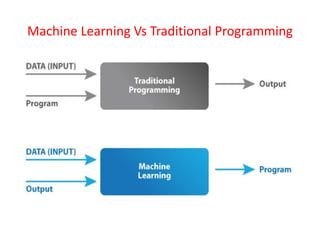
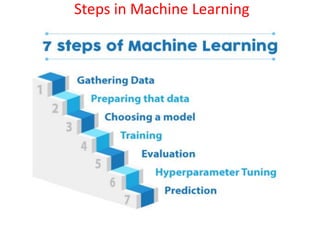
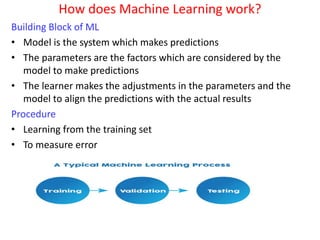
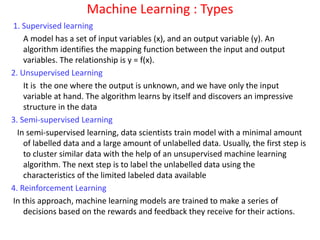
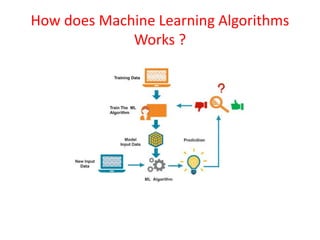
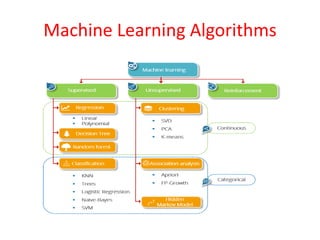
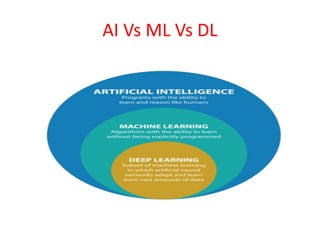
This document provides an overview of machine learning, including definitions, types, steps, and applications. It defines machine learning as a field that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. The document outlines the main types of machine learning as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning, and reinforcement learning. It also describes the typical steps in a machine learning process as gathering data, preparing data, choosing a model, training, evaluation, and prediction. Examples of machine learning applications discussed include prediction, image recognition, natural language processing, and personal assistants. Popular machine learning languages and packages are also listed.