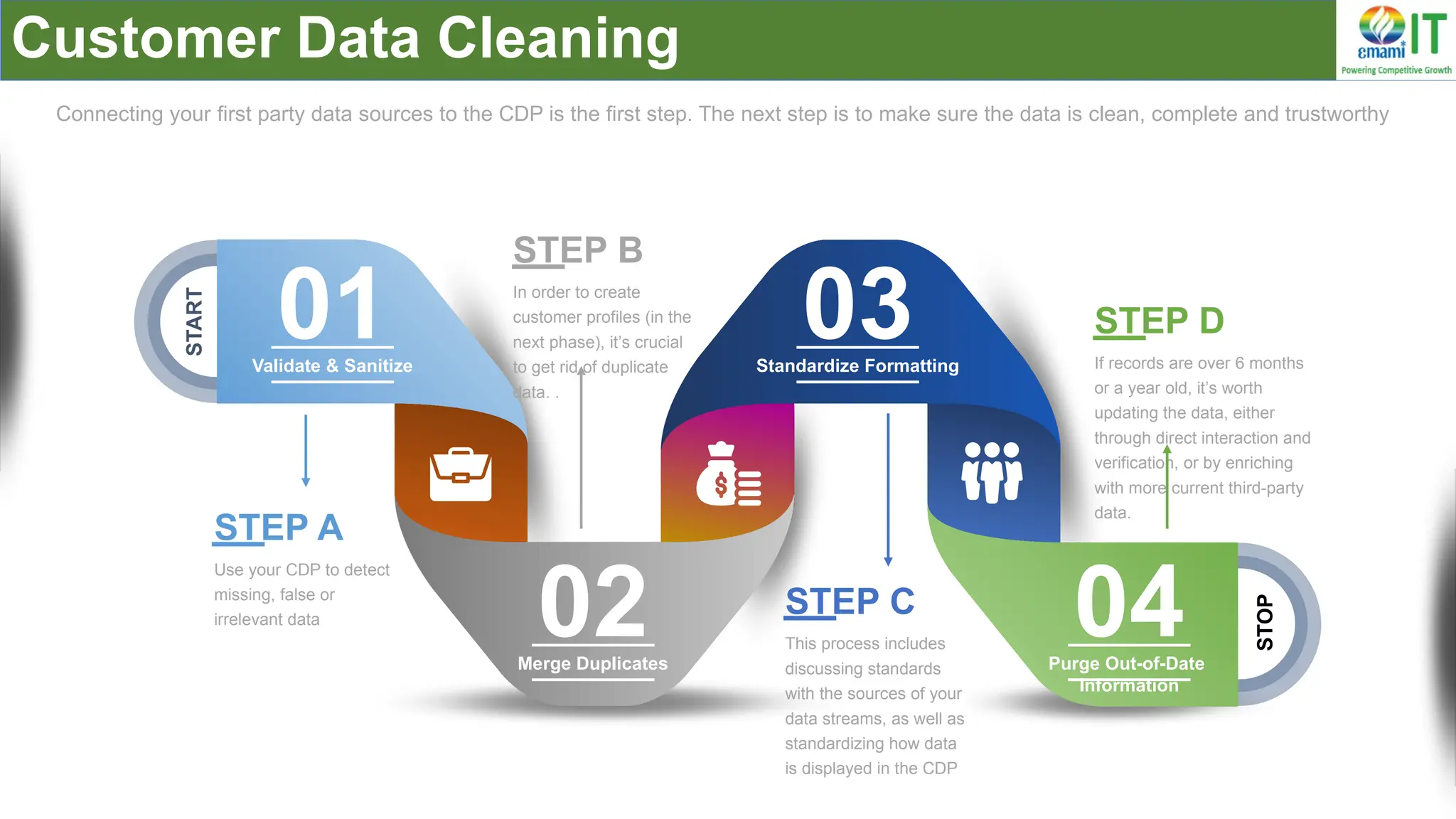
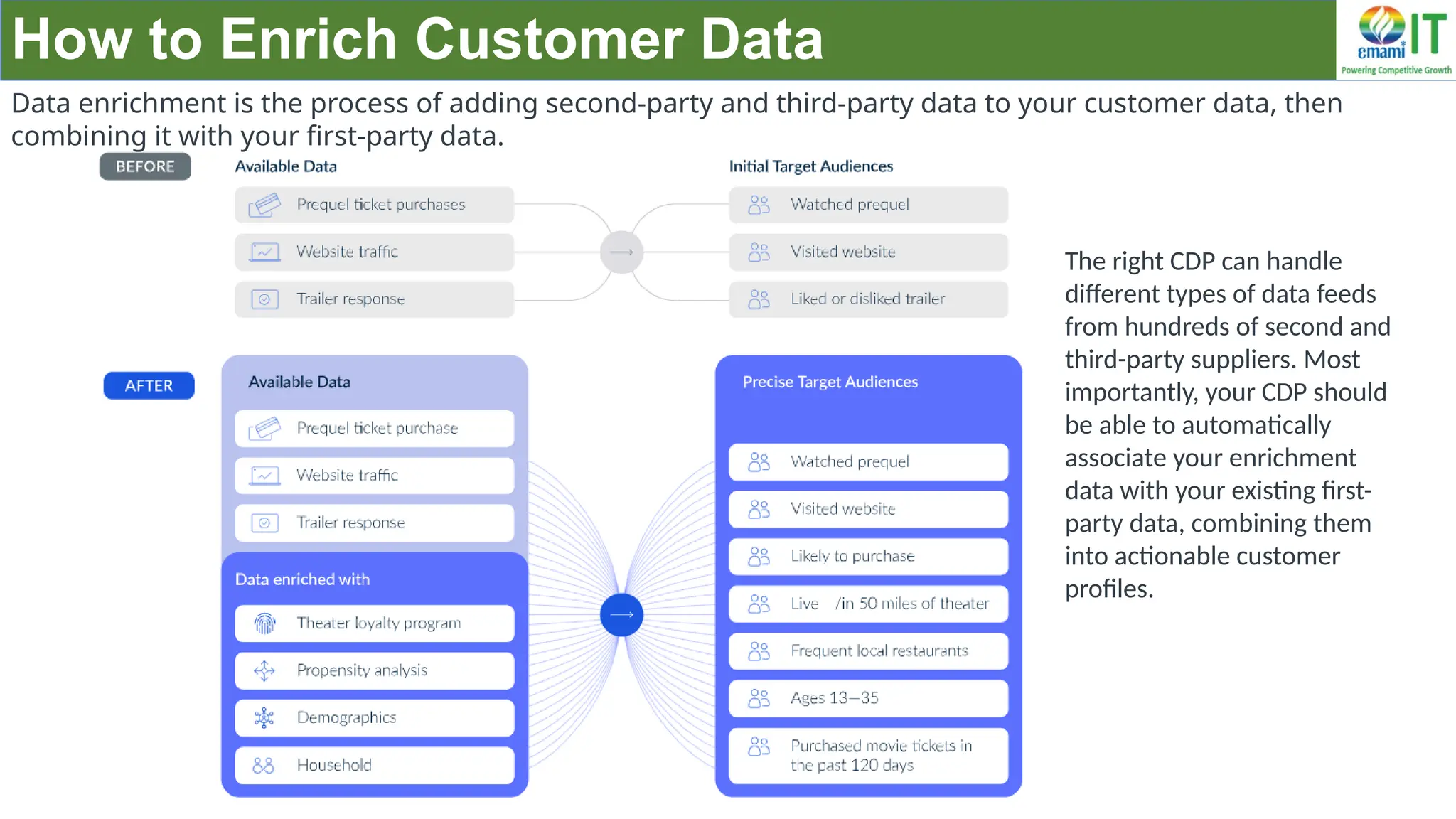
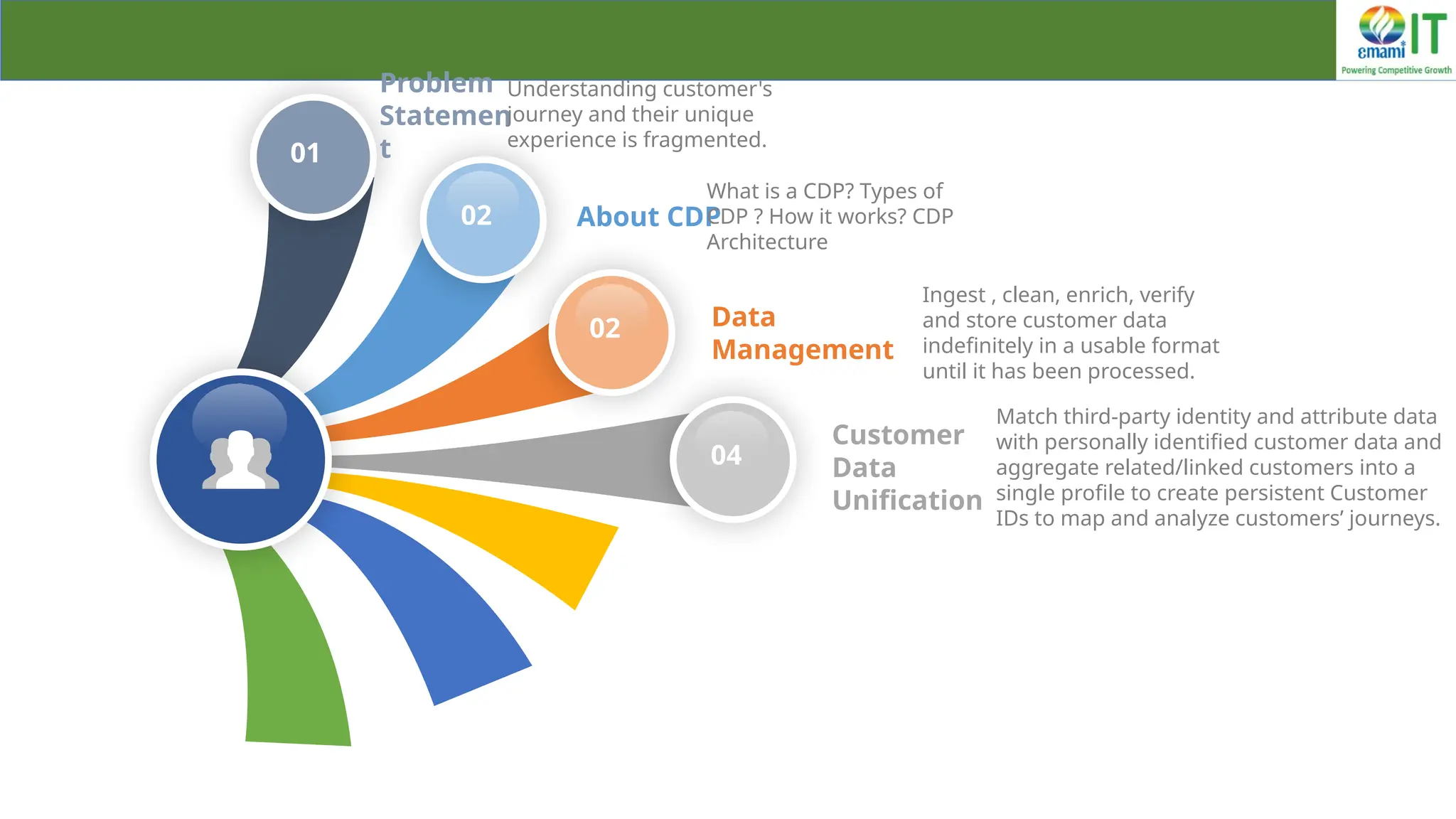
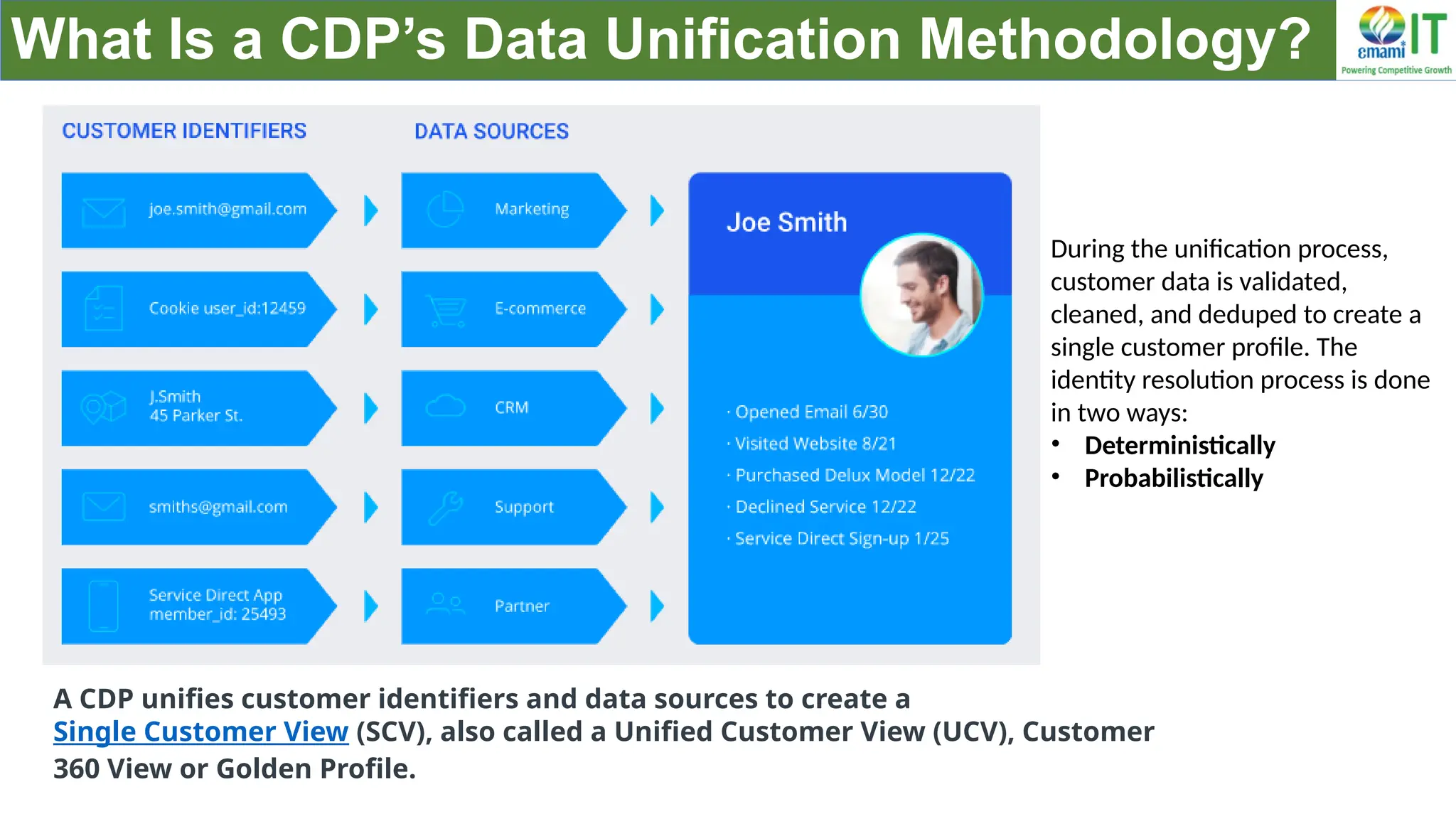
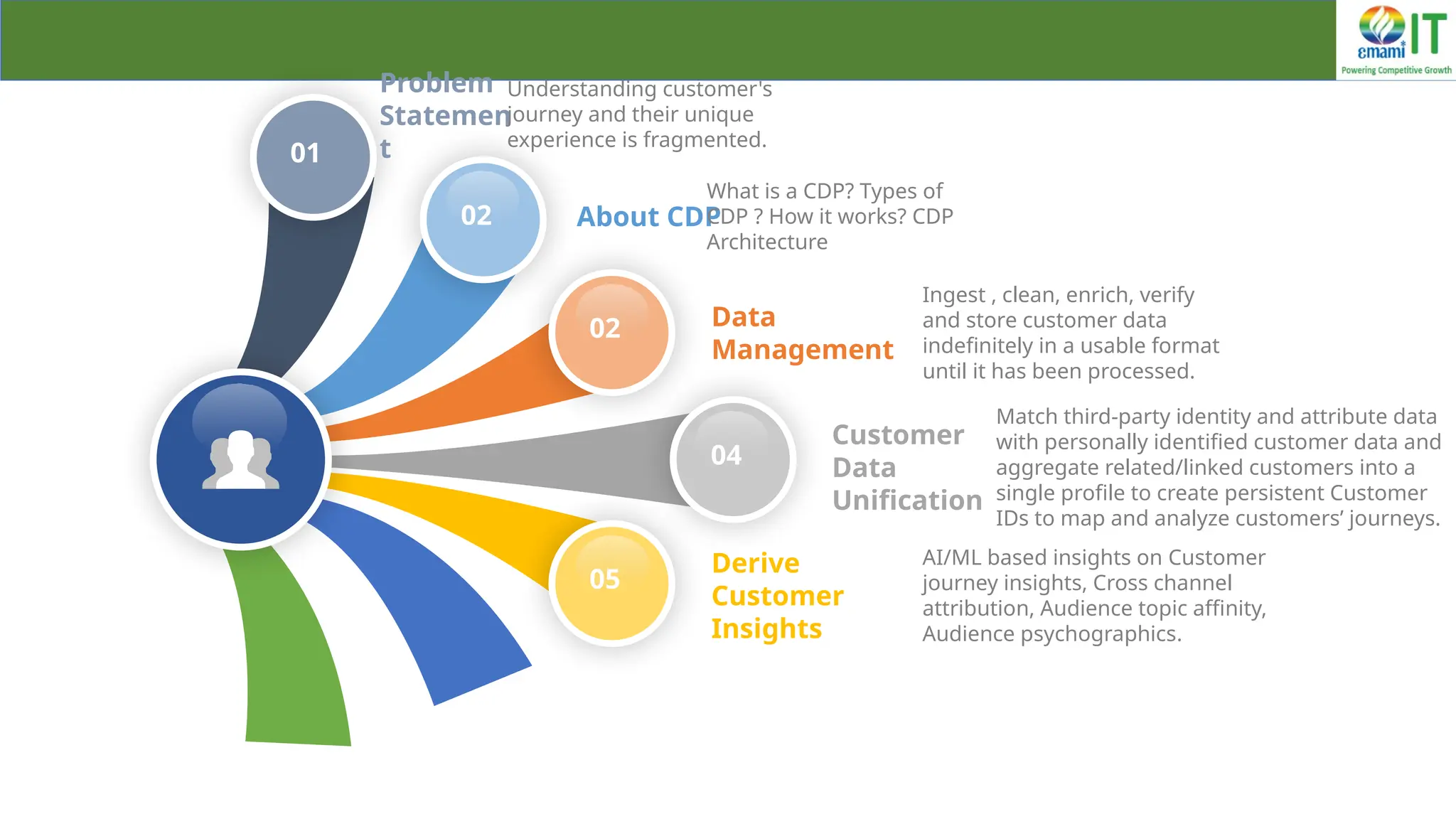
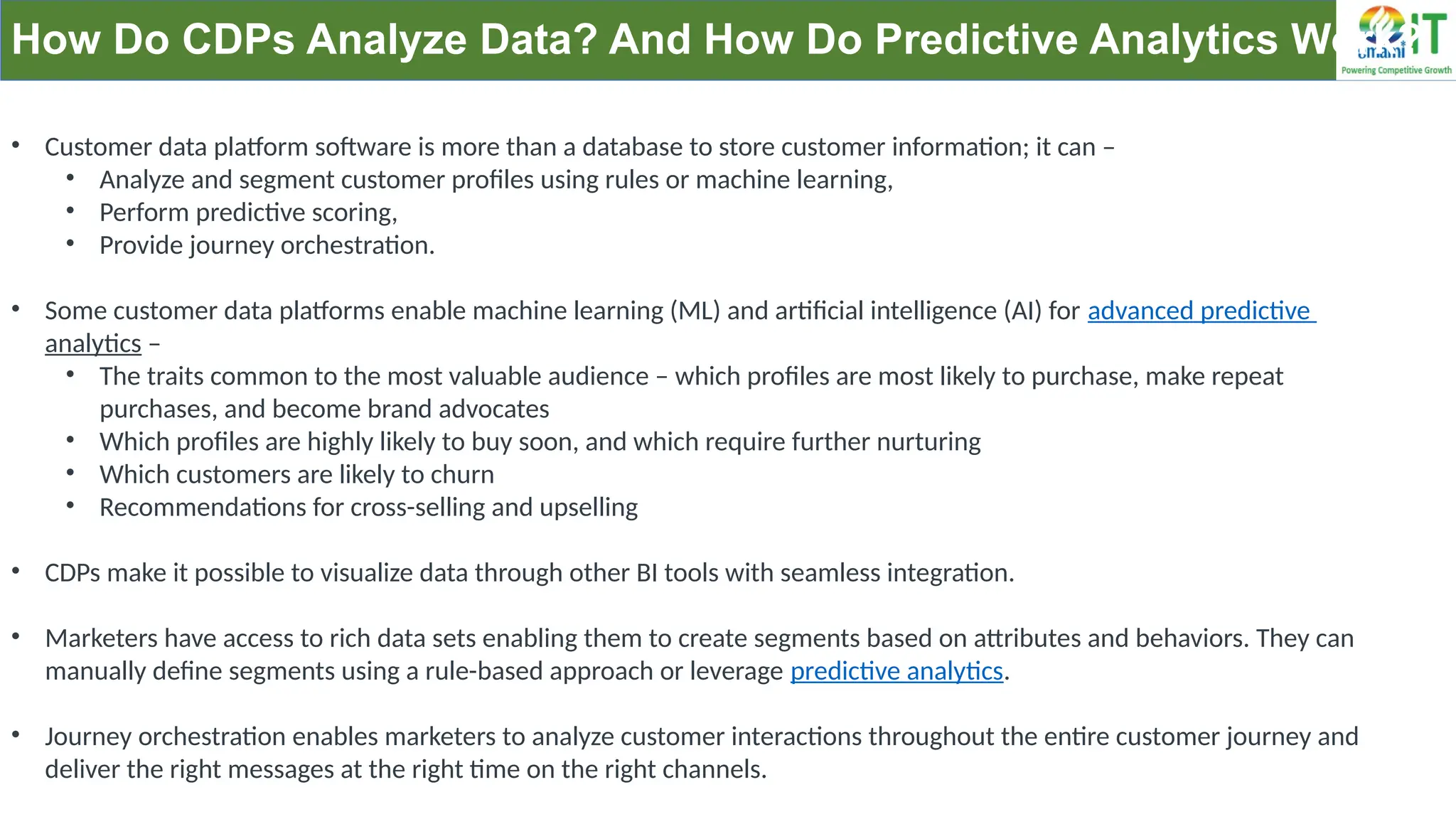
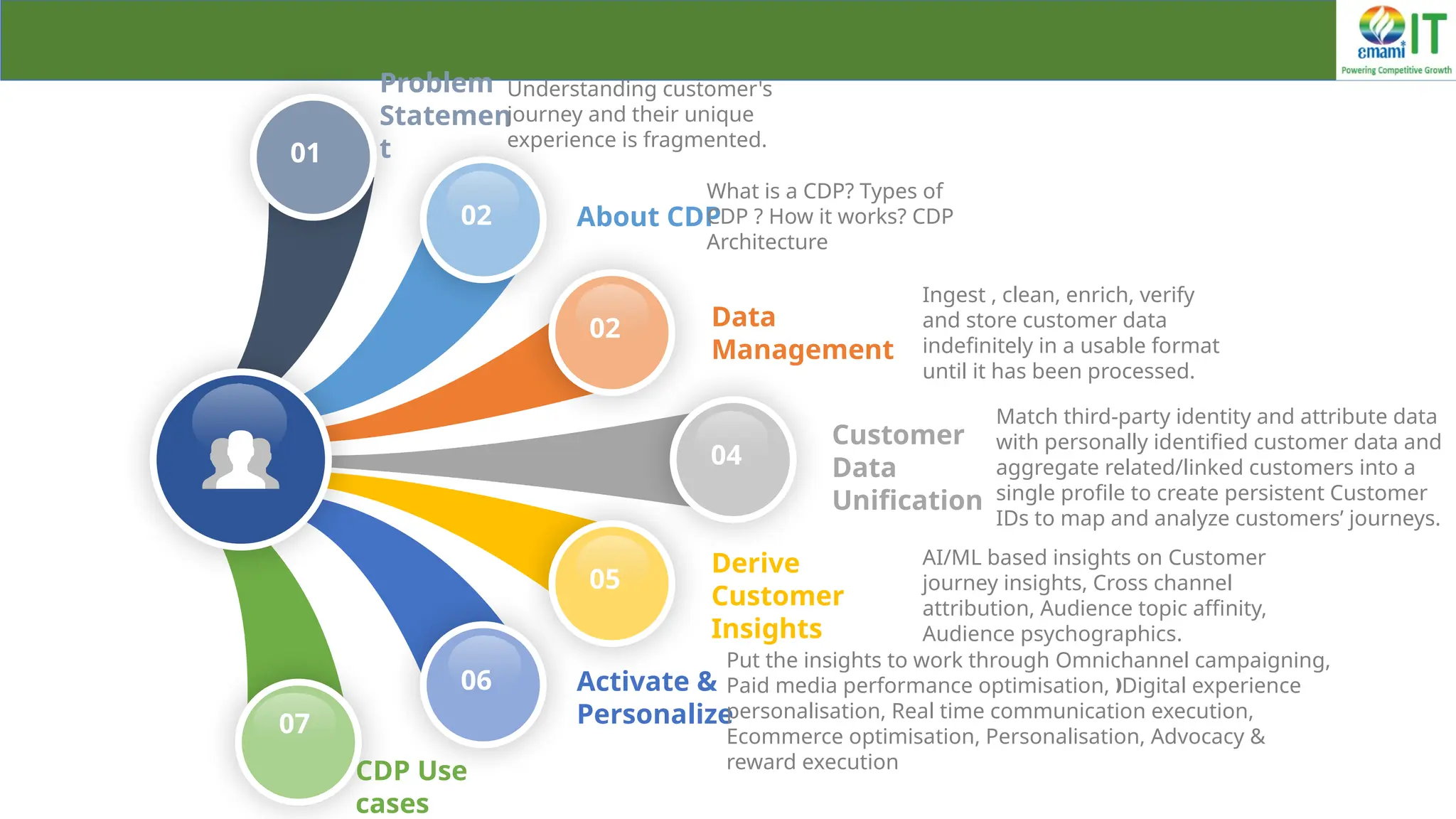
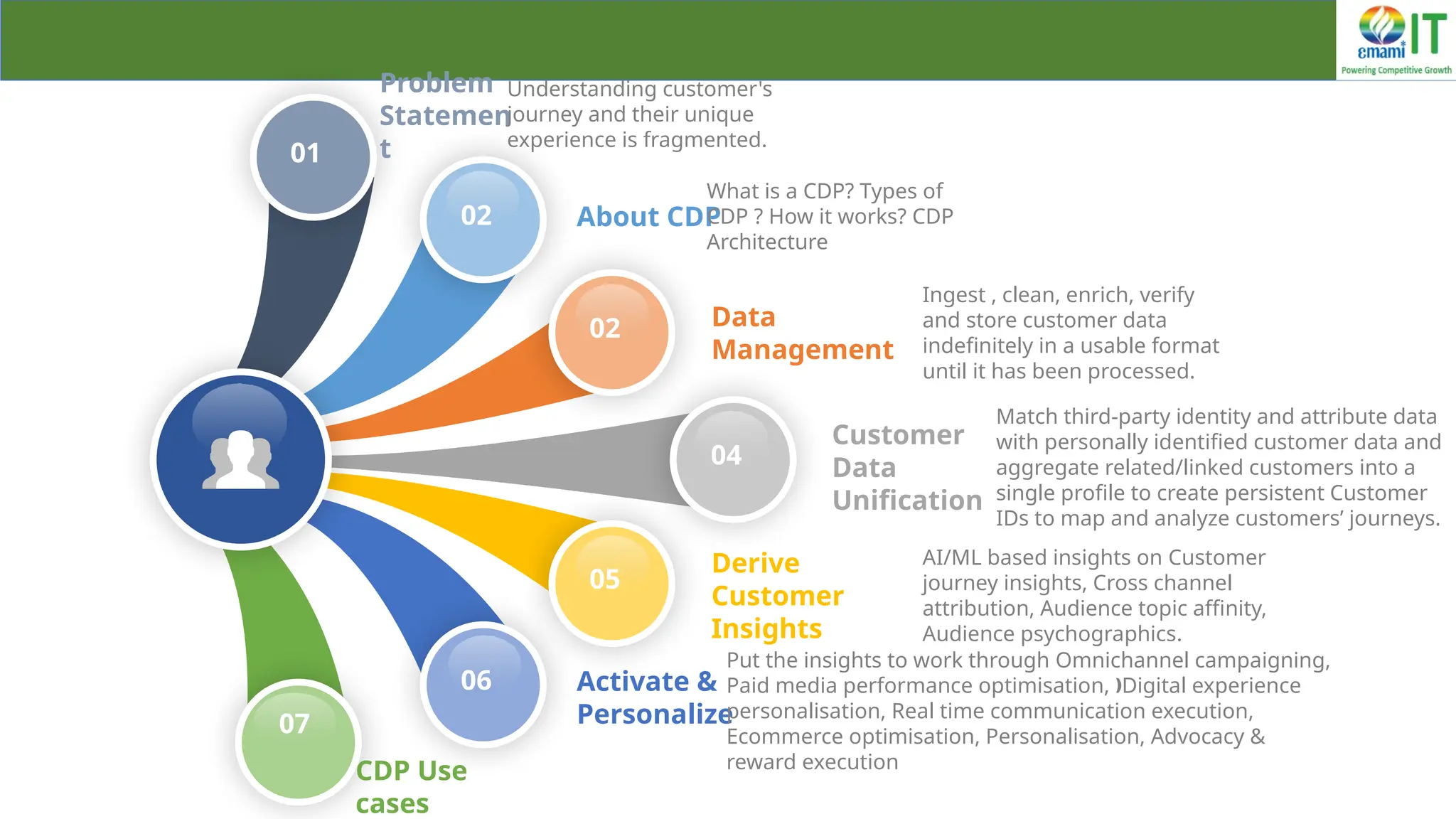
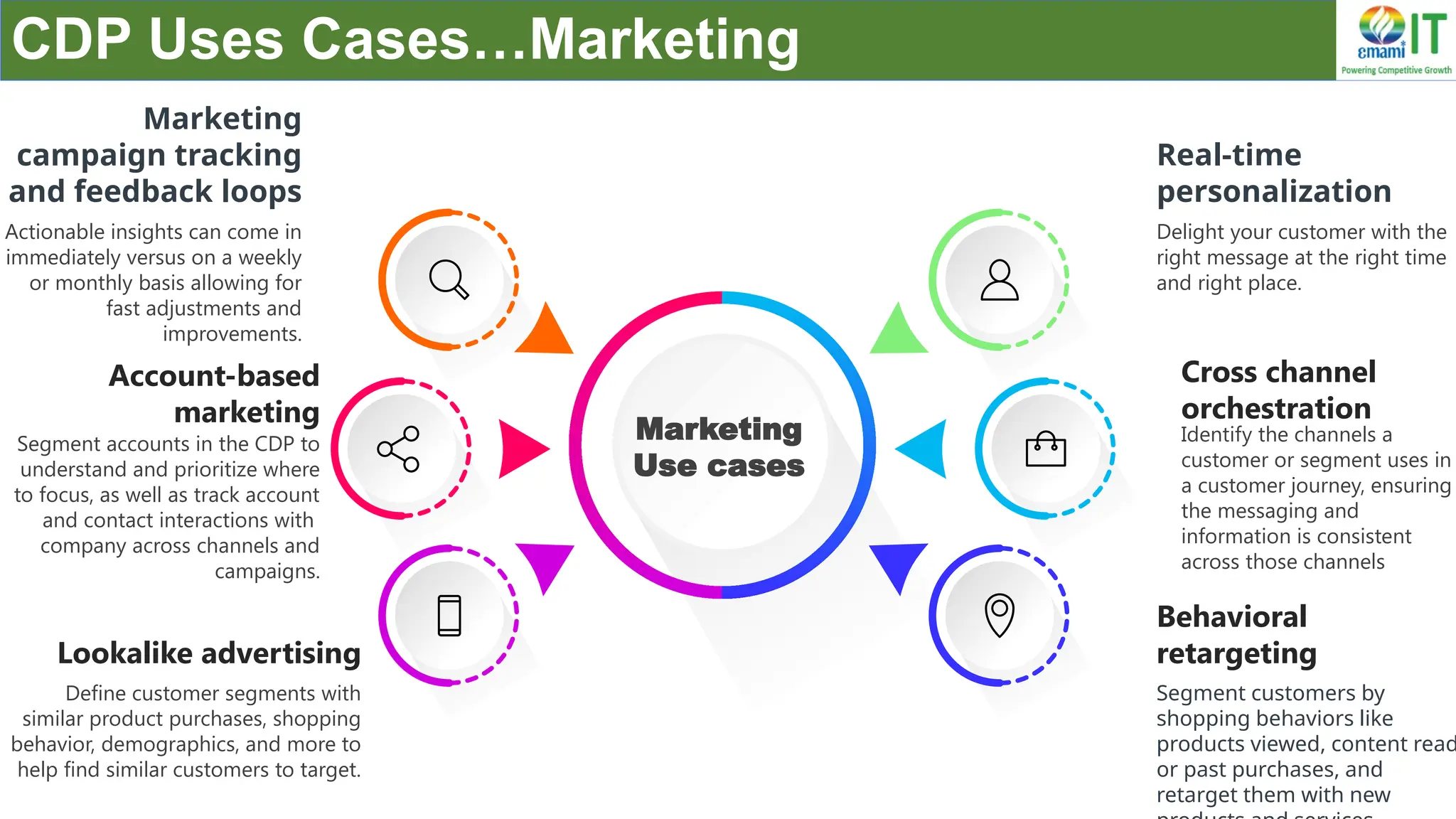
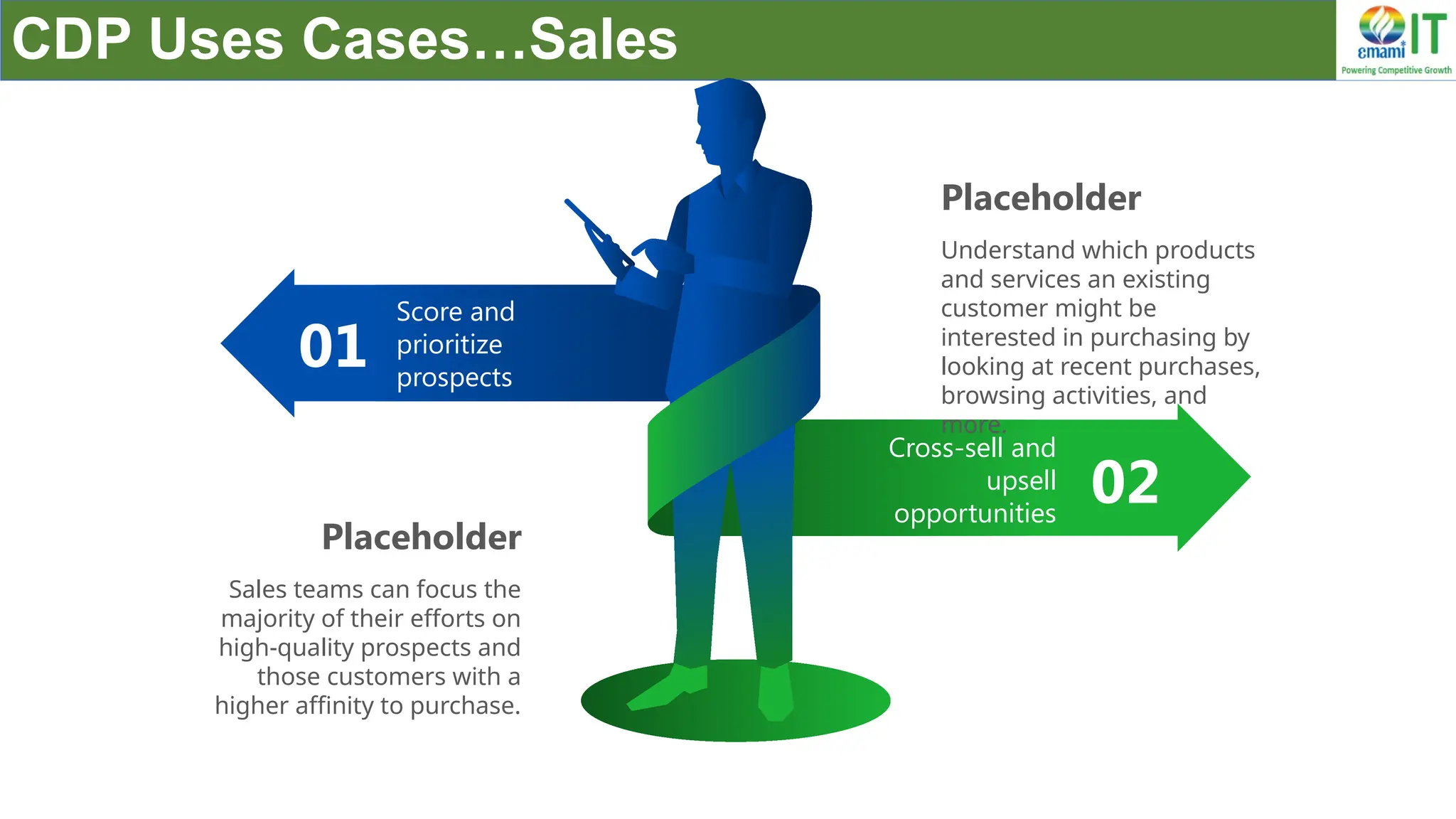
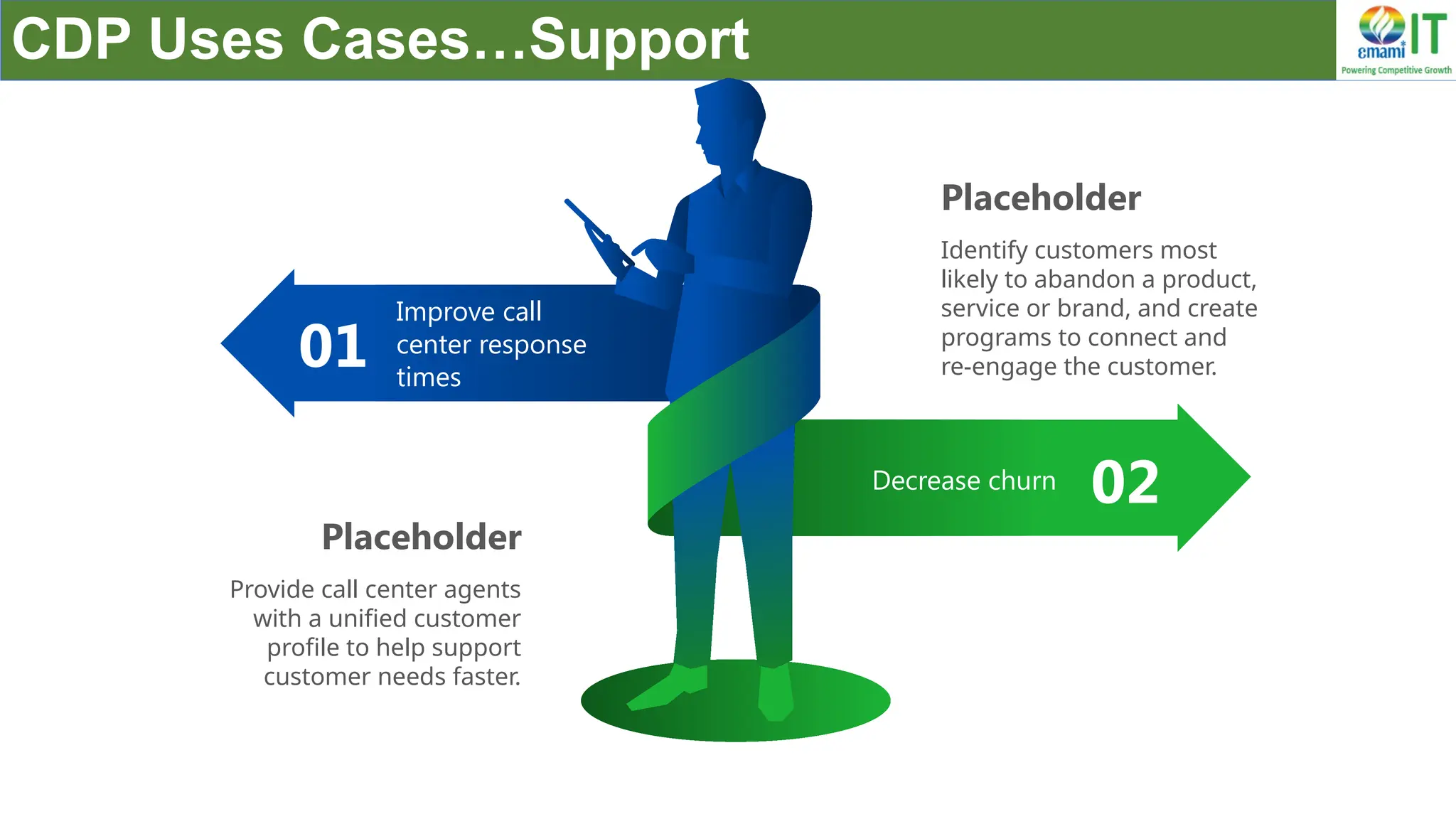
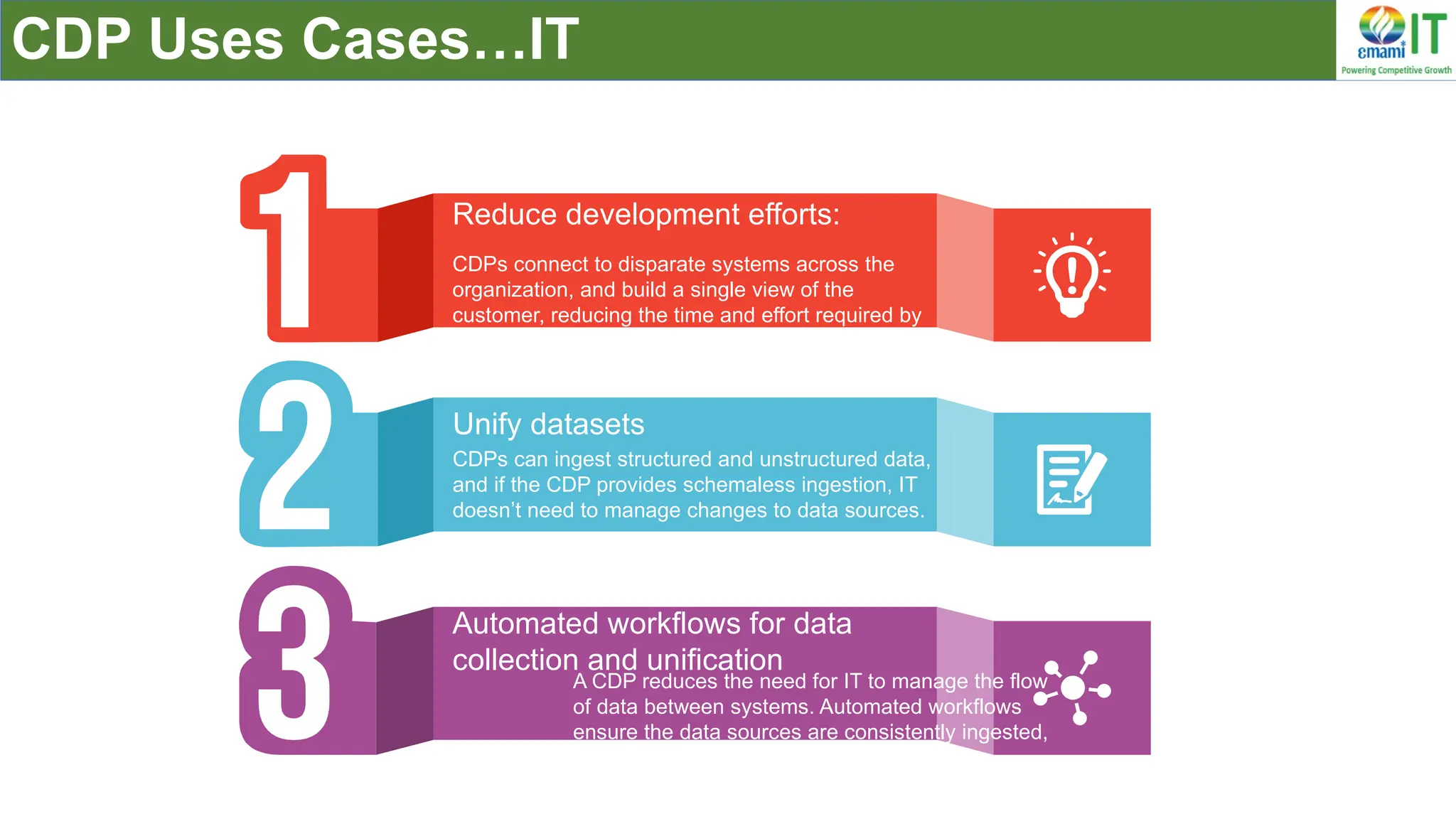
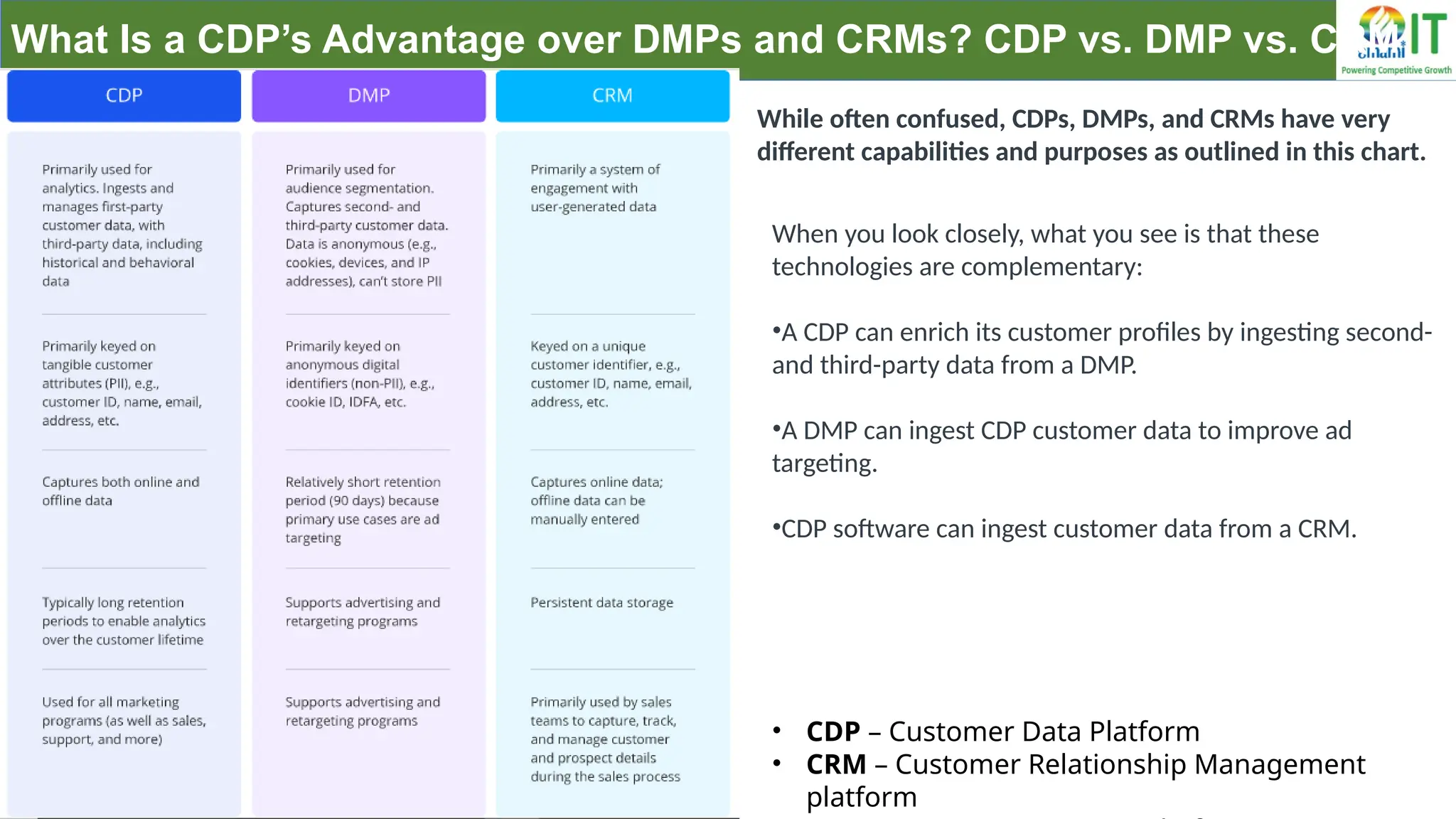
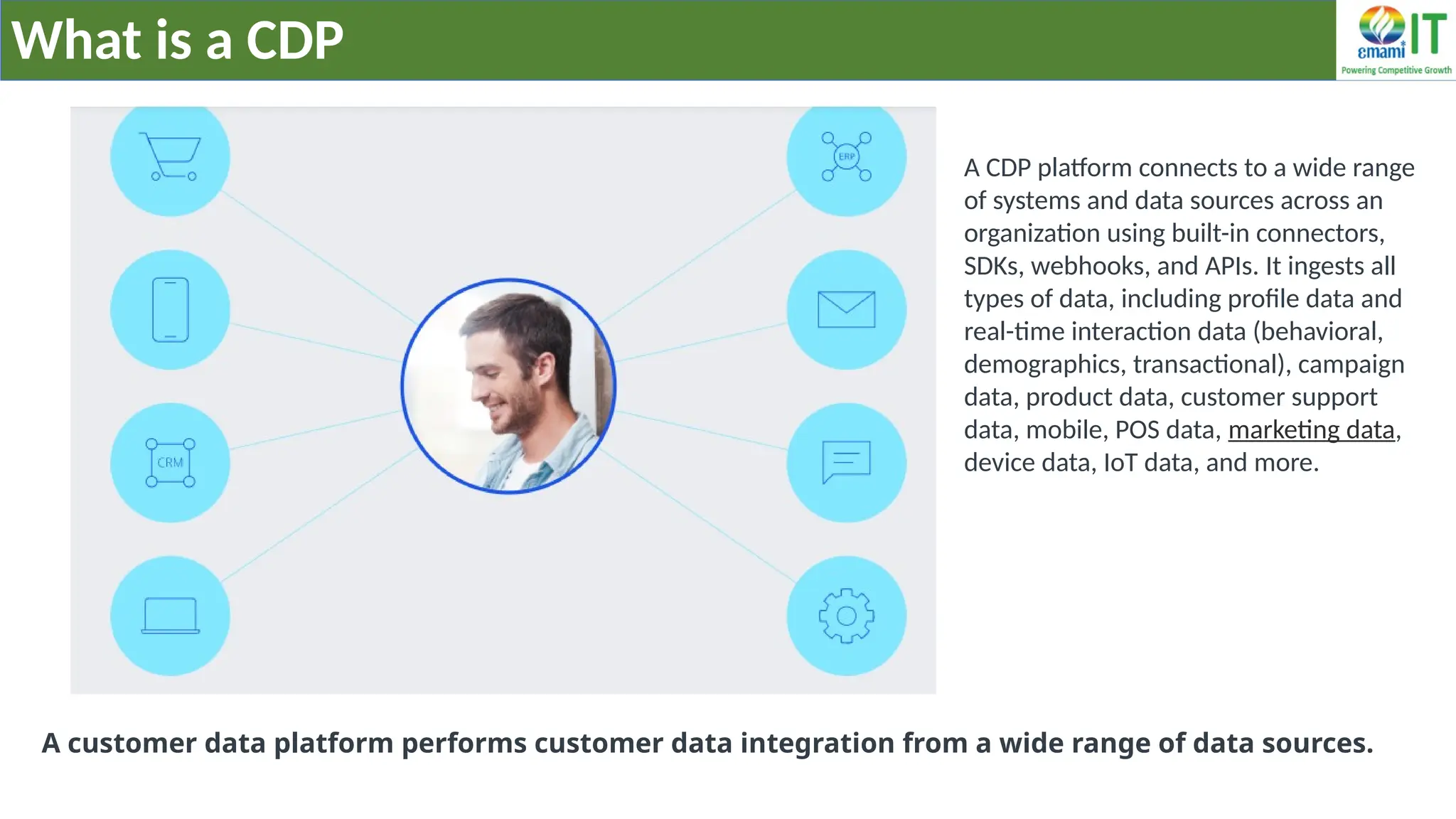
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) integrates and centralizes customer data from various sources to provide a unified view of customer interactions and journeys, facilitating personalized marketing and decision-making. It addresses challenges such as fragmented customer experiences and disparate data silos by enabling real-time data management, predictive analytics, and actionable insights for businesses. CDPs are valuable for marketing, sales, and customer support teams, offering tools for audience segmentation, campaign orchestration, and data activation across channels.